Configuring EVPN E-LAN over mLDP P2MP Tunnels
An EVPN can carry multicast services. To reduce redundant traffic and conserve bandwidth resources, you can configure EVPN to use an mLDP P2MP tunnel for service transmission.
Usage Scenario
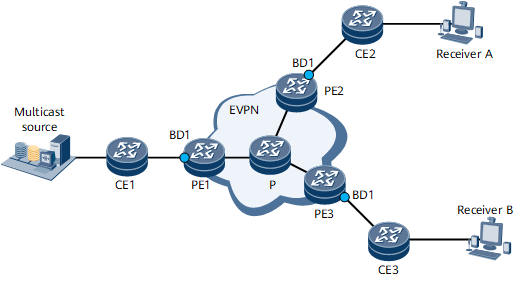
Multicast services, such as IPTV, multimedia conferencing, and Massive Multiplayer Online Role Playing Game (MMORPG) services, are becoming more and more common. As a result, the number of multicast services carried over EVPNs is growing. On the network shown in Figure 1, PE1 is the root node, and PE2 and PE3 are leaf nodes. The access side is the multicast source and the receiver. By default, an EVPN sends multicast service traffic from PE1 to PE2 and PE3 by means of ingress replication. Specifically, PE1 replicates a multicast packet into two copies and sends them to the P. The P then sends one copy to PE2 and the other copy to PE3. For each additional receiver, an additional copy of the multicast packet is sent. This increases the volume of traffic on the link between PE1 and the P, consuming bandwidth resources. To conserve bandwidth resources, you can configure EVPN to use an mLDP P2MP tunnel to transmit multicast services. After the configuration is complete, PE1 sends only one copy of multicast traffic to the P. The P replicates the multicast traffic into copies and sends them to the leaf nodes, reducing the volume of traffic between PE1 and P.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring EVPN E-LAN over mLDP P2MP tunnels, complete the following tasks:
Configure BD-based EVPN functions over the EVPN.
Procedure
- Perform the following steps on the root node:
- Perform the following steps on each leaf node:
Verifying the Configuration of EVPN to Use an mLDP P2MP Tunnel for Service Transmission
Run the display evpn vpn-instance name vpn-instance-name inclusive-provider-tunnel verbose command to check information about EVPN using an mLDP P2MP tunnel for service transmission.