Example for Configuring Inter-AS IPv6 NG MVPN Option C
The inter-AS IPv6 NG MVPN Option C solution is implemented by establishing a multi-hop MP-EBGP peer relationship between PEs in different ASs.
Networking Requirements
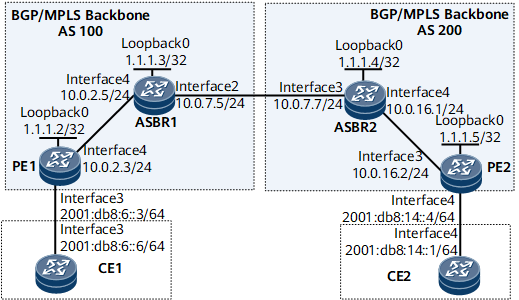
As shown in Figure 1, CE1 and CE2 belong to the same VPN. CE1 accesses the backbone network by means of PE1 in AS100, and CE2 accesses the backbone network by means of PE2 in AS200.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Establish an MP-EBGP peer relationship between the PEs in different ASs and configure the maximum number of hops between the PEs.
Configure a routing policy on each ASBR. Assign an MPLS label to the loopback interface route received from the PE within the local AS and advertised to the remote ASBR. Assign new MPLS labels to the labeled IPv4 routes advertised to the PE within the local AS.
Configure the PE and ASBR in the same AS to exchange labeled IPv4 routes.
Configure ASBR1 and ASBR2 to exchange labeled IPv4 routes.
Configure IPv6 NG MVPN.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
MPLS LSR IDs of the PEs and ASBRs (1.1.1.2, 1.1.1.3, 1.1.1.4, and 1.1.1.5)
Name (ngv6), RD (1:3 and 1:5), and export and import VPN targets (1:1) of the VPN instance on each PE
Routing policies used by ASBRs
Procedure
- Configure an IGP on the MPLS backbone networks in AS100 and AS200, so that the PE and ASBR on the same MPLS backbone network can communicate.
This example uses IS-IS. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this example.
- Configure basic MPLS functions and MPLS LDP on the MPLS backbone networks of AS100 and AS200 to establish LDP LSPs. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this example.
- Configure an automatic mLDP P2MP LSP on PEs and ASBRs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls ldp [~PE1-mpls-ldp] mldp p2mp [*PE1-mpls-ldp] commit [~PE1-mpls-ldp] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls ldp [~PE2-mpls-ldp] mldp p2mp [*PE2-mpls-ldp] mldp recursive-fec [*PE2-mpls-ldp] commit [~PE2-mpls-ldp] quit
# Configure ASBR1.
[~ASBR1] mpls ldp [~ASBR1-mpls-ldp] mldp p2mp [*ASBR1-mpls-ldp] mldp recursive-fec [*ASBR1-mpls-ldp] commit [~ASBR1-mpls-ldp] quit
The procedure for configuring ASBR2 is similar to the procedure for configuring ASBR1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this example.
- Configure IBGP peer relationships in the IPv4 address family view for AS100 and AS200. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this example.
- Configure a VPN instance on each PE and bind the interface connecting a PE to a CE to the VPN instance.

The import VPN target of the VPN instance on PE1 must match the export VPN target of the VPN instance on PE2. The import VPN target of the VPN instance on PE2 must match the export VPN target of the VPN instance on PE1.
- Enable the capability of exchanging labeled IPv4 routes.
# Configure PE1 to exchange labeled IPv4 routes with ASBR1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [~PE1-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [~PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.3 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.3 label-route-capability [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] undo synchronization [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] commit [~PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] quit
# Enable MPLS on GigabitEthernet0/1/2 connecting ASBR1 to ASBR2.
[~ASBR1] interface ethernet 0/1/2 [~ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ip address 10.0.7.5 24 [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls ldp [*ASBR1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*ASBR1] commit
# Create a routing policy on ASBR1.
[~ASBR1] route-policy policy1 permit node 1 [*ASBR1-route-policy] apply mpls-label [*ASBR1-route-policy] quit [*ASBR1] route-policy policy2 permit node 1 [*ASBR1-route-policy] if-match mpls-label [*ASBR1-route-policy] apply mpls-label [*ASBR1-route-policy] quit [*ASBR1] commit
# Apply the routing policy to the routes advertised by ASBR1 to PE1 and enable ASBR1 to exchange labeled IPv4 routes with PE1.
[~ASBR1] bgp 100 [~ASBR1-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [~ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.2 enable [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.2 route-policy policy2 export [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.2 label-route-capability [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] quit
# Apply the routing policy to the routes advertised by ASBR1 to ASBR2 and enable ASBR1 to exchange labeled IPv4 routes with ASBR2.
[*ASBR1-bgp] peer 10.0.7.7 as-number 200 [*ASBR1-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 10.0.7.7 enable [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 10.0.7.7 route-policy policy1 export [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 10.0.7.7 label-route-capability [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] quit
# Configure ASBR1 to advertise PE1's loopback route to ASBR2 and then to PE2.
[*ASBR1-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] network 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 [*ASBR1-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [*ASBR1-bgp] quit [*ASBR1] commit
The configurations on PE2 and ASBR2 are similar to those on PE1 and ASBR1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this example.
- Establish an MP-EBGP peer relationship between PE1 and PE2 and configure the PEs to filter received VPNv4 routes based on VPN targets.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 1.1.1.5 as-number 200 [*PE1-bgp] peer 1.1.1.5 connect-interface LoopBack0 [*PE1-bgp] peer 1.1.1.5 ebgp-max-hop 10 [*PE1-bgp] ipv6-family vpnv6 [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 1.1.1.5 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv6] policy vpn-target [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv6] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 200 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.2 as-number 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.2 ebgp-max-hop 10 [*PE2-bgp] ipv6-family vpnv6 [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv6] peer 1.1.1.2 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv6] policy vpn-target [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv6] quit [*PE2-bgp] quit [*PE2] commit
- Configure BGP MVPN peers.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [~PE1-bgp] ipv4-family unicast [~PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] undo synchronization [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] peer 1.1.1.5 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] commit [~PE1-bgp-af-ipv4] quit [~PE1-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance ngv6 [~PE1-bgp-af-vpn-ngv6] import-route isis 2 [*PE1-bgp-af-vpn-ngv6] commit [~PE1-bgp-af-vpn-ngv6] quit [~PE1-bgp] ipv6-family mvpn [~PE1-bgp-af-mvpnv6] policy vpn-target [*PE1-bgp-af-mvpnv6] peer 1.1.1.5 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-mvpnv6] commit [~PE1-bgp-af-mvpnv6] quit [~PE1-bgp] quit
The configuration on PE2 is similar to the configuration on PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this example.
- Configure a P2MP LSP on PEs to carry multicast traffic.
# Configure PE1 as the sender PE.
[~PE1] multicast ipv6 mvpn 1.1.1.2 [~PE1] ip vpn-instance ngv6 [~PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6] ipv6-family [~PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6] multicast ipv6 routing-enable [*PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6] mvpn [*PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn] sender-enable [*PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn] c-multicast signaling bgp [*PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn] auto-discovery inter-as [*PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn] ipmsi-tunnel [*PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn-ipmsi] mldp [*PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn-ipmsi] commit [~PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn-ipmsi] quit [~PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn] quit [~PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6] quit [~PE1-vpn-instance-ngv6] quit
# Configure PE2 as the receiver PE.
[~PE2] multicast ipv6 mvpn 1.1.1.5 [~PE2] ip vpn-instance ngv6 [~PE2-vpn-instance-ngv6] ipv6-family [~PE2-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6] multicast ipv6 routing-enable [~PE2-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6] mvpn [*PE2-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn] c-multicast signaling bgp [*PE2-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn] auto-discovery inter-as [*PE2-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn-ipmsi] commit [~PE2-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn-ipmsi] quit [~PE2-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6-mvpn] quit [~PE2-vpn-instance-ngv6-af-ipv6] quit [~PE2-vpn-instance-ngv6] quit
- Configure PIM.
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] pim-ipv6 [~CE1-pim6] static-rp 2001:db8:6::3 [*CE1-pim6] commit [~CE1-pim6] quit [~CE1] multicast ipv6 routing-enable [*CE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim ipv6 sm [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [~CE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/3 [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] pim ipv6 sm [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] commit [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit
# Configure CE2.
[~CE2] pim-ipv6 [~CE2-pim6] static-rp 2001:db8:6::3 [*CE2-pim6] commit [~CE2-pim6] quit [~CE2] multicast ipv6 routing-enable [*CE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim ipv6 sm [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mld enable [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mld static-group FF3E::1 source 2001:DB8:5::2 [*CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~CE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [~CE2] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/4 [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/4] pim ipv6 sm [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/4] commit [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/4] quit
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] pim-ipv6 vpn-instance ngv6 [*PE1-pim6-ngv6] static-rp 2001:db8:6::3 [*PE1-pim6-ngv6] source-lifetime 60 [*PE1-pim6-ngv6] commit [~PE1-pim6-ngv6] quit [~PE1] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/3 [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] pim ipv6 sm [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] commit [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit
The configuration on PE2 is similar to the configuration on PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this example.
- Verify the configuration.
After the configuration is complete, CEs can learn the routes to each other's interfaces and ping each other.
The following example uses the command output on CE1.
[~CE1] ping ipv6 2001:db8:14::1 PING 2001:DB8:14::1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 2001:DB8:14::1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=252 time=102 ms Reply from 2001:DB8:14::1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=252 time=89 ms Reply from 2001:DB8:14::1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=252 time=106 ms Reply from 2001:DB8:14::1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=252 time=104 ms Reply from 2001:DB8:14::1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=252 time=56 ms --- 2001:DB8:14::1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 56/91/106 msRun the display pim ipv6 routing-table command on a PE to check the PIM routing table.
The following example uses the command output on PE2.
<PE2> display pim ipv6 vpn-instance ngv6 routing-table VPN-Instance: ngv6 Total 1 (S, G) entry (2001:DB8:5::2, FF3E::1) Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag: UpTime: 00:24:09 Upstream interface: through-BGP, Refresh time: 00:24:09 Upstream neighbor: ::FFFF:1.1.1.2 RPF prime neighbor: ::FFFF:1.1.1.2 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/3 Protocol: pim-ssm, UpTime: 00:24:09, Expires: 00:02:35
Configuration Files
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # multicast ipv6 routing-enable # isis 2 is-level level-2 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:5::6 64 isis ipv6 enable 2 pim ipv6 sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:6::6 64 isis ipv6 enable 2 pim ipv6 sm # pim-ipv6 static-rp 2001:DB8:6::3 # return
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # multicast ipv6 mvpn 1.1.1.2 # ip vpn-instance ngv6 ipv6-family route-distinguisher 1:3 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity multicast ipv6 routing-enable mvpn sender-enable c-multicast signaling bgp auto-discovery inter-as ipmsi-tunnel mldp # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.2 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.000b.00 # isis 2 vpn-instance ngv6 is-level level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0006.00 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 import-route bgp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance ngv6 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:6::3 64 isis ipv6 enable 2 pim ipv6 sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/4 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.2.3 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.3 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.3 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 1.1.1.5 as-number 200 peer 1.1.1.5 ebgp-max-hop 10 peer 1.1.1.5 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.3 enable peer 1.1.1.3 label-route-capability peer 1.1.1.5 enable # ipv6-family mvpn policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.5 enable # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.5 enable # ipv6-family vpn-instance ngv6 import-route isis 2 # pim-ipv6 vpn-instance ngv6 static-rp 2001:DB8:6::3 source-lifetime 60 # returnASBR1 configuration file
# sysname ASBR1 # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.3 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp mldp recursive-fec # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.000c.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.7.5 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/4 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.2.5 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.3 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 10.0.7.7 as-number 200 peer 1.1.1.2 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 1.1.1.2 255.255.255.255 peer 10.0.7.7 enable peer 10.0.7.7 route-policy policy1 export peer 10.0.7.7 label-route-capability peer 1.1.1.2 enable peer 1.1.1.2 route-policy policy2 export peer 1.1.1.2 label-route-capability # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label route-policy policy2 permit node 1 if-match mpls-label apply mpls-label # ip route-static 1.1.1.4 255.255.255.255 10.0.7.7 # return
ASBR2 configuration file
# sysname ASBR2 # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.4 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp mldp recursive-fec # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.000d.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.7.7 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/4 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.16.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.4 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 200 peer 10.0.7.5 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.5 as-number 200 peer 1.1.1.5 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 1.1.1.5 255.255.255.255 peer 10.0.7.5 enable peer 10.0.7.5 route-policy policy1 export peer 10.0.7.5 label-route-capability peer 1.1.1.5 enable peer 1.1.1.5 route-policy policy2 export peer 1.1.1.5 label-route-capability # route-policy policy1 permit node 1 apply mpls-label route-policy policy2 permit node 1 if-match mpls-label apply mpls-label # ip route-static 1.1.1.3 255.255.255.255 10.0.7.5 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # multicast ipv6 mvpn 1.1.1.5 # ip vpn-instance ngv6 ipv6-family route-distinguisher 1:5 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity multicast ipv6 routing-enable mvpn c-multicast signaling bgp auto-discovery inter-as ipmsi-tunnel mldp # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.5 # mpls # mpls ldp mldp p2mp mldp recursive-fec # isis 1 is-level level-2 cost-style wide network-entity 10.0000.0000.000e.00 # isis 2 vpn-instance ngv6 is-level level-2 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0007.00 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 ipv6 import-route bgp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip address 10.0.16.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/4 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance ngv6 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:14::4 64 isis ipv6 enable 2 pim ipv6 sm # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.5 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 200 peer 1.1.1.2 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.2 ebgp-max-hop 10 peer 1.1.1.2 connect-interface LoopBack0 peer 1.1.1.4 as-number 200 peer 1.1.1.4 connect-interface LoopBack0 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.2 enable peer 1.1.1.4 enable peer 1.1.1.4 label-route-capability # ipv6-family mvpn policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.2 enable # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.2 enable # ipv6-family vpn-instance ngv6 import-route isis 2 # pim-ipv6 vpn-instance ngv6 static-rp 2001:DB8:6::3 source-lifetime 60 # returnCE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # multicast ipv6 routing-enable # isis 2 is-level level-2 ipv6 enable topology ipv6 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:3::1 64 isis ipv6 enable 2 pim ipv6 sm mld enable mld static-group FF3E::1 source 2001:DB8:5::2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/4 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:14::1 64 isis ipv6 enable 2 pim ipv6 sm # pim-ipv6 static-rp 2001:DB8:6::3 # return