Example for Configuring EVC VPLS Accessing L3VPN
Networking Requirements
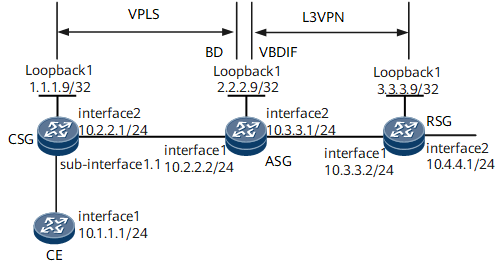
On the network shown in Figure 1, on the access network, the CSG provides a BD for user site access and connects to the ASG over a VPLS PW; on the bearer network, the ASG uses the VBDIF interface to terminate the VPLS PW and establishes an L3VPN with the RSG.

In this example, interface 1, sub-interface 1.1, and interface 2 stand for GE 0/1/0, GE 0/1/0.1, and GE 0/1/8, respectively.
Configuration Roadmap
Configure IP addresses and IGPs on the CSG, ASG, and RSG.
Configure LDP LSPs on the CSG, ASG, and RSG.
- Configure EVC VPLS on the CSG and ASG.
Create an EVC Layer 2 sub-interface and a BD and add the sub-interface to the BD.
Create a BD VSI, specify the signaling protocol as LDP, and bind the VSI to the corresponding BD.
- Configure an L3VPN on the ASG and RSG.
Configure VPN instances using the IPv4 address family.
Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship.
Create a VBDIF interface on the ASG and bind the VBDIF interface to the L3VPN.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
BD IDs on the CSG and ASG
VSI IDs on the CSG and ASG (must be the same)
VSI names and interfaces bound to VSIs on the CSG and ASG
MPLS LSR IDs on the CSG, ASG, and RSG
VPN instance names and VPN targets on the ASG and RSG
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each node interface, including the loopback interface.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files.
- Configure an IGP on each node. In this example, OSPF is used.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files.
- Configure an MPLS LDP tunnel on each node.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files.
- Configure EVC VPLS on the CSG and ASG.
- Configure an L3VPN on the ASG and RSG.
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the configuration, run the display bridge-domain command to view BD information, including the BD to which a Layer 2 sub-interface belongs and the BD status. The following example uses the command output on the CSG.
[~CSG] display bridge-domain 1 -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- MAC_LRN: MAC learning; STAT: Statistics; SPLIT: Split-horizon; BC: Broadcast; MC: Unknown multicast; UC: Unknown unicast; *down: Administratively down; FWD: Forward; DSD: Discard; U: Up; D: Down; -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- BDID Ports -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 GE0/1/0.1(U) BDID State MAC-LRN STAT BC MC UC SPLIT Description -------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 1 up enable disable FWD FWD FWD disable
Run the display vsi name evc-vsi command. The command output shows that the VSI named evc-vsi is up. The following example uses the command output on the CSG.
[~CSG] display vsi name evc-vsi -------------------------------------------------------------------------- Vsi Mem PW Mac Encap Mtu Vsi Name Disc Type Learn Type Value State -------------------------------------------------------------------------- evc-vsi -- ldp qualify vlan 1500 upRun the display ip routing-table vpn-instance command. The command output shows IPv4 VPN instance routing table information. The following example uses the command output on the ASG.
[~ASG] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpna Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : vpna Destinations : 5 Routes : 5 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 10.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 10.1.1.2 Vbdif1 10.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vbdif1 10.1.1.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Vbdif1 10.4.4.0/24 IBGP 255 0 RD 3.3.3.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 255.255.255.255/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Configuration Files
CSG configuration file
# sysname CSG # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 # mpls # mpls l2vpn # vsi evc-vsi bd-mode pwsignal ldp vsi-id 10 peer 2.2.2.9 # bridge-domain 1 l2 binding vsi evc-vsi pw-tag 1 # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0.1 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 1 rewrite pop single bridge-domain 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.2.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 # return
ASG configuration file
# sysname ASG # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:100 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 100:100 export-extcommunity vpn-target 100:100 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 # mpls # mpls l2vpn # vsi evc-vsi bd-mode pwsignal ldp vsi-id 10 peer 1.1.1.9 # bridge-domain 1 l2 binding vsi evc-vsi pw-tag 1 # mpls ldp # interface Vbdif 1 ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.2.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.3.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna import-route direct # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.3.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return
RSG configuration file
# sysname RSG # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:100 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 100:100 export-extcommunity vpn-target 100:100 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.3.3.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.4.4.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.0 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna import-route direct # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.3.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return