Application of iFIT Automatic Learning for Dynamic Flows
During iFIT measurement for dynamic flows, iFIT can automatically learn dynamic flows by matching source and destination addresses. In addition, iFIT allows you to configure whitelists on an interface to flexibly monitor service quality in real time. The implementation of automatic learning for dynamic flows is as follows:
- Configure iFIT automatic learning for dynamic iFIT flows on the ingress, including specifying a VPN domain and binding an interface to the VPN domain.
- Set parameters such as the flow learning type and flow learning measurement type to implement mask-based matching or exact matching for the source or destination address as required, and create whitelists to filter learned flows.
- Set other measurement points based on the statistics collection mode.
- End-to-end statistics collection: Only the egress is configured as the iFIT measurement point to collect performance statistics.
- Hop-by-hop measurement: iFIT measurement points are configured on each node that traffic passes through to collect performance statistics.
- Each measurement point reports the statistics to the NMS. Users can view the statistics on the GUI.
Figure 1 shows the typical networking of iFIT end-to-end automatic learning for dynamic flows. iFIT measurement points are deployed on the inbound and outbound interfaces of traffic in the VPN domain to flexibly monitor network performance in real time.
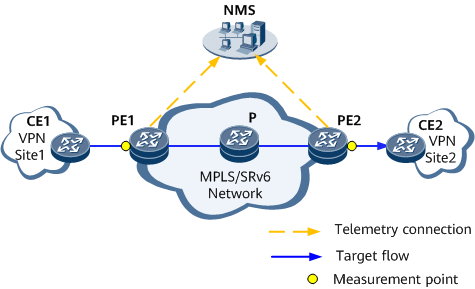
Figure 2 shows the typical networking of iFIT hop-by-hop automatic learning for dynamic flows. iFIT measurement points are deployed on each node through which network traffic in the VPN domain passes to flexibly monitor network performance in real time.
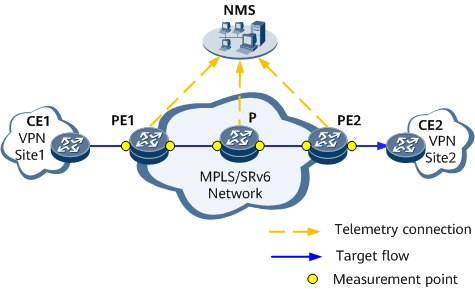

iFIT automatic learning for dynamic flows applies to all private network scenarios that support 5-tuple-based measurement.