Example for Configuring a Remote LDP Session
This section provides an example for configuring a remote LDP session. A remote LDP session is used to transmit VPN services.
Context
Networking Requirements
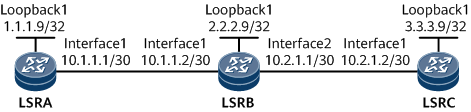
In Figure 1, LSRA and LSRC are on the edge of a backbone network. To deploy VPN services over the backbone network, establish a remote LDP session between LSRA and LSRC to establish an LSP.
Device Name |
Interface Name |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
LSRA |
Loopback1 |
1.1.1.9/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.1.1.1/30 |
|
LSRB |
Loopback1 |
2.2.2.9/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.1.1.2/30 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
10.2.1.1/30 |
|
LSRC |
Loopback1 |
3.3.3.9/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.2.1.2/30 |
Configuration Notes
When configuring a remote LDP session, note the following:
An LSR ID must be configured before you run other MPLS commands.
An LSR ID of an LSR must be manually configured because no default LSR ID is available.
It is recommended that the IP address of a reachable loopback interface on an LSR be configured as the LSR ID.
The IP address of a remote LDP peer must be the LSR ID of the remote LDP peer. When an LDP LSR ID is different from an MPLS LSR ID, the LDP LSR ID must be used.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Assign an IP address to each interface and configure OSPF to advertise the route to the network segment to which each interface is connected and the host route to each LSR ID.
Enable MPLS and MPLS LDP globally on each LSR.
Specify the name and IP address of the remote peer on LSRs of both ends of a remote LDP session.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
IP address of each interface as shown in Figure 1, OSPF process ID, and OSPF area ID
LSR ID of each LSR
Name and IP address of each remote peer of a remote LDP session
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface.
According to Figure 1, assign an IP address to each interface, configure the loopback interface addresses as LSR IDs, and configure OSPF to advertise the route to the network segment to which each interface is connected and the host route to each LSR ID. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable MPLS and MPLS LDP globally on each LSR.
# Configure LSRA.
<LSRA> system-view [~LSRA] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [*LSRA] mpls [*LSRA-mpls] quit [*LSRA] mpls ldp [*LSRA-mpls-ldp] commit [~LSRA-mpls-ldp] quit
# Configure LSRC.
<LSRC> system-view [~LSRC] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 [*LSRC] mpls [*LSRC-mpls] quit [*LSRC] mpls ldp [*LSRC-mpls-ldp] commit [~LSRC-mpls-ldp] quit
- Specify the name and IP address of the remote peer on LSRs of both ends of a remote LDP session.
# Configure LSRA.
[~LSRA] mpls ldp remote-peer LSRC [*LSRA-mpls-ldp-remote-LSRC] remote-ip 3.3.3.9 [*LSRA-mpls-ldp-remote-LSRC] commit [~LSRA-mpls-ldp-remote-LSRC] quit
# Configure LSRC.
[~LSRC] mpls ldp remote-peer LSRA [*LSRC-mpls-ldp-remote-LSRA] remote-ip 1.1.1.9 [*LSRC-mpls-ldp-remote-LSRA] commit [~LSRC-mpls-ldp-remote-LSRA] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# After completing the configuration, run the display mpls ldp session command on an LSR. You can view that the status of the remote LDP session between LSRA and LSRC is Operational.
The following example uses the command output on LSRA.
<LSRA> display mpls ldp session LDP Session(s) in Public Network Codes: LAM(Label Advertisement Mode), SsnAge Unit(DDDD:HH:MM) An asterisk (*) before a session means the session is being deleted. -------------------------------------------------------------------------- PeerID Status LAM SsnRole SsnAge KASent/Rcv -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 3.3.3.9:0 Operational DU Passive 0000:00:01 6/6 -------------------------------------------------------------------------- TOTAL: 1 Session(s) Found.# Run the display mpls ldp remote-peer command on either of the LSRs on both ends of the remote LDP session. You can view information about the remote peer of the LSR.
The following example uses the command output on LSRA.
<LSRA> display mpls ldp remote-peer LDP Remote Entity Information ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Remote Peer Name : LSRC Description : ---- Remote Peer IP : 3.3.3.9 LDP ID : 1.1.1.9:0 Transport Address : 1.1.1.9 Entity Status : Active Configured Keepalive Hold Timer : 45 Sec Configured Keepalive Send Timer : ---- Configured Hello Hold Timer : 45 Sec Negotiated Hello Hold Timer : 45 Sec Configured Hello Send Timer : ---- Configured Delay Timer : 10 Sec Hello Packet sent/received : 6347/6307 Label Advertisement Mode : Downstream Unsolicited Auto-config : ---- Session-Protect effect : NO Session-Protect Duration : ---- Session-Protect Remain : ---- ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ TOTAL: 1 Remote-Peer(s) Found.
Configuration Files
LSRA configuration file
# sysname LSRA # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # mpls ldp remote-peer LSRC remote-ip 3.3.3.9 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 # returnLSRB configuration file
# sysname LSRB # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.252 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.3 # return
LSRC configuration file
# sysname LSRC # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # ipv4-family # mpls ldp remote-peer LSRA remote-ip 1.1.1.9 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.252 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 10.2.1.0 0.0.0.3 # return