Overview of EFM OAM
Ethernet operation, administration and maintenance (OAM) effectively improves Ethernet manageability and maintainability and ensures network stability.
Easy-to-use Ethernet techniques support good bandwidth expansibility on low-cost hardware. With these advantages, Ethernet services and structures have been widely used on enterprise networks, metropolitan area networks (MANs), and wide area networks (WANs). As Ethernet applications become increasingly popular, carriers are eager to use improved Ethernet OAM functions to maintain and operate Ethernets.
Ethernet OAM consists of fault management and performance management.
Ethernet OAM is classified as link- or network-level Ethernet OAM. Link-level Ethernet OAM technologies, such as Ethernet in the First Mile (EFM) OAM defined in IEEE 802.3ah, are introduced to implement Ethernet OAM in the last mile. Link-level Ethernet OAM provides continuity check, fault monitoring, remote fault notification, and remote loopback functions for the link between directly connected devices.
EFM Association
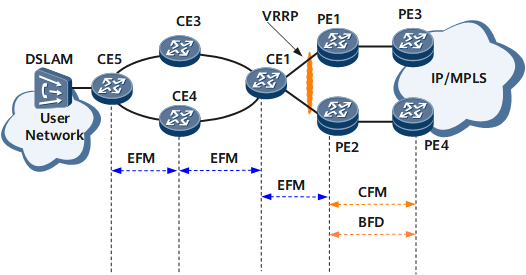
On the network shown in Figure 1, multiple detection protocols such as EFM, BFD, CFM are deployed to detect link connectivity. The link CE5-CE4-CE1-PE2-PE4 is used as an example.
If the link between CE5 and CE4 goes faulty, CE1 cannot detect the fault. As a result, return traffic continues to be forwarded to CE4.
If the link between PE2 and PE4 goes faulty, CE1 cannot detect the fault. As a result, services are interrupted.
If the link between CE1 and PE2 goes faulty, PE4 cannot detect the fault. As a result, a large volume of unnecessary traffic continues to be forwarded to PE4.
To address the preceding problems, association between EFM and detection protocols can be configured so that faults can be reported to remote devices. This association enables network administrators to dynamically understand link status based on alarm information and rectify faults in time.
Table 1 lists associations between EFM and protocols and their usage scenarios.
| Association Type | Usage Scenario |
|---|---|
Association between EFM and CFM |
On the network shown in Figure 1, when EFM is deployed for the link between CE1 and PE2 and CFM is deployed for the link between PE2 and PE4, association between EFM and CFM can be deployed on PE2. The following results will be achieved:
|
Association between EFM and BFD |
On the network shown in Figure 1, when EFM is deployed for the link between CE1 and PE2 and BFD is deployed for the link between PE2 and PE4, association between EFM and BFD can be deployed on PE2. The following results will be achieved:
|
Association between EFM and VRRP |
On the network shown in Figure 1, EFM is deployed for the links between CE1 and PE1 and between CE1 and PE2, and VRRP is configured on PE1 and PE2. After association between EFM and VRRP is configured, EFM will notify VRRP of detected faults, triggering a master/backup VRRP switchover. |
Association between EFM and interfaces can be used to rapidly switch traffic to a backup link when a device carrying IP services is usually dual-homed to an IP network. An EFM association triggers MAC entry deletion if link faults are detected in VLL PW.