Application of Route Import Between VPN and Public Network in the Traffic Cleaning Networking
This section describes how to apply the function of route import between VPN and public network to the traffic cleaning networking.
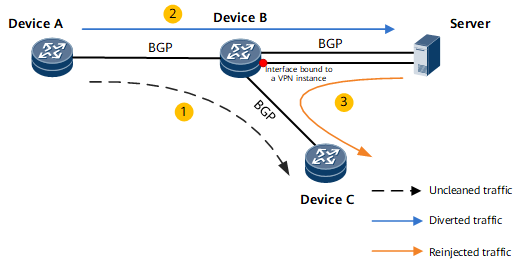
In BGP/MPLS IP VPN networking, the users of a VPN can communicate with the users of another VPN if the two VPNs have matching VPN targets, but cannot communicate with public network users. Figure 1 shows a traffic cleaning scenario. If attack traffic is detected, it is imported to the traffic cleaning server for cleaning. The cleaned traffic is injected back to the network through Device B. In this case, the public network routes destined for Device C need to be imported to the VPN routing table of Device B to forward the cleaned traffic to Device C. In addition, the public network routes sent by the cleaning server should not be imported to the VPN routing table. This prevents the reinjected traffic from being sent back to the cleaning server after reaching Device B, thereby preventing loops. To implement the preceding process, configure route import between VPN and public network on Device B, and configure a route-policy on the Device B sub-interface bound to a VPN instance.
If no attack traffic is detected, Device A learns public network routes from Device C, and traffic is forwarded along the expected path Device A -> Device B -> Device C.
If attack traffic is detected, the server advertises a public network route with a 32-bit mask as a traffic diversion route to Device B, which then diverts the Device A -> Device C traffic to the server for cleaning.
The server sends the cleaned traffic to Device B through a sub-interface. A VPN instance is bound to a sub-interface of Device B and is used to establish a VPN BGP peer relationship with the server. This allows Device B to import the public network service routes sent from Device C into its VPN routing table. After receiving the reinjected traffic through the VPN sub-interface, Device B searches its VPN routing table and forwards the traffic to Device C.