Configuring EVPN to Advertise UMR Routes
Configuring EVPN to advertise unknown MAC routes (UMRs) helps mitigate the MAC address learning pressure of RRs and aggregation devices.
Context
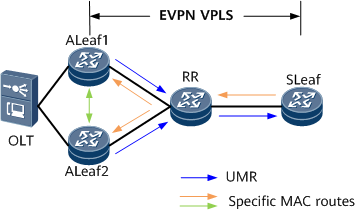
In the standard EVPN VPLS networking solution, all user-side specific MAC routes are transmitted through an RR on the entire network. As a result, the RR has heavy MAC address learning pressure. In addition, an aggregation device usually connects to multiple access devices. Therefore, aggregation devices also have heavy MAC address learning pressure, and the MAC address table capacity of aggregation devices limits the number of access users.
To solve this problem, configure EVPN to advertise UMRs. On the network shown in Figure 1, configure each ALeaf node at the access layer to generate and advertise a UMR to the RR, but not to advertise specific MAC routes to the RR. This can reduce the MAC address learning pressure of the RR. Meanwhile, configure the RR to reflect only the UMRs sent by ALeaf nodes to the SLeaf node at the aggregation layer. This can reduce the MAC address learning pressure of the SLeaf node and prevent the MAC address table capacity of the SLeaf node from limiting the number of access users. Moreover, you need to configure ALeaf nodes to send only specific MAC routes to each other and configure the RR to reflect only received specific MAC routes to ALeaf nodes, so that EVPN VPLS services can run properly.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring EVPN to advertise UMRs, complete one of the following tasks:
Procedure
- Enable UMR generation on each ALeaf node.
- Configure an ALeaf node to advertise only specific MAC routes to other ALeaf nodes.
- Configure the RR to advertise only specific MAC routes to ALeaf nodes.
- Enable UMR forwarding on the SLeaf node.
Verifying the Configuration
After completing the configuration, perform the following operations to verify it:
- Run the display bgp evpn all routing-table mac-route 0:48:0000-0000-0000:0:0.0.0.0 command on an ALeaf node to check the advertised UMR or on the SLeaf node to check the received UMR.
- If specific MAC route suppression is specified when UMR generation is enabled on an ALeaf node, you can run the display bgp evpn all routing-table mac-route prefix command on the ALeaf node to view a specified specific MAC route. The command output shows that the route is marked with the suppressed flag.