Example for Configuring Dynamic BGP IPv6 Flow Specification
If the characteristics of DoS or DDoS attack traffic is unknown, a traffic analysis server can help implement BGP IPv6 Flow Specification to ensure network security.
Networking Requirements
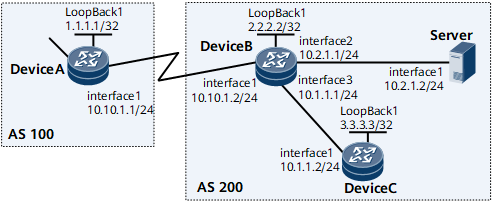
As shown in Figure 1, Device A belongs to AS 100, while Device B, Device C, and Server belong to AS 200. Device B is an ingress of AS 200. AS 200 communicates with AS 100 through Device B.
The attack source in AS 100 may flow into AS 200 through Device B, posing a threat to AS 200. In this situation, configure dynamic BGP IPv6 Flow Specification to ensure network security. The operation process is as follows: Deploy a traffic analysis server and establish a BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer relationship between the traffic analysis server and Device B. Device B samples traffic periodically and sends the sampled traffic to the traffic analysis server. The traffic analysis server generates a BGP IPv6 Flow Specification route based on the characteristics of sampled attack traffic and sends the route to Device B. Device B converts the route into a traffic policy to filter and control attack traffic, ensuring proper service running in AS 200.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Assign an IP address to each interface.
Establish a BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer relationship between Device B and Server to enable the generated BGP IPv6 Flow Specification routes to be sent to Device B. Then a traffic policy is generated.

The traffic analysis server is a non-Huawei device, and it must be a BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer of another device.
Data Preparation
Router ID of Device A (1.1.1.1) and router ID of Device B (2.2.2.2)
AS number (100) of Device A and AS number (200) of Device B, Device C, and Server
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface.
For detailed configurations, see the configuration files in this example.
- Configure an IPv4 peer.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] bgp 100 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 10.10.1.2 as-number 200 [*Device-bgp] commit
- Configure a BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer and disable route authentication.
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] bgp 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 10.10.1.1 as-number 100 [*DeviceB-bgp] ipv6-family flow [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] peer 10.2.1.2 enable [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] peer 10.2.1.2 validation-disable [*DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] commit [~DeviceB-bgp-af-ipv6-flow] quit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Check BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer connection status on Device B. BGP IPv6 Flow Specification peer relationships are successfully established.
<DeviceB> display bgp flow ipv6 peer BGP local router ID : 2.2.2.2 Local AS number : 200 Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 10.2.1.2 4 200 9 10 0 00:00:35 Established 1# Check BGP IPv6 Flow Specification routes received by Device B.
<DeviceB> display bgp flow ipv6 routing-table BGP Local router ID is 2.2.2.2 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 1 * > ReIndex : 2 Dissemination Rules: FragmentType : match (Don't fragment) MED : 0 PrefVal : 0 LocalPref: 100 Path/Ogn : i# Check the traffic policy in each BGP IPv6 Flow Specification route based on the ReIndex shown in the preceding output.
<DeviceB> display bgp flow ipv6 routing-table 2 BGP local router ID : 2.2.2.2 Local AS number : 200 Paths: 1 available, 1 best ReIndex : 2 Order : 2147483647 Dissemination Rules : FragmentType : match (Don't fragment) BGP flow-ipv6 routing table entry information of 2: Match action : apply deny From: 10.2.1.2 (10.2.1.2) Route Duration: 0d00h02m26s AS-path Nil, origin igp, MED 0, localpref 100, pref-val 0, internal, pre 255 Not advertised to any peers yet
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
sysname DeviceA # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 100 peer 10.10.1.2 as-number 200 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 10.10.1.2 enable # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 200 peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 200 peer 10.10.1.1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 10.2.1.2 enable peer 10.10.1.1 enable # ipv6-family flow peer 10.2.1.2 enable peer 10.2.1.2 validation-disable # return