Configuring Static Layer 2 Multicast
If a user host needs to receive multicast data for a specific multicast group from a router port over a long period of time, static Layer 2 multicast can be used to ensure a stable multicast data transmission. Before configuring static Layer 2 multicast, familiarize yourself with the usage scenario and complete the pre-configuration tasks.
Usage Scenario
Layer 2 multicast can be implemented in either dynamic or static mode. In dynamic mode, multicast forwarding tables are dynamically generated based on multicast protocols, whereas in static mode, multicast forwarding tables are manually configured and multicast entries are statically bound to interfaces. After static Layer 2 multicast is deployed on a device, multicast entries on the device do not age and users attached to the device can regularly receive multicast data for specific multicast groups, while avoiding network attacks.
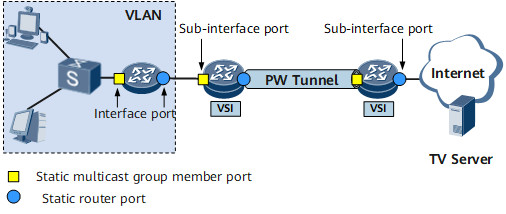
- Static router ports (blue circles) receive multicast traffic.
- Static member ports (yellow squares) send data for specific multicast groups.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring static Layer 2 multicast, complete the following tasks:
Configure a link layer protocol to ensure link connectivity between devices.
Enable global IGMP snooping.
- Configuring Static Router Ports
- Static router ports can be configured to enable users to regularly receive multicast data packets because static router ports do not age.
- Configuring Static Member Ports
- Static member ports send data for specific multicast groups.
- Verifying the Static Layer 2 Multicast Configuration
- After configuring static Layer 2 multicast, verify the port information table and Layer 2 multicast forwarding table to verify that the static Layer 2 multicast configurations are complete.