EVPN Service Modes
Service Mode |
Application Scenario |
|---|---|
The physical interface connected to a user network is directly bound to a common EVI. This service mode is used to carry only Layer 2 services. |
|
The physical interface connected to a user network is divided into different sub-interfaces. Each sub-interface is added to a specific BD, and each BD is bound to a specific EVI. One EVI is required per user. This service mode is used to carry Layer 2 or Layer 3 services. |
|
Users are divided based on VLANs. Each VLAN is added to a specific BD, and each BD is bound to a specific EVI. This service mode is used to carry Layer 2 or Layer 3 services. |
|
Users are divided based on VLANs. Each VLAN is added to a specific BD, and all these BDs are bound to the same EVI. This service mode is used to carry Layer 2 or Layer 3 services. |
Port Based
In port-based mode, an entire interface is used for service access. Specifically, the physical interface connected to a user network is directly bound to a common EVI (not an EVI in BD or VPWS mode) and has no sub-interfaces created. This service mode is used to carry Layer 2 services.
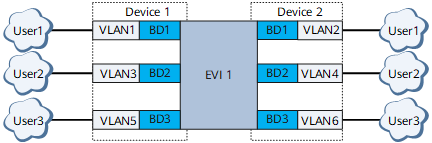
VLAN Based
On the network shown in Figure 1, in VLAN-based mode, the physical interfaces connected to user networks each have different sub-interfaces created. Each sub-interface is associated with a unique VLAN and added to a specific BD, and each BD is bound to a specific EVI. In this service mode, the sub-interface, VLAN, BD, and EVI are exclusively used by a user to access the network, and a separate MAC forwarding table is used on the forwarding plane for each user. Although this mode effectively ensures service isolation, it consumes a large amount of EVI resources because each user requires one EVI. This service mode is used to carry Layer 2 or Layer 3 services.
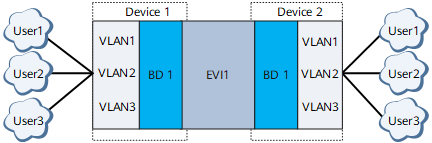
VLAN Bundle
On the network shown in Figure 2, in VLAN bundle mode, an EVI connects to multiple users that are divided by VLAN, and the EVI is bound to a BD. In this service mode, the users connected to the same EVI share a MAC forwarding table, requiring each user on the network to have a unique MAC address. This service mode is used to carry Layer 2 or Layer 3 services.

In a VLAN bundle scenario, only EVC VLAN tag termination sub-interfaces support both Layer 2 and Layer 3 interfaces. Other EVC sub-interfaces support only Layer 2 services.
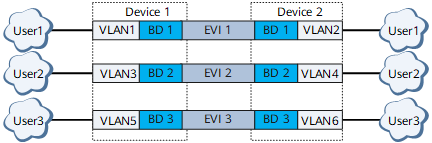
VLAN-Aware Bundle
On the network shown in Figure 3, in VLAN-aware bundle mode, an EVI connects to multiple users divided by VLAN. Additionally, the EVI can be bound to multiple BDs. In this case, the EVI must have a different BD tag configured when being bound to a BD. When EVPN peers send routes to each other, a BD tag is encapsulated into the Ethernet Tag ID field of Ethernet auto-discovery route, MAC/IP advertisement route, and inclusive multicast route packets. In this service mode, users connected to the same EVI use separate forwarding entries. During traffic forwarding, the system uses the BD tag carried in packets to locate the corresponding BD MAC forwarding table and searches the table for a forwarding entry based on a MAC address.
Mode |
Difference |
|---|---|
Unqualify |
MAC addresses can be learned based on only BDs. The VLANs to which routes with the same MAC address in a BD belong cannot be identified. The sub-interface bound to each BD can encapsulate only a single VLAN tag into a packet. |
Qualify |
MAC addresses can be learned based on a combination of MAC addresses and VLANs. The VLANs to which routes with the same MAC address in a BD belong can be identified based on VLAN IDs. The sub-interface bound to each BD can encapsulate multiple VLAN tags into a packet in batches. |
Load balancing: In VLAN-aware bundle mode, load balancing can be implemented only if a MAC/IP advertisement route and Ethernet auto-discovery route have the same Ethernet segment identifier (ESI) and the same BD tag. If the BD tags are inconsistent, load balancing cannot be implemented because the routes belong to different BDs.
- DF election:
For interface-based DF election, the system chooses the first interface to go up in a BD for DF election.
If AC interfaces are enabled to influence DF election, a PE cannot participate in DF election if the system does not receive any Ethernet auto-discovery route advertised by the PE. In this scenario, if the VLAN-aware bundle mode is enabled, an Ethernet auto-discovery route is generated for each BD tag. As such, a PE can participate in DF election only if the system receives Ethernet auto-discovery routes in all BDs bound to a specified EVI.
Host migration: When the system generates a local MAC/IP advertisement route, the system checks whether it has received an identical route from the remote end. If it has, the system adds the MAC address transfer attribute to the locally generated route or increments the value of the Sequence field in the MAC address transfer attribute by 1. In VLAN-aware bundle mode, a BD tag is the prefix key of a MAC/IP advertisement route. The system compares the BD tags carried in the received MAC/IP advertisement route and the locally generated one when checking MAC/IP advertisement routes. This prevents host migration failures caused by MAC address conflicts between different BDs.
Route re-origination: In the DCI solution, a DCI-PE re-originates a MAC/IP advertisement route received from a peer device and then sends the new route to the peer device. If the VLAN-aware bundle mode is enabled on a DCI-PE, the DCI-PE can re-originate a MAC/IP advertisement route only if the Ethernet tag ID is consistent with the BD tag in the route.