Configuring an MCE
Multi-VPN-instance can be configured for routing protocols on a CE to isolate different types of services on a LAN.
Usage Scenario
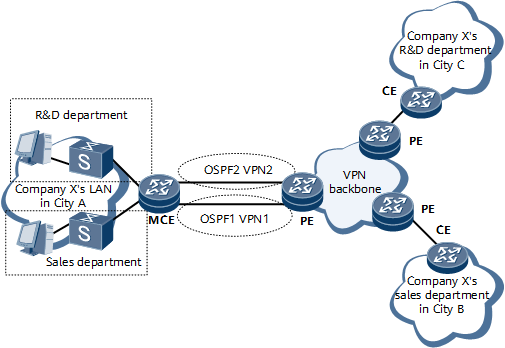
VPN services are becoming increasingly refined and the demand for VPN service security is growing. Carriers must isolate different types of VPN services on networks to meet this demand. The traditional BGP/MPLS VPN technology isolates VPN services by deploying one CE for each VPN, which is expensive and complicates network deployment. If multiple VPNs use the same CE to access upper-layer devices, these VPNs share the same routing and forwarding table, and data security for these VPNs cannot be ensured. The MCE technology addresses the conflict between network costs and data security problems caused by multiple VPNs sharing the same CE.
- The sales departments in cities A and B can communicate with each other.
- The R&D departments in cities A and C can communicate with each other.
- The R&D departments are isolated from the sales departments.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring an MCE, complete the following tasks:
Configure a VPN instance for each service on the MCE and the PE to which the MCE is connected (for details, see Configuring a VPN Instance)
Configure link and network layer protocols for LAN interfaces, and connect the LAN interface for each type of service to the MCE.
Bind the MCE's interfaces and the PE's interfaces connecting to the MCE to VPN instances (for details, see Binding Interfaces to a VPN Instance), and configure IP addresses for these interfaces.
- Configuring a Routing Protocol on an MCE
- To enable an MCE to communicate with provider edge PEs and VPN devices, configure a routing protocol for each type of service on the MCE.
- Configuring a Routing Protocol on the PE Connected to an MCE
- To enable a PE to communicate with an MCE, configure routing protocol multi-VPN-instance on the MCE.
- Verifying the MCE Configuration
- After configuring the MCE, check the routes to the LAN and remote sites for each type of service in the VRF table of the MCE.