EVPN 6VPE
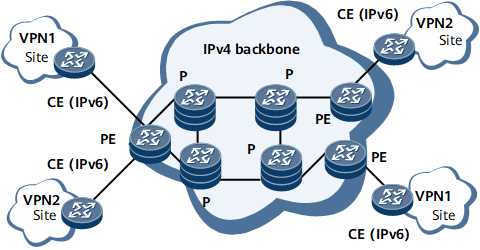
6VPE is a VPN technology that allows connections to multiple IPv6 private sites over an IPv4 public network or IPv4 backbone network. This ensures service isolation between the IPv6 private sites of different users. On the network shown in Figure 1, the components involved in the 6VPE function are the edge router (PE), customer edge router (CE), and core router (P) of the backbone network. The virtual routing and forwarding (VRF) tables stored on PEs are used to process the IPv6 routes of VPN sites. CEs that distribute user routes are connected to PEs through physical or logical interfaces. Ps are the backbone network devices used to forward VPN packets into which tunnel attributes are encapsulated.
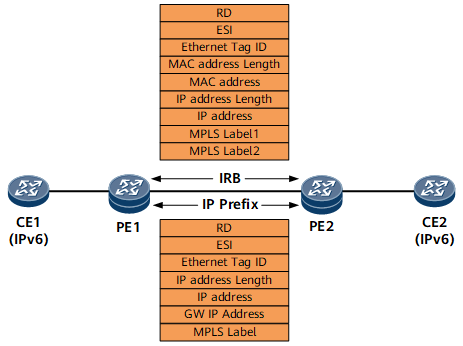
- Fields in host routes:
Route Distinguisher (RD): Specifies the RD value set for an EVPN instance.
Ethernet Segment Identifier (ESI): Uniquely identifies a connection between a PE and a CE.
Ethernet Tag ID: In VLAN-Aware accessing BD EVPN scenarios, the value is BD-Tag. In other scenarios, the value contains all 0s.
MAC Address Length: Specifies the MAC address length in an ND entry.
MAC Address: Specifies a MAC address in an ND entry.
IPAddress Length: Specifies the IPv6 address length in an ND entry.
IP Address: Specifies an IPv6 address in an ND entry.
MPLS Label1: Specifies the VPN label of EVPN.
MPLS Label2: Specifies the label used for Layer 3 traffic forwarding.
- Fields in IP prefix routes:
RD: Specifies the RD value set for an EVPN instance.
ESI: Uniquely identifies a connection between a PE and a CE.
Ethernet Tag ID: Currently, the value of this field contains all 0s.
IPAddress Length: Specifies the IPv6 address length in an ND entry.
IP Address: Specifies an IPv6 address in an ND entry.
GW IP Address: Specifies the default gateway address.
MPLS Label: Specifies the VPN label of EVPN.
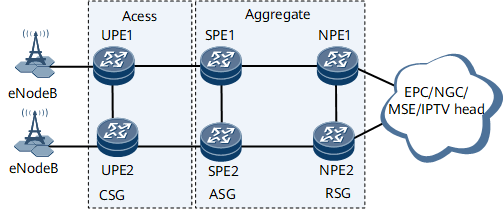
In Figure 3, the network has been deployed with the IP RAN solution and a large number of IPv4-related services. If new services need to be deployed, IPv6 addresses may be used in consideration of IPv4 address exhaustion. In this case, deploy EVPN L3VPNv6 HVPN in the 6VPE model to carry IPv6 services. The processing mechanism of EVPN 6VPE is similar to that of L3VPN HVPN.
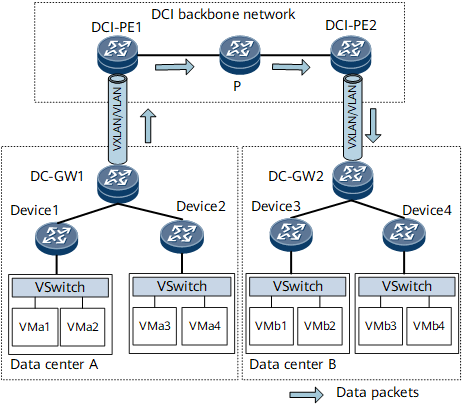
Similarly, EVPN 6VPE can be deployed in DCI scenarios to carry IPv6-related services. On the network shown in Figure 4, DCs are connected to the DCI backbone network over VXLAN tunnels or through VLAN sub-interfaces. The DCI backbone network uses the EVPN 6VPE function to transmit IPv6 routes between DCs. An MPLS or SR tunnel can be deployed between DCI-PEs to carry IPv6 services.