Example for Configuring the Static VXLAN Active-Active Scenario (in VLAN-Aware Bundle Mode)
In the scenario where a data center is interconnected with an enterprise site, a CE is dual-homed to a VXLAN network. In this way, carriers can enhance VXLAN access reliability to improve the stability of user services so that rapid convergence can be implemented in case of a fault. The VLAN-aware bundle access mode allows different VLANs configured on a physical interface to access the same EVPN instance (EVI) and isolates the BDs to which the VLAN-configured sub-interfaces belong.
Networking Requirements
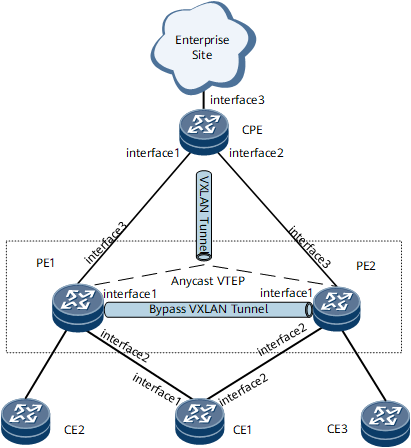
On the network shown in Figure 1, CE1 is dual-homed to PE1 and PE2 through an Eth-Trunk. PE1 and PE2 use a virtual address as the source virtual tunnel end point (VTEP) address of a Network Virtualization Edge (NVE) interface, that is, anycast VTEP address. In this way, the CPE only detects the remote NVE interface, and a static VXLAN tunnel is established between the CPE and the anycast VTEP address.
Packets sent by the CPE are forwarded to CE1 through either PE1 or PE2. However, a CE may be single-homed to a PE on the network, for example, CE2 and CE3. In this case, the CPE sends packets to one PE, and the packets may be sent to another PE before being forwarded to the single-homed CE. Therefore, a bypass VXLAN needs to be established between PE1 and PE2 to forward packets.
To allow different VLANs configured on a physical interface to access the same EVI and isolate the BDs to which the VLAN-configured sub-interfaces belong, configure the VLAN-aware bundle mode for the access of a CE to the PEs.

Interfaces 1 through 3 in this example represent GE 0/1/1, GE 0/1/2, and GE 0/1/3, respectively.
Device Name |
Interface Name |
IP Address and Mask |
|---|---|---|
PE1 |
GE 0/1/1 |
10.1.20.1/24 |
GE 0/1/2 |
- |
|
GE 0/1/3 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
|
Loopback1 |
1.1.1.1/24 |
|
Loopback2 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
|
PE2 |
GE 0/1/1 |
10.1.20.2/24 |
GE 0/1/2 |
- |
|
GE 0/1/3 |
10.1.2.1/24 |
|
Loopback1 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
|
Loopback2 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
|
CE1 |
GE 0/1/1 |
- |
GE 0/1/2 |
- |
|
CPE |
GE 0/1/1 |
10.1.1.2/24 |
GE 0/1/2 |
10.1.2.2/24 |
|
GE 0/1/3 |
- |
|
Loopback1 |
4.4.4.4/32 |
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Configure an IGP on each PE and the CPE to ensure Layer 3 connectivity.
- Configure fast traffic switching on PE1 and PE2. If a PE fails, this configuration allows downstream traffic on the CPE to be switched to another PE, which then forwards the traffic to a CE.
- Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between PE1 and PE2 so that they can exchange VXLAN EVPN routes.
- Create an EVPN instance in BD mode and a BD and bind the BD to the EVPN instance with a BD tag set on each of PE1 and PE2.
- Configure the same anycast VTEP address (virtual address) on PE1 and PE2 as the NVE interface's source address, which is used to establish a VXLAN tunnel with the CPE. Establish static VXLAN tunnels between PE1 and the CPE and between PE2 and the CPE, allowing the PEs to communicate with the CPE.
- Configure PE1 and PE2 as service access points, and manually configure the same ESI on PE1 and PE2 for the access links connected to CE1, allowing CE1 to be dual-homed to the PEs.
- Enable inter-chassis VXLAN on PE1 and PE2, configure different bypass addresses for the PEs, and establish a bypass VXLAN tunnel between the PEs, allowing communication between PE1 and PE2.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Interfaces and their IP addresses
VPN and EVPN instance names
Import and export VPN targets for the VPN and EVPN instances
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each device interface, including the loopback interfaces.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure an IGP on each PE and the CPE. IS-IS is used in this example.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure fast traffic switching on each PE.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] evpn [*PE1-evpn] vlan-extend private enable [*PE1-evpn] vlan-extend redirect enable [*PE1-evpn] local-remote frr enable [*PE1-evpn] bypass-vxlan enable [*PE1-evpn] quit [*PE1] commit
Repeat this step for PE2. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Establish a BGP EVPN peer relationship between PE1 and PE2 so that they can exchange VXLAN EVPN routes.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack 0 [*PE1-bgp] l2vpn-family evpn [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] undo policy vpn-target [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2.2.2.2 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] peer 2.2.2.2 advertise encap-type vxlan [*PE1-bgp-af-evpn] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
Repeat this step for PE2. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Establish VXLAN tunnels.
- Perform access-side configurations on each PE.
# Configure PE1.
[*PE1] e-trunk 1 [*PE1-e-trunk-1] priority 10 [*PE1-e-trunk-1] peer-address 2.2.2.2 source-address 1.1.1.1 [*PE1-e-trunk-1] quit [*PE1] interface eth-trunk 1 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] mac-address 00e0-fc12-3456 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] mode lacp-static [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] e-trunk 1 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] e-trunk mode force-master [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] es track evpn-peer 2.2.2.2 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] esi 0000.0001.0001.0001.0001 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1] quit [*PE1] interface eth-trunk1.1 mode l2 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1.1] encapsulation dot1q vid 100 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1.1] bridge-domain 10 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1.1] quit [*PE1] interface eth-trunk1.2 mode l2 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1.2] encapsulation dot1q vid 200 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1.2] bridge-domain 20 [*PE1-Eth-Trunk1.2] quit [~PE1] commit
Repeat this step for PE2. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display vxlan tunnel command on PE1 and check information about the VXLAN tunnels. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display vxlan tunnel Number of vxlan tunnel : 2 Tunnel ID Source Destination State Type Uptime ----------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 4026531841 3.3.3.3 4.4.4.4 up static 00:30:12 4026531842 1.1.1.1 2.2.2.2 up dynamic 00:12:28Run the display bgp evpn all routing-table command on PE1. The command output shows that EVPN routes carrying Ethernet tag IDs are received from PE2.
[~PE1] display bgp evpn all routing-table Local AS number : 100 BGP Local router ID is 1.1.1.1 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete EVPN address family: Number of A-D Routes: 4 Route Distinguisher: 11:11 Network(ESI/EthTagId) NextHop *> 0000.0001.0001.0001.0001:100 0.0.0.0 * i 3.3.3.3 *> 0000.0001.0001.0001.0001:200 0.0.0.0 * i 3.3.3.3 EVPN-Instance evpn1: Number of A-D Routes: 4 Network(ESI/EthTagId) NextHop *> 0000.0001.0001.0001.0001:100 0.0.0.0 i 3.3.3.3 *> 0000.0001.0001.0001.0001:200 0.0.0.0 i 3.3.3.3 EVPN address family: Number of Inclusive Multicast Routes: 4 Route Distinguisher: 11:11 Network(EthTagId/IpAddrLen/OriginalIp) NextHop *> 100:32:3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 * i 3.3.3.3 *> 200:32:3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 * i 3.3.3.3 EVPN-Instance evpn1: Number of Inclusive Multicast Routes: 4 Network(EthTagId/IpAddrLen/OriginalIp) NextHop *> 100:32:3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 * i 3.3.3.3 *> 200:32:3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 * i 3.3.3.3
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # evpn vlan-extend private enable vlan-extend redirect enable local-remote frr enable bypass-vxlan enable # evpn vpn-instance evpn1 bd-mode route-distinguisher 11:11 vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # bridge-domain 10 vxlan vni 10 split-horizon-mode evpn binding vpn-instance evpn1 bd-tag 100 # bridge-domain 20 vxlan vni 20 split-horizon-mode evpn binding vpn-instance evpn1 bd-tag 200 # e-trunk 1 priority 10 peer-address 2.2.2.2 source-address 1.1.1.1 # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 # interface Eth-Trunk1 mac-address 00e0-fc12-3456 mode lacp-static e-trunk 1 e-trunk mode force-master es track evpn-peer 2.2.2.2 esi 0000.0001.0001.0001.0001 # interface Eth-Trunk1.1 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 1 bridge-domain 10 # interface Eth-Trunk1.2 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 2 bridge-domain 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.20.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # interface LoopBack2 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # interface Nve1 source 3.3.3.3 bypass source 1.1.1.1 mac-address 00e0-fc12-7890 vni 10 head-end peer-list protocol bgp vni 10 head-end peer-list 4.4.4.4 vni 20 head-end peer-list protocol bgp vni 20 head-end peer-list 4.4.4.4 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.2 enable # l2vpn-family evpn undo policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 2.2.2.2 advertise encap-type vxlan # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # evpn vlan-extend private enable vlan-extend redirect enable local-remote frr enable bypass-vxlan enable # evpn vpn-instance evpn1 bd-mode route-distinguisher 11:11 vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # bridge-domain 10 vxlan vni 10 split-horizon-mode evpn binding vpn-instance evpn1 bd-tag 100 # bridge-domain 20 vxlan vni 20 split-horizon-mode evpn binding vpn-instance evpn1 bd-tag 200 # e-trunk 1 priority 10 peer-address 1.1.1.1 source-address 2.2.2.2 # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # interface Eth-Trunk1 mac-address 00e0-fc12-3456 mode lacp-static e-trunk 1 e-trunk mode force-master es track evpn-peer 1.1.1.1 esi 0000.0001.0001.0001.0001 # interface Eth-Trunk1.1 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 1 bridge-domain 10 # interface Eth-Trunk1.2 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 2 bridge-domain 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.20.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # interface LoopBack2 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # interface Nve1 source 3.3.3.3 bypass source 2.2.2.2 mac-address 00e0-fc12-7890 vni 10 head-end peer-list protocol bgp vni 10 head-end peer-list 4.4.4.4 vni 20 head-end peer-list protocol bgp vni 20 head-end peer-list 4.4.4.4 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable # l2vpn-family evpn undo policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable peer 1.1.1.1 advertise encap-type vxlan # return
CE configuration file
# sysname CE # vlan batch 1 to 4094 # interface Eth-Trunk1 portswitch port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 1 2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown eth-trunk 1 # return
CPE configuration file
# sysname CPE # bridge-domain 10 vxlan vni 10 split-horizon-mode # bridge-domain 20 vxlan vni 20 split-horizon-mode # isis 1 network-entity 20.0000.0000.0001.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown esi 0000.0000.0000.0000.0017 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3.1 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 100 bridge-domain 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3.2 mode l2 encapsulation dot1q vid 200 bridge-domain 10 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # interface Nve1 source 4.4.4.4 vni 10 head-end peer-list 3.3.3.3 vni 20 head-end peer-list 3.3.3.3 # return