Example for Configuring a MAC Address Table
This section describes an example for configuring static MAC address entries and configuring an aging time for dynamic MAC address entries.
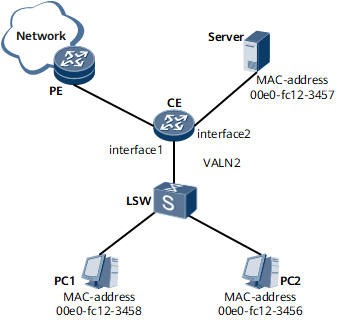
Networking Requirements
If the internal network of an enterprise has fixed users and the internal network connects to an important server, to prevent hackers from attacking the device or the server, static MAC address entries need to be configured on the device. A device automatically generates dynamic MAC address entries by learning source MAC addresses. As the network topology constantly changes, the device will learn more and more MAC addresses. To avoid the explosive growth of MAC address entries, set a proper aging time for dynamic MAC address entries to have the invalid MAC addresses deleted in time.
To prevent MAC address attacks, add a static entry to the MAC address table on the CE for each of PC1 and PC2 and configure the aging time of dynamic MAC entries as 500 seconds.
To prevent hackers from using the MAC address of the server to obtain important information, configure the MAC address of the server as a static MAC address on the CE.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Create a VLAN and add the interfaces to the VLAN.
Add the static MAC address entries to enable the packet with the specified destination MAC address to be forwarded from the specified interface. This can protect the CE from the attack of the forged MAC address.
Configure an aging time for the dynamic MAC entries to prevent the explosive growth of MAC entries.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
MAC address of PC1
MAC address of PC2
MAC address of the server
ID of VLAN to which the CE belongs
Number of the interface connecting the LSW to the CE
Number of the interface connecting the server to the CE
Aging time of dynamic MAC entries
Procedure
- Add static MAC entries.
# Create VLAN 2 and add GE 0/1/1 and GE 0/1/9 to VLAN 2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE] vlan 2 [*CE-vlan2] quit [*CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port default vlan 2 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/9 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] undo shutdown [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] portswitch [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] port default vlan 2 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] quit
# Add the static MAC address entries.
[*CE] mac-address static 00e0-fc12-3458 gigabitethernet 0/1/1 vlan 2 [*CE] mac-address static 00e0-fc12-3456 gigabitethernet 0/1/1 vlan 2 [*CE] mac-address static 00e0-fc12-3457 gigabitethernet 0/1/9 vlan 2
- Set the aging time of the dynamic MAC address entries.
[*CE] mac-address aging-time 500 [*CE] commit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display mac-address command to check whether the static address entries are added successfully.
[~CE] display mac-address static vlan 2 MAC address table of slot 0: ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- MAC Address VLAN/BD/ PEVLAN CEVLAN Port Type LSP/LSR-ID VSI/SI/EVPN MAC-Tunnel ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 00e0-fc12-3458 2 - - GE0/1/1 static - 00e0-fc12-3456 2 - - GE0/1/1 static - 00e0-fc12-3457 2 - - GE0/1/9 static - ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Total matching items on slot 0 displayed = 3
# Run the display mac-address aging-time command to check whether the aging time is set for the dynamic entries successfully.
[*CE] display mac-address aging-time Aging time: 500 second(s)
Configuration Files
# sysname CE # vlan batch 2 # mac-address aging-time 500 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port default vlan 2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/9 portswitch undo shutdown port default vlan 2 # mac-address static 00e0-fc12-3458 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 vlan 2 mac-address static 00e0-fc12-3456 GigabitEthernet0/1/1 vlan 2 mac-address static 00e0-fc12-3457 GigabitEthernet0/1/9 vlan 2 # return