(Optional) Configuring FRR
In EVPN VPWS over MPLS multi-homing single-active scenarios, FRR needs to be configured to prevent traffic loss if the primary PE fails.
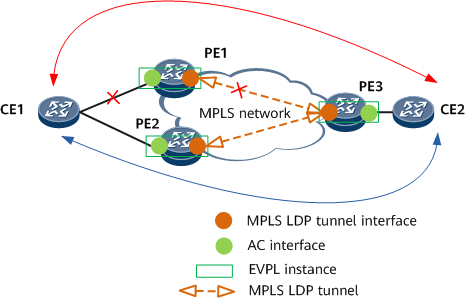
Usage Scenario
As shown in Figure 1, in the EVPN VPWS over MPLS multi-homing single-active scenario, a CE is dual-homed to PE1 and PE2 in active-active mode, and PE3 forwards traffic to PE1 and PE2 working in active/standby mode. When PE1 is the active device, the red path between CE1 and CE2 is the active path, and the blue path is the standby path. To prevent traffic loss if the active path fails, FRR needs to be configured.
In normal situations, downstream traffic of PE3 is sent to PE1. The local and remote FRR function for MAC routes is enabled on PE1 and PE2. If PE1 detects a fault on the link between itself and CE1, PE1 forwards traffic to PE2 and then to CE1. Remote FRR is enabled on PE3. When PE3 detects a fault between itself and PE1, PE3 rapidly switches traffic to PE2 and then sends traffic to CE1, preventing traffic loss.