Configuring an EVPN L3VPN HVPN over MPLS
An EVPN L3VPN hierarchical VPN (HVPN) over MPLS is a hierarchical EVPN, on which PEs play different roles and provide different functions. These PEs form a hierarchical architecture to provide functions that are provided by one PE on a non-hierarchical VPN. EVPN L3VPN HVPNs over MPLS lower the performance requirements for PEs.
Usage Scenario
At present, the IP bearer network uses L2VPN and L3VPN (HVPN) to carry Layer 2 and Layer 3 services, respectively. The protocols are complex. EVPN can carry both Layer 2 and Layer 3 services. To simplify service bearer protocols, many IP bearer networks will evolve to EVPN. Specifically, L3VPN HVPN, which carries Layer 3 services, needs to evolve to EVPN L3VPN HVPN over MPLS.
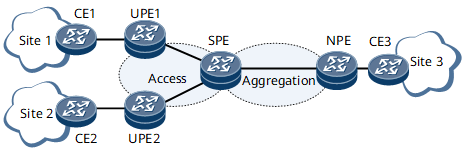
- UPE: A UPE is a device that is directly connected to a user and is referred to as an underlayer PE or a user-end PE, therefore shortened as UPE. UPEs provide access services for users.
- SPE: An SPE is a superstratum PE or service provider-end PE, which is connected to UPEs and located at the core of a network. An SPE manages and advertises VPN routes.
- NPE: An NPE is a network provider-end PE that is connected to SPEs and located at the network side.
The UPEs and SPE are connected at the access layer. The SPE and NPE are connected at the aggregation layer. An EVPN L3VPN HVPN over MPLS can be deployed only after separate IGPs are deployed at the access and aggregation layers to implement interworking.
EVPN L3VPN HoVPN over MPLS: An SPE advertises only default routes or summarized routes to UPEs. UPEs do not have specific routes to NPEs and can only send service data to SPEs over default routes. As a result, route isolation is implemented. An EVPN L3VPN HoVPN over MPLS can use devices with relatively poor route management capabilities as UPEs, reducing network deployment costs.
EVPN L3VPN H-VPN over MPLS: SPEs advertise specific routes to UPEs. UPEs function as RR clients to receive the specific routes reflected by SPEs functioning as RRs. This mechanism facilitates route management and traffic forwarding control.
Interworking between EVPN L3VPN HoVPN over MPLS and common L3VPN: EVPN L3VPN HoVPN over MPLS is deployed between the UPEs and SPE, and L3VPN is deployed between the SPE and NPE. The SPE advertises only default routes or summarized routes to the UPEs. After receiving specific routes (EVPN routes) from the UPEs, the SPE encapsulates these routes into VPNv4 routes and advertises them to the NPE.
Interworking between L3VPN HoVPN and EVPN L3VPN over MPLS: L3VPN HoVPN is deployed between the UPEs and SPE, and EVPN L3VPN over MPLS is deployed between the SPE and NPE. The SPE advertises only default routes or summarized routes to the UPEs. After receiving specific routes (L3VPN routes) from the UPEs, the SPE encapsulates these routes into EVPN routes and advertises them to the NPE.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring an EVPN L3VPN HVPN over MPLS, complete the following tasks:
Configure an IGP on each network layer (between the UPEs and SPE, and between the SPE and NPE) to implement interworking. Different IGPs can be deployed at the access and aggregation layers, or the same IGP with different process IDs can be deployed at the different layers.
- Configuring an EVPN L3VPN HoVPN over MPLS
- On an EVPN L3VPN HoVPN over MPLS, a UPE only needs to obtain a default route from an SPE. This mechanism isolates routes and reduces the route storage space required on a UPE.
- Configuring an EVPN L3VPN H-VPN over MPLS
- On an EVPN L3VPN H-VPN over MPLS, SPEs function as route reflectors (RRs), and UPEs and NPEs function as RR clients. UPEs and NPEs receive specific routes from SPEs.
- Configuring Interworking Between an EVPN L3VPN HoVPN over MPLS with a Common L3VPN
- As L3VPN HoVPN evolves towards EVPN L3VPN HoVPN over MPLS, interworking between EVPN L3VPN HoVPN over MPLS and common L3VPN occurs. An EVPN L3VPN HoVPN over MPLS is deployed between UPEs and SPEs, and a common L3VPN is deployed between SPEs and NPEs.
- Configuring Interworking Between an L3VPN HoVPN and an EVPN L3VPN over MPLS
- As L3VPN HoVPN evolves towards EVPN HoVPN over MPLS, interworking between L3VPN HoVPN and EVPN L3VPN over MPLS occurs. An L3VPN HoVPN is deployed between UPEs and SPEs, and an EVPN L3VPN over MPLS is deployed between SPEs and NPEs.
- Verifying the EVPN L3VPN HVPN over MPLS Configuration
- After configuring an EVPN L3VPN HVPN over MPLS, verify the configuration.