Configuring IGMP Snooping
IGMP snooping enables a Layer 2 device to analyze IGMP messages exchanged between a connected Layer 3 device and downstream user hosts and use these IGMP messages to set up mappings between interfaces and multicast MAC addresses. Based on the mappings, the Layer 2 device can then implement on-demand multicast data forwarding at the data link layer.
Usage Scenario
If IGMP snooping is not configured on any Layer 2 device, multicast data will be broadcast, wasting bandwidth resources. After IGMP snooping is configured on relevant Layer 2 devices, multicast data will be forwarded only to these Layer 2 devices.
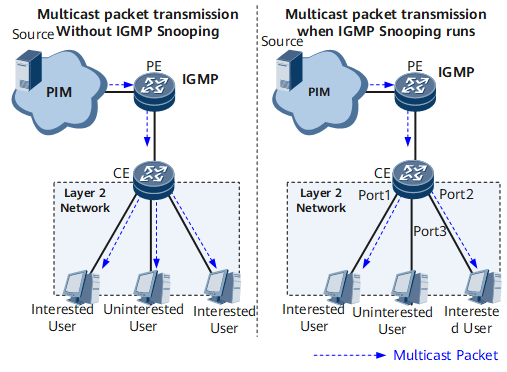

The CEs in this figure need to be deployed with IGMP Snooping.
On the network shown in Figure 1, after IGMP snooping is configured on the CE, multicast data will be sent only to user hosts that request it, instead of being broadcast.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Configure basic VPLS or VLAN functions.
Data Preparation
To configure IGMP snooping, you need the following data.
No. |
Data |
|---|---|
1 |
VLAN ID or VSI name (used for configuring IGMP snooping) |
2 |
(Optional) Aging time of a router port |
3 |
(Optional) Dynamic aging time of a group member and range of groups or sources that user hosts can be promptly join or leave |
4 |
(Optional) Aging time of entries triggered by multicast traffic |
5 |
(Optional) Range and number of multicast groups to be limited |
6 |
(Optional) Configuring Rapid Multicast Data Forwarding on a Backup Device |
- Configuring Basic IGMP Snooping Functions
- Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions is the prerequisite for implementing Layer 2 multicast. Configuring basic IGMP snooping functions involves enabling IGMP snooping, setting the version for IGMP messages that can be processed by IGMP snooping, and setting the IGMP snooping forwarding mode.
- (Optional) Setting the Aging Time for Router Ports
- The aging time of router ports can be set based on the network stability condition so that multicast entries are updated upon network changes.
- (Optional) Configuring Rapid Group Member Information Update
- Rapid group member information update can be configured to enable devices to quickly update Layer 2 multicast entries generated based on Report/Leave messages received from group members, improving the multicast data forwarding efficiency.
- (Optional) Configuring Prompt Response to Layer 2 Network Topology Changes
- Prompt response to Layer 2 network topology changes enables a device to correctly forward multicast data based on the current network topology, ensuring uninterrupted service forwarding.
- (Optional) Setting the Aging Time for Entries Triggered by Multicast Traffic
- Setting the aging time for Layer 2 multicast forwarding entries triggered by multicast traffic can balance the forwarding efficiency and system performance.
- (Optional) Configuring a Multicast Group Security Policy
- A multicast group policy can be configured to limit the range and number of multicast groups that some hosts can join or to add security messages to multicast data packets.
- (Optional) Configuring Rapid Multicast Data Forwarding on a Backup Device
- In a VPLS network, you can configure a backup device to quickly switch and forward multicast data traffic in the event of a master link or device failure.
- Verifying the IGMP Snooping Configuration
- After configuring IGMP snooping, verify the router port and member port lists, forwarding table, and querier parameters.