Example for Configuring VPN FRR
In CE dual-homing networking, you can configure VPN FRR to quickly switch VPN services to another link if a PE fails.
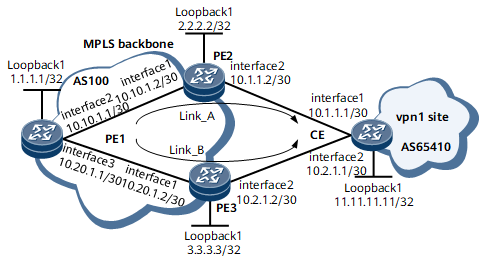
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, it is required that a backup next hop be configured on PE1 with PE3 serving as a backup to PE2, so that when PE2 fails, the traffic can be quickly switched to PE3.
Configuration Notes
- When configuring VPN FRR, ensure that the CE is dual-homed to two PEs configured with VPN instances of different RDs.
- In a VPN FRR scenario, after the primary path recovers, traffic switches back to this path. Because the order in which nodes undergo IGP convergence differs, packet loss may occur during the switchback. To resolve this problem, run the route-select delay delay-value command to configure a route selection delay so that traffic is switched back only after forwarding entries on the devices along the primary path are updated. The delay specified using delay-value depends on various factors, such as the number of routes on the devices. Set a proper delay as needed.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure OSPF for PEs on the MPLS backbone network to communicate.
Configure MPLS and MPLS LDP both globally and per interface on each node and establish LDP LSPs on the MPLS backbone network.
Configure a VPN instance on each PE and bind the interfaces that connect PE2 and PE3 to CE1 to the VPN instances on PE2 and PE3.
Establish MP-EBGP peer relationships between each PE and the CE to import VPN routes. Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PE1 and PE2 and between PE1 and PE3.
Configure dynamic BFD for LDP LSP on PE1, PE2, and PE3.
Configure BGP auto FRR on PE1.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Number of the AS where the PEs reside (100) and number of the AS where the CE resides (65410)
Names of the VPN instances configured on PEs
The BFD configuration name, local discriminator, and remote discriminator.
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each interface of devices on the MPLS backbone network and VPN sites. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure OSPF for PEs on the MPLS backbone network to communicate. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure MPLS and MPLS LDP both globally and per interface on each node and establish LDP LSPs on the MPLS backbone network.
# Configure PE1.
<PE1> system-view [~PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*PE1] mpls [*PE1-mpls] quit [*PE1] mpls ldp [*PE1-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls ldp [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/16 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] mpls [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] mpls ldp [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] commit [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit
# Configure PE2.
<PE2> system-view [~PE2] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 [*PE2] mpls [*PE2-mpls] quit [*PE2] mpls ldp [*PE2-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure PE3.
<PE3> system-view [~PE3] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 [*PE3] mpls [*PE3-mpls] quit [*PE3] mpls ldp [*PE3-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE3] interface gigabitethernet0/1/0 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
Run the display mpls lsp command on PEs. The command output shows that an LSP is established between PE1 and PE2 and between PE1 and PE3. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
<PE1> display mpls lsp Flag after Out IF: (I) - RLFA Iterated LSP, (I*) - Normal and RLFA Iterated LSP Flag after LDP FRR: (L) - Logic FRR LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- LSP Information: LDP LSP ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- FEC In/Out Label In/Out IF Vrf Name 1.1.1.1/32 3/NULL -/- 2.2.2.2/32 NULL/3 -/GE0/1/8 2.2.2.2/32 4096/3 -/GE0/1/8 3.3.3.3/32 NULL/3 -/GE0/1/16 3.3.3.3/32 4097/3 -/GE0/1/16 - Configure a VPN instance on each PE and bind the interfaces that connect PE2 and PE3 to CE1 to the VPN instances on PE2 and PE3.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure PE2.
[*PE2] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:2 [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE2-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.1.1.2 30 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:3 [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] vpn-target 111:1 [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE3] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 10.2.1.2 30 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
- Establish an MP-EBGP peer relationship between PE2 and the CE and between PE3 and the CE to import VPN routes destined for the CE's loopback interface.
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE2-bgp-vpn1] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410 [*PE2-bgp-vpn1] commit [~PE2-bgp-vpn1] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] bgp 100 [*PE3-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE3-bgp-vpn1] peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65410 [*PE3-bgp-vpn1] commit [~PE3-bgp-vpn1] quit
# Configure the CE.
[~CE] interface loopback 1 [*CE-Loopback1] ip address 11.11.11.11 32 [*CE-Loopback1] quit [*CE] bgp 65410 [*CE-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 [*CE-bgp] peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 100 [*CE-bgp] network 11.11.11.11 32 [*CE-bgp] quit [*CE] commit
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] commit [~PE1-bgp-vpn1] quit
After completing the configurations, run the display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance peer command on PE2 and PE3. The command output shows that an EBGP peer relationship has been established between PE2 and the CE and between PE3 and the CE.
The following example uses the command output on PE2.
<PE2> display bgp vpnv4 vpn-instance vpn1 peer BGP local router ID : 10.10.1.2 Local AS number : 100 VPN-Instance vpn1, Router ID 10.10.1.2: Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 10.1.1.1 4 65410 29 28 0 00:22:20 Established 1
- Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PEs.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [~PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 2.2.2.2 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 3.3.3.3 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] commit [~PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] bgp 100 [~PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 [*PE2-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable [*PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] commit [~PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] bgp 100 [~PE3-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 [*PE3-bgp] peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE3-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*PE3-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.1 enable [*PE3-bgp-af-vpnv4] commit [~PE3-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit
After completing the configurations, run the display bgp vpnv4 all peer command on PEs. The command output shows that the MP-IBGP peer relationships have been established.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
<PE1> display bgp vpnv4 all peer BGP local router ID : 10.10.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 2 Peers in established state : 2 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 2.2.2.2 4 100 43 30 0 00:21:55 Established 1 3.3.3.3 4 100 36 25 0 00:18:12 Established 1
- Configure dynamic BFD for LDP LSP.
# Configure dynamic BFD for LDP LSP on PE1.
[~PE1] bfd [*PE1-bfd] quit [*PE1] mpls [*PE1-mpls] mpls bfd enable [*PE1-mpls] mpls bfd-trigger-tunnel host [*PE1-mpls] quit [*PE1] commit
# Configure dynamic BFD for LDP LSP on PE2.
[~PE2] bfd [*PE2-bfd] mpls-passive [*PE2-bfd] quit [*PE2] commit
# Configure dynamic BFD for LDP LSP on PE3.
[~PE3] bfd [*PE3-bfd] mpls-passive [*PE3-bfd] quit [*PE3] commit
# Run the display bfd session all verbose command on PE1 and PE2. The command output shows that the State field is displayed as Up and the BFD Bind Type field is displayed as LDP_TUNNEL.
- Enable BGP auto FRR.
[~PE1] bgp 100 [~PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] auto-frr [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] route-select delay 300 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] commit
# View the backup next hop, backup label, and backup tunnel ID.
<PE1> display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 11.11.11.11 verbose Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table : vpn1 Summary Count : 1 Destination: 11.11.11.11/32 Protocol: IBGP Process ID: 0 Preference: 255 Cost: 0 NextHop: 2.2.2.2 Neighbour: 0.0.0.0 State: Active Adv Relied Age: 00h08m28s Tag: 0 Priority: low Label: 4098 QoSInfo: 0x0 IndirectID: 0x6400006D RelayNextHop: 10.10.1.2 Interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 TunnelID: 0x0000000001004c4b42 Flags: RD BkNextHop: 3.3.3.3 BkInterface: GigabitEthernet0/1/16 BkLabel: 4098 SecTunnelID: 0x0 BkPETunnelID: 0x0000000001004c4b43 BkPESecTunnelID: 0x0 BkIndirectID: 0x6400006F
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity # bfd # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls mpls bfd enable mpls bfd-trigger-tunnel host # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.1.1 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.20.1.1 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.2 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.2 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 3.3.3.3 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.3 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.2 enable peer 3.3.3.3 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 auto-frr route-select delay 300 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 10.10.1.0 0.0.0.3 network 10.20.1.0 0.0.0.3 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:2 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity # bfd mpls-passive # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.252 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.10.1.2 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 10.10.1.0 0.0.0.3 # return
PE3 configuration file
# sysname PE3 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:3 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 111:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 111:1 import-extcommunity # bfd mpls-passive # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.20.1.2 255.255.255.252 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.252 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.1 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.1 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.1 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65410 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 10.20.1.0 0.0.0.3 # return
CE configuration file
# sysname CE # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.252 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.252 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65410 peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255 peer 10.1.1.2 enable peer 10.2.1.2 enable # return