Application of HVPN on an IP RAN
Service Overview
As 3G and Long Term Evolution (LTE) services develop, mobile operators keep building and expanding RANs. This situation imposes high requirements on the bandwidth, scalability, and configuration flexibility of the IP RAN between base transceiver stations (BTSs)/NodeBs/eNodeBs and base station controllers (BSCs)/radio network controllers (RNCs)/mobility management entities (MMEs). IP datacom networks, as the mainstream of datacom networks, are large in scale and provide a variety of access modes. To maximize carriers' return on investment, reduce network construction costs, and evolve the existing network smoothly to an LTE network, an IP RAN solution is introduced.
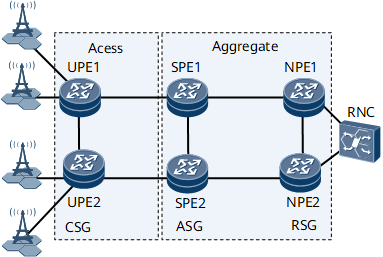
In the HVPN bearer solution, the RAN provides excellent fixed-mobile convergence (FMC) capabilities and has simple and flexible networking. The hierarchical network between CSGs and radio service gateways (RSGs) can bear various types of services.
Networking Description
CSG: On an HVPN, CSGs function as UPEs to provide access services for BTSs/NodeBs/eNodeBs.
Access service gateway (ASG): On an HVPN, ASGs function as SPEs to provide access services for UPEs.
RSG: On an HVPN, RSGs function as NPEs to connect to BSCs/RNCs/MMEs.
Feature Deployment
The HVPN bearer solution applies to large-scale networks with dynamic routing capabilities. Table 1 uses an HoVPN bearer solution as an example to describe feature deployment for E2E Ethernet service bearer and protection.
Feature |
Description |
|---|---|
Service |
|
IGP |
IGP multi-processes must be deployed between CSGs and RSGs to ensure proper data forwarding. A routing policy needs to be configured on ASGs to aggregate and filter routes. This configuration reduces bandwidth requirements for updating and maintaining routes. Recommended routing protocol: IS-IS multi-processes |
MPLS tunnel |
MPLS tunnels must be established between CSGs and ASGs, and between ASGs and RSGs. Recommended tunnel protocol: MPLS TE (tunnel selectors must be configured) |
VPN |
Hierarchical L3VPN must be configured between CSGs and ASGs, and between ASGs and RSGs to isolate services. |
Protection switching |
Protection switching must be configured for nodes and links to provide high availability:
|
QoS |
E2E QoS must be configured between CSGs and RSGs to ensure service quality. Recommended QoS solutions: DiffServ |
Clock synchronization |
E2E clock synchronization must be configured between CSGs and RSGs to ensure real-time data transmission. Recommended clock synchronization technologies: synchronous Ethernet and 1588v2 |