Configuring an MCP
A Measurement Control Point (MCP) collects statistics reported by Data Collecting Points (DCPs), summarizes and calculates the statistics, and reports measurement results to user terminals or the network management system (NMS).
Context
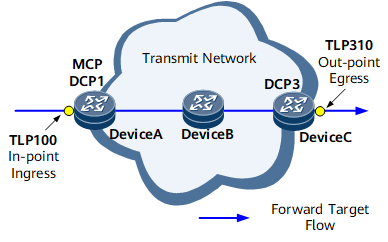
As shown in Figure 1, Device A functions as an MCP to collect statistics reported by DCP1 and DCP3, summarize and calculate the statistics, and report measurement results to user terminals or the NMS.
Perform the following steps on Device A:
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run nqa ipfpm mcp
MCP is enabled globally, and the IPFPM-MCP view is displayed.
- Run mcp id mcp-id
An MCP ID is configured.
Using the Router ID of a device that is configured as an MCP as its MCP ID is recommended.
The MCP ID must be an IP address reachable to DCPs. The MCP ID configured on an MCP must be the same as that specified in the mcp mcp-id [ port port-number ] command run in the IP FPM instance view of all DCPs associated with this MCP. If an MCP ID is changed on an MCP, it must be changed for all DCPs associated with this MCP in an IP FPM instance. Otherwise, the MCP cannot process the statistics reported by the DCPs.
- (Optional) Run protocol udp port port-number
A UDP port number is specified for the MCP to communicate with DCPs.
The UDP port number configured on an MCP must be the same as that specified in the mcp mcp-id [ port port-number ] command run in the IP FPM instance view of all DCPs associated with this MCP. If a UDP port number is changed on an MCP, it must be changed for all DCPs associated with this MCP in an IP FPM instance. Otherwise, the MCP cannot process the statistics reported by the DCPs.
- (Optional) Run authentication-mode hmac-sha256 key-id key-id [ cipher ] [ password | password ]
The authentication mode and password are configured on the MCP.
The authentication mode and password configured on an MCP must be the same as those configured in the authentication-mode hmac-sha256 key-id key-id [ cipher ] [ password | password ] command run on all DCPs associated with this MCP. Otherwise, the MCP cannot process the statistics reported by the DCPs.
- Run instance instance-id
An IP FPM instance is created, and the instance view is displayed.
instance-id must be unique on an MCP and all its associated DCPs. The MCP and all its associated DCPs must have the same IP FPM instance configured. Otherwise, statistics collection does not take effect.
- (Optional) Run description text
The description is configured for the IP FPM instance.
The description of an IP FPM instance can contain the functions of the instance, facilitating applications.
- Run dcp dcp-id
A DCP ID is specified in the IP FPM instance.
The DCP ID configured in an IP FPM instance must be the same as that specified in the dcp id dcp-id command run on a DCP. Otherwise, the MCP associated with this DCP cannot process the statistics reported by the DCP.
- Run commit
The configuration is committed.
Follow-up Procedure
When DCP configurations are being changed, the MCP may receive incorrect statistics from the DCP. To prevent this, run the measure disable command to disable IP FPM performance statistics collection of a specified instance on the MCP. After the DCP configuration change is complete, run the undo measure disable or measure enable command to enable IP FPM performance statistics collection for the specified instance on the MCP. This ensures accurate measurement.