Example for Configuring Static BGP IPv6 Flow Specification
If the characteristics of DoS or DDoS attack traffic are known, use the static IPv6 BGP Flow Specification function by manually configuring BGP IPv6 Flow Specification routes to ensure network security.
Networking Requirements
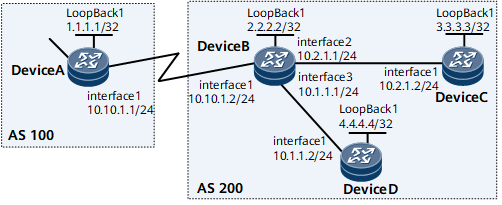
As shown in Figure 1, Device A belongs to AS 100, while Device B, Device C, and Device D belong to AS 200. Device B is an ingress of AS 200. AS 200 communicates with AS 100 through Device B.
The attack source in AS 100 may flow into AS 200 through Device B, posing a threat to AS 200.
In this situation, configure static BGP IPv6 Flow Specification to address this problem. The operation process is as follows: Configure a BGP IPv6 Flow Specification route manually and establish a BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer relationship between Device C and Device B as well as Device D and Device B. Then the route is sent to Device B to discard the attack traffic or limit its rate.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure OSPF on Device B, Device C, and Device D in AS 200 to enable them to communicate with each other.
Configure a BGP IPv6 Flow Specification route FlowSpec1 manually on Device C to discard attack traffic with the source port ID of 159.
Configure a BGP IPv6 Flow Specification route FlowSpec2 manually on Device D to limit the rate of attack traffic with the source port ID of 170.
Establish BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer relationships between Loopback interfaces of Device B and Device C as well as Device B and Device D. In this situation, BGP IPv6 Flow Specification routes can be sent to Device B where a traffic policy is generated.
Data Preparation
Router ID of Device A (1.1.1.1), router ID of Device B (2.2.2.2), router ID of Device C (3.3.3.3), and router ID of Device D (4.4.4.4)
AS number (100) of Device A and AS number (200) of Device B, Device C, and Device D
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface.
For detailed configurations, see the configuration files in this example.
- Configure OSPF.
For detailed configurations, see the configuration files in this example.
- Configure BGP connections.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] bgp 100 [*DeviceA-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 10.10.1.2 as-number 200 [*Device-bgp] commit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.10.1.1 as-number 100 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack1 [*DeviceB-bgp] commit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] bgp 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 [*DeviceC-bgp] commit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] bgp 200 [*DeviceD-bgp] router-id 4.4.4.4 [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceD-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 [*DeviceD-bgp] commit
- Configure BGP IPv6 Flow Specification routes.
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] flow-route FlowSpec1 ipv6 [*DeviceC-flow-route-ipv6] if-match source-port equal 159 [*DeviceC-flow-route-ipv6] apply deny [*DeviceC-flow-route-ipv6] commit [~DeviceC-flow-route-ipv6] quit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] flow-route FlowSpec2 ipv6 [*DeviceD-flow-route-ipv6] if-match source-port equal 170 [*DeviceD-flow-route-ipv6] apply traffic-rate 10000 [*DeviceD-flow-route-ipv6] commit [~DeviceD-flow-route-ipv6] quit
- Establish a BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer relationship.
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB]bgp 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] ipv6-family flow [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] peer 3.3.3.3 enable [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] peer 4.4.4.4 enable [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] commit [~DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] quit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC]bgp 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] ipv6-family flow [*DeviceC-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] peer 2.2.2.2 enable [*DeviceC-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] commit [~DeviceC-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] quit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD]bgp 200 [*DeviceD-bgp] ipv6-family flow [*DeviceD-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] peer 2.2.2.2 enable [*DeviceD-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] commit [~DeviceD-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] quit [~DeviceD-bgp] quit
The BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer connections between Device B and other routers are successfully established.
- Verify the configuration.
# Check BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer connection status on Device B. BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer relationships are successfully established.
<DeviceB> display bgp flow ipv6 peer BGP local router ID : 2.2.2.2 Local AS number : 200 Total number of peers : 2 Peers in established state : 2 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 3.3.3.3 4 200 6 5 0 01:38:07 Established 1 4.4.4.4 4 200 5 4 0 01:38:07 Established 1# Check BGP IPv6 Flow Specification routes received by Device B.
<DeviceB> display bgp flow ipv6 routing-table BGP Local router ID is 2.2.2.2 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 2 * > ReIndex : 1 Dissemination Rules: Src. Port : eq 170 MED : 0 PrefVal : 0 LocalPref: 100 Path/Ogn : i * > ReIndex : 2 Dissemination Rules: Src. Port : eq 159 MED : 0 PrefVal : 0 LocalPref: 100 Path/Ogn : i# Check the traffic policy in each BGP IPv6 Flow Specification route based on the ReIndex shown in the preceding output.
<DeviceB> display bgp flow ipv6 routing-table 2 BGP local router ID : 2.2.2.2 Local AS number : 200 ReIndex : 2 Order : 0 Dissemination Rules : Src. Port : eq 159 BGP flow-ipv6 routing table entry information of 2: Match action : apply deny From: 3.3.3.3 (3.3.3.3) Route Duration: 0d00h22m05s AS-path Nil, origin igp, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, valid, internal, best, pre 255 Not advertised to any peer yet
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 10.10.1.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 10.10.1.2 enable # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 200 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 4.4.4.4 as-number 200 peer 4.4.4.4 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 10.10.1.1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 4.4.4.4 enable peer 10.10.1.1 enable # ipv6-family flow peer 3.3.3.3 enable peer 4.4.4.4 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 200 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv6-family flow peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.255 # flow-route FlowSpec1 ipv6 if-match source-port equal 159 apply deny # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.4 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 router-id 4.4.4.4 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 200 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ipv6-family flow peer 2.2.2.2 enable # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 4.4.4.4 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # flow-route FlowSpec2 ipv6 if-match source-port equal 170 apply traffic-rate 10000 # return