Configuring EVPN HVPN to Carry Layer 2 Services
The EVPN HVPN function can be configured as a replacement of HVPLS to carry Layer 2 services on a hierarchical network.
Context
On an HVPLS-deployed network, if users want to evolve the VPLS function to the EVPN function, users can deploy the EVPN HVPN function as a replacement of HVPLS to carry Layer 2 services.
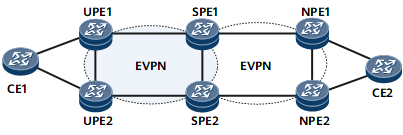
As shown in Figure 1, UPEs and SPEs are connected over the access network, and SPEs and NPEs are connected over the aggregation network. An IGP needs to be deployed on both the access network and aggregation network to achieve route communication at each layer. The BD EVPN function needs to be deployed between neighboring devices. In addition, the EVPN RR function can be deployed on SPEs to allow CE1 and CE2 to transmit information, such as the MAC address.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring EVPN HVPN to carry Layer 2 services, complete the following tasks:
Configure BD EVPN between SPEs and NPEs.
Perform the following operations on each SPE to implement the EVPN RR function:
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run bgp { as-number-plain | as-number-dot }
The BGP view is displayed.
- Run l2vpn-family evpn
The BGP-EVPN address family view is displayed.
- Specify a UPE and an RR client.
Run peer { ipv4-address | group-name } upe
A peer is configured as the UPE.
Specify an RR client.
To configure the RR function and specify the UPE as an RR client, run the peer { ipv4-address | group-name } reflect-client command.
To configure a device to use its own IP address as the next-hop IP address during route advertisement, run the peer { ipv4-address | group-name } next-hop-local command.
To allow an SPE to use its own IP address as the next-hop IP address when advertising routes to UPEs and NPEs, run the peer next-hop-local command on the SPE twice with different parameters specified for UPEs and NPEs.
- (Optional) Run apply-label per-nexthop
The next-hop-based label distribution function is enabled for EVPN routes.
In an EVPN HVPN scenario, if an SPE needs to send a large number of EVPN routes but the MPLS labels are insufficient, next-hop-based label distribution can be configured on the SPE to conserve MPLS label resources.

After next-hop-based label distribution is enabled or disabled, the label allocated by the SPE changes, causing packet loss.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
Follow-up Procedure
On NPEs, configure the MAC-based load balancing function to improve network resource utilization.
Run the system-view command to enter the system view.
Enter the EVPN instance view or BD-EVPN instance view.
To enter the EVPN instance view, run the evpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name command .
To enter the BD-EVPN instance view, run the evpn vpn-instance vpn-instance-name bd-mode command.
Run the mac load-balancing command to enable MAC-based load balancing.
Run the commit command to commit the configuration.
Verifying the Configuration
Run the display bgp evpn { all | route-distinguisher route-distinguisher | vpn-instance vpn-instance-name } routing-table { ad-route | es-route | inclusive-route | mac-route | prefix-route } prefix command on a SPE to view details about BGP EVPN routes.