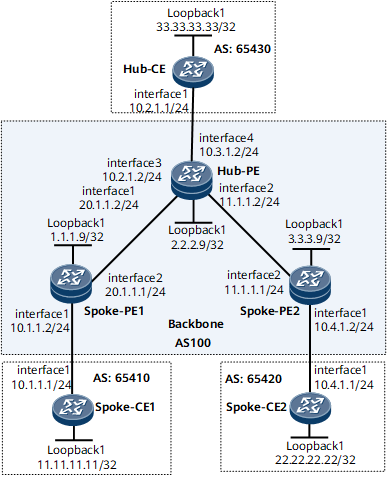
Example 1 for Configuring Hub and Spoke (Single Link Between a Hub-PE and a Hub-CE)
In hub and spoke networking, an access control device is specified in the VPN, and users communicate with each other through the access control device.
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, the communication between Spoke-CEs is controlled by the Hub-CE at a central site. In other words, the traffic between Spoke-CEs is forwarded through the Hub-CE, not only through the Hub-PE. The Hub-PE connects to the Hub-CE over a link.
Precautions
When configuring hub and spoke, note the following:
The import and export VPN targets configured on a Spoke-PE are different.
A VPN instance (vpnhub) is created on the Hub-PE. The VPN targets received by vpnhub are the VPN targets advertised by the two Spoke-PEs; the VPN targets advertised by vpnhub are the VPN targets received by the two Spoke-PEs and are different from the VPN targets received by vpnhub.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Establish MP-IBGP peer relationships between the Hub-PE and Spoke-PEs. There is no need to establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship or exchange VPN route information between the two Spoke-PEs.
Create a VPN instance on each PE and enable the pop-go function on the Hub-PE.
Configure EBGP connections between CEs and PEs. Configure a default route destined for the Hub-PE on the Hub-CE.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
MPLS LSR IDs of PEs
Names, RDs, and VPN targets of VPN instances on Hub-PEs and Spoke-PEs
Procedure
- Configure an IGP on the MPLS backbone network for the Hub-PE and Spoke-PEs to communicate at Layer 3.
This example uses OSPF as the IGP. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
After the configurations are complete, OSPF neighbor relationships are set up between the Hub-PE and Spoke-PEs. Run the display ospf peer command. The command output shows that the neighbor status is Full. Run the display ip routing-table command. The command output shows that the Hub-PE and Spoke-PEs have learned the routes to each other's loopback interface.
- Configure MPLS and MPLS LDP both globally and per interface on each node of the backbone network and set up LDP LSPs.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
After the configurations are complete, LDP neighbor relationships are set up between the Hub-PE and Spoke-PEs. Run the display mpls ldp session command each router. The command output shows that Session State is Operational.
- Configure an IPv4-address-family-supporting VPN instance on each PE and bind the interface that connects a PE to a CE to the VPN instance on that PE.

The import VPN target list of a VPN instance on the Hub-PE must contain the export VPN targets of all Spoke-PEs.
The export VPN target list of another VPN instance on the Hub-PE must contain the import VPN targets of all Spoke-PEs.
# Configure Spoke-PE1.
<Spoke-PE1> system-view [~Spoke-PE1] ip vpn-instance vpna [*Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv4-family [*Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity [*Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity [*Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [*Spoke-PE1-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*Spoke-PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*Spoke-PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*Spoke-PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.1.1.2 24 [*Spoke-PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~Spoke-PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure Spoke-PE2.
<Spoke-PE2> system-view [~Spoke-PE2] ip vpn-instance vpna [*Spoke-PE2-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv4-family [*Spoke-PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:3 [*Spoke-PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity [*Spoke-PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity [*Spoke-PE2-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv4] quit [*Spoke-PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*Spoke-PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*Spoke-PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 10.4.1.2 24 [*Spoke-PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~Spoke-PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
# Configure the Hub-PE.
<Hub-PE> system-view [~Hub-PE] ip ip-prefix defaultip index 10 permit 0.0.0.0 0 [*Hub-PE] route-policy policy_in permit node 1 [*Hub-PE-route-policy] if-match ip-prefix defaultip [*Hub-PE-route-policy] quit [*Hub-PE] route-policy policy_in deny node 2 [*Hub-PE-route-policy] quit [*Hub-PE] ip vpn-instance vpnhub [*Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpnhub] ipv4-family [*Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpnhub-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:21 [*Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpnhub-af-ipv4] export route-policy policy_in [*Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpnhub-af-ipv4] vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity [*Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpnhub-af-ipv4] vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity [*Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpnhub-af-ipv4] apply-label per-route pop-go [*Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpnhub-af-ipv4] quit [*Hub-PE-vpn-instance-vpnhub] quit [*Hub-PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/16 [*Hub-PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ip binding vpn-instance vpnhub [*Hub-PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] ip address 10.2.1.2 24 [*Hub-PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] commit [~Hub-PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit
# Assign an IP address to each interface on CEs, as shown in Figure 1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
After completing the configurations, run the display ip vpn-instance verbose command on PEs to view the configurations of VPN instances. Each PE can ping its connected CEs using the ping -vpn-instance vpn-name ip-address command.

If a PE has multiple interfaces bound to the same VPN instance, you must specify a source IP address by specifying -a source-ip-address in the ping -vpn-instance vpn-instance-name -a source-ip-address dest-ip-address command to ping the CE connected to the remote PE. Otherwise, the ping operation fails.
- Set up EBGP peer relationships between PEs and CEs to import VPN routes.
# Configure Spoke-CE1.
[~Spoke-CE1] interface loopback 1 [*Spoke-CE1-Loopback1] ip address 11.11.11.11 32 [*Spoke-CE1-Loopback1] quit [*Spoke-CE1] bgp 65410 [*Spoke-CE1-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 [*Spoke-CE1-bgp] network 11.11.11.11 32 [*Spoke-CE1-bgp] quit [*Spoke-CE1] commit
# Configure Spoke-PE1.
[~Spoke-PE1] bgp 100 [*Spoke-PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna [*Spoke-PE1-bgp-vpna] peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410 [*Spoke-PE1-bgp-vpna] commit [~Spoke-PE1-bgp-vpna] quit [~Spoke-PE1-bgp] quit
# Configure Spoke-CE2.
[~Spoke-CE2] interface loopback 1 [*Spoke-CE2-Loopback1] ip address 22.22.22.22 32 [*Spoke-CE2-Loopback1] quit [*Spoke-CE2] bgp 65420 [*Spoke-CE2-bgp] peer 10.4.1.2 as-number 100 [*Spoke-CE2-bgp] network 22.22.22.22 32 [*Spoke-CE2-bgp] commit [~Spoke-CE2-bgp] quit
# Configure Spoke-PE2.
[~Spoke-PE2] bgp 100 [*Spoke-PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna [*Spoke-PE2-bgp-vpna] peer 10.4.1.1 as-number 65420 [*Spoke-PE2-bgp-vpna] commit [~Spoke-PE2-bgp-vpna] quit [~Spoke-PE2-bgp] quit
# Configure the Hub-CE.
[~Hub-CE] interface loopback 1 [*Hub-CE-Loopback1] ip address 33.33.33.33 32 [*Hub-CE-Loopback1] quit [*Hub-CE] bgp 65430 [*Hub-CE-bgp] peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 100 [*Hub-CE-bgp] peer 10.2.1.2 default-route-advertise [*Hub-CE-bgp] network 33.33.33.33 32 [*Hub-CE-bgp] quit [*Hub-CE] commit
# Configure the Hub-PE.
[~Hub-PE] bgp 100 [*Hub-PE-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpnhub [*Hub-PE-bgp-vpnhub] peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65430 [*Hub-PE-bgp-vpnhub] quit [*Hub-PE-bgp] commit [~Hub-PE-bgp] quit
After completing the configurations, run the display bgp vpnv4 all peer command on PEs. The command output shows that BGP peer relationships have been established between PEs and CEs.
- Set up an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PEs.
# Configure Spoke-PE1.
[~Spoke-PE1] bgp 100 [~Spoke-PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 [*Spoke-PE1-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*Spoke-PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*Spoke-PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 2.2.2.9 enable [*Spoke-PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] commit [~Spoke-PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit
# Configure Spoke-PE2.
[~Spoke-PE2] bgp 100 [~Spoke-PE2-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 [*Spoke-PE2-bgp] peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*Spoke-PE2-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*Spoke-PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 2.2.2.9 enable [*Spoke-PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] commit [~Spoke-PE2-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit
# Configure the Hub-PE.
[~Hub-PE] bgp 100 [~Hub-PE-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 [*Hub-PE-bgp] peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*Hub-PE-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 [*Hub-PE-bgp] peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*Hub-PE-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*Hub-PE-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 1.1.1.9 enable [*Hub-PE-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 3.3.3.9 enable [*Hub-PE-bgp-af-vpnv4] commit [~Hub-PE-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit
After completing the configurations, run the display bgp peer or display bgp vpnv4 all peer command on PEs. The command output shows that BGP peer relationships have been established between PEs and CEs.
- Verify the configuration.
After the configurations are complete, the Spoke-CEs can successfully ping each other.
The following example uses the command output on Spoke-CE1.
<Spoke-CE1> ping -a 11.11.11.11 22.22.22.22 PING 22.22.22.22: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 22.22.22.22: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=250 time=80 ms Reply from 22.22.22.22: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=250 time=129 ms Reply from 22.22.22.22: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=250 time=132 ms Reply from 22.22.22.22: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=250 time=92 ms Reply from 22.22.22.22: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=250 time=126 ms --- 22.22.22.22 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 80/111/132 msRun the display bgp routing-table command on each Spoke-CE. The command output shows BGP routing table information.
The following example uses the command output on Spoke-CE1.
<Spoke-CE1> display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 10.1.1.1 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete RPKI validation codes: V - valid, I - invalid, N - not-found Total Number of Routes: 2 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> 0.0.0.0/0 10.1.1.2 0 100 65430i *> 11.11.11.11/32 0.0.0.0 0 0 i
Configuration Files
Spoke-CE1 configuration file
# sysname Spoke-CE1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65410 peer 10.1.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 11.11.11.11 255.255.255.255 peer 10.1.1.2 enable # returnSpoke-PE1 configuration file
# sysname Spoke-PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna peer 10.1.1.1 as-number 65410 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Spoke-PE2 configuration file
# sysname Spoke-PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:3 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 100:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 200:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ip address 10.4.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 2.2.2.9 as-number 100 peer 2.2.2.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 2.2.2.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpna peer 10.4.1.1 as-number 65420 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.9 0.0.0.0 network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Spoke-CE2 configuration file
# sysname Spoke-CE2 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.4.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65420 peer 10.4.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 22.22.22.22 255.255.255.255 peer 10.4.1.2 enable # returnHub-CE configuration file
# sysname Hub-CE # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.2.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 33.33.33.33 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65430 peer 10.2.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization network 33.33.33.33 255.255.255.255 peer 10.2.1.2 enable peer 10.2.1.2 default-route-advertise # returnHub-PE configuration file
# sysname Hub-PE # ip vpn-instance vpnhub ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:21 export route-policy policy_in apply-label per-route pop-go vpn-target 200:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 100:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpnhub ip address 10.2.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 1.1.1.9 enable peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.9 enable peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpnhub peer 10.2.1.1 as-number 65430 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # route-policy policy_in permit node 1 if-match ip-prefix defaultip # route-policy policy_in deny node 2 # ip ip-prefix defaultip index 10 permit 0.0.0.0 0 # return