Example for Configuring a VLAN-based MAC Address Learning Limit Rule
Configuring a VLAN-based MAC address learning limit rule can control the number of users in a VLAN. If the number of learned MAC addresses reaches the maximum, no additional MAC addresses will be learned. In addition, the packet discarding and alarm functions can be configured to prevent MAC address attacks and improve network security.
Networking Requirements
Networks with poor security management such as community networks are vulnerable to hackers' MAC address attacks. The capacity of a MAC address table is limited. When hackers forge a large number of packets with different source MAC addresses and send the packets to a device, the MAC address table of the device will be filled up. Even if the device can receive valid packets, it cannot learn the source MAC addresses of the packets.
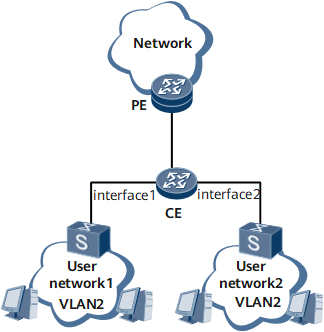
As shown in Figure 1, user network 1 connects to the CE through S1. S1 connects to interface1 on the CE. User network 2 connects to the CE through S2. S2 connects to interface2 on the CE. Interface1 and interface2 belong to VLAN 2. To prevent MAC address attacks and control the number of users in VLAN 2, configure a MAC address learning limit for VLAN 2.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Create a VLAN and add the interfaces to the VLAN.
Configure a VLAN-based MAC address learning limit rule to control the number of users in the VLAN, preventing MAC address attacks and improving network safety.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
ID of the VLAN to which the interfaces belong
Number of each user interface
Maximum number of MAC addresses that can be learned
Procedure
- Configure a MAC address learning limit rule.
# Add GE 0/1/1 and GE 0/1/9 to VLAN 2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE] vlan 2 [*CE-vlan2] quit [*CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port link-type trunk [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/9 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] undo shutdown [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] portswitch [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] port link-type trunk [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] quit
# Configure the MAC address learning limit rule for VLAN 2: a maximum of 100 MAC addresses can be learned; additional packets are forwarded but their MAC addresses cannot be added to the MAC address table.
[*CE] vlan 2 [*CE-vlan2] mac-limit maximum 100 rate 50 action forward [*CE-vlan2] commit [~CE-vlan2] quit
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display mac-limit command to check whether the MAC address learning limit rule is configured successfully.
[*CE] display mac-limit MAC limit is enabled Total MAC limit rule count : 1 PORT VLAN/BD/VSI SLOT Maximum Rate(ms) Action Alarm ---------------------------------------------------------------------------- - 2 - 100 50 forward disable
Configuration Files
# sysname CE # vlan batch 2 # vlan 2 mac-limit maximum 100 rate 50 action forward # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/9 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 2 # return