(Optional) Configuring Rapid Multicast Data Forwarding on a Backup Device
In a VPLS network, you can configure a backup device to quickly switch and forward multicast data traffic in the event of a master link or device failure.
Context
As the Internet grows, more and more data, voice, and video information is exchanged across networks. These kinds of information are transmitted in multicast mode. In multicast mode, master and backup links and devices are deployed to ensure uninterrupted service transmission on a network.
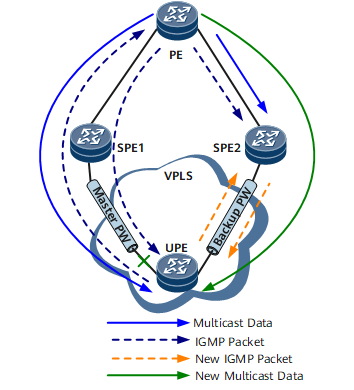
On the network shown in Figure 1, the UPE is dual-homed to SPE1 and SPE2 through a VPLS network. SPE1 functions as the master device, and SPE2 as the backup device. The status of the PWs between the UPE and the SPEs is as follows:
- The PW between SPE1 and the UPE is the master PW, responsible for forwarding multicast protocol and data packets.
- The PW between SPE2 and the UPE is the backup PW, and is blocked from forwarding multicast protocol and data packets since it has not learned any multicast forwarding entries.

The UPE, SPE1 and SPE2 in the figure needs to be deployed with Rapid Multicast Data Forwarding on a Backup Device.
If the master link or device fails, the backup device cannot forward multicast data traffic immediately because it does not have a multicast forwarding table, resulting in a significant service interruption.
To enable the rapid switchover of multicast traffic to a backup link or device, configure the backup device (SPE2) to forward multicast protocol packets so SPE2 can also learn the Layer 2 multicast forwarding entries. If master PW fails and the backup PW becomes the master, it can immediately forward multicast protocol packets to ensure uninterrupted service transmission.
Procedure
- Run system-view
The system view is displayed.
- Run vsi vsi-name
The VSI view is displayed.
- Run igmp-snooping enable
The IGMP snooping function is enabled in the VSI view.
- Run l2-multicast backup-query forward [ source-mac-replace ]
The backup device is configured to forward IGMP Query messages along the backup link.
If source-mac-replace is set, the backup device replaces the source MAC addresses of IGMP Query messages with its own MAC address.
- Run l2-multicast backup-report forward [ source-mac-replace ]
The backup device is configured to receive IGMP Report/Leave messages along the backup link.
If source-mac-replace is specified, the backup device replaces the source MAC addresses of IGMP Report/Leave messages with its own MAC address.