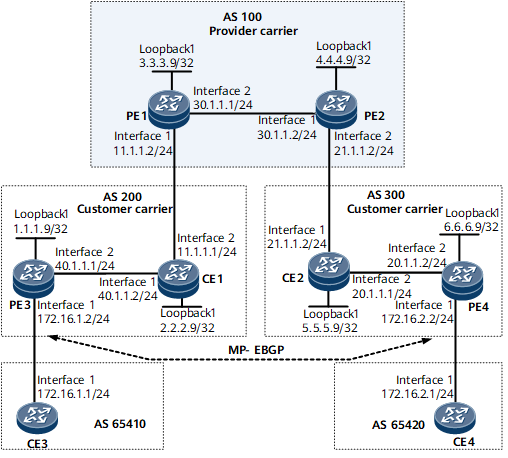
Example for Configuring Carrier's Carrier Solution 1 (LDP Multi-Instance)
This section provides an example for configuring intra-AS carrier's carrier in the scenario where a Level 1 carrier and Level 2 carriers belong to the same AS. The Level 2 carrier can provide BGP/MPLS IP VPN services.
Networking Requirements
The Level 1 carrier and Level 2 carrier are in the same AS. The Level 2 carrier provides the BGP/MPLS IP VPN service for its customers, on the network shown in Figure 1:
PE1 and PE2 are deployed on the Level 1 carrier's backbone network.
CE1 and CE2 are devices of the Level 2 carrier and are used to access the Level 1 carrier's backbone network.
PE3 and PE4 are also devices of the Level 2 carrier and are used to provide the access service for customers.
CE3 and CE4 are the customers of the Level 2 carrier.
Deployment Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
The two types of routes are exchanged as follows:
Exchange of the internal routes of the Level 2 carrier on the backbone network of Level 1 carrier: Configure the Level 2 carrier to access the Level 1 carrier as the Level 1 carrier CE.
Exchange of the external routes of the Level 2 carrier between the PE devices of the Level 2 carrier: Set up an MP-IBGP peer relationship between PEs (PE3 and PE4) of the Level 2 carrier.
Configure the carrier's carrier of the same AS and configure an IGP and LDP between the Level 1 carrier PE and the Level 1 carrier CE.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
MPLS LSR IDs of the Level 1 carrier PE and the Level 2 carrier PE and CE
Data required for configuring an IGP
Names, RDs, and VPN targets of the VPN instances created on PEs
Procedure
- Configure a BGP/MPLS IP VPN on the Level 1 carrier's backbone network.
Configure IS-IS as an IGP, enable LDP between PE1 and PE2, and establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between them.
# Configure PE1.
<~HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface loopback 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 3.3.3.9 32 [*PE1-LoopBack1] commit [~PE1-LoopBack1] quit [~PE1] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 [*PE1] mpls [*PE1-mpls] quit [*PE1] mpls ldp [*PE1] commit [~PE1-mpls-ldp] quit [~PE1] isis 1 [*PE1-isis-1] network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 [*PE1-isis-1] quit [*PE1] interface loopback 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] isis enable 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 30.1.1.1 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] isis enable 1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls ldp [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [~PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 100 [*PE1-bgp] peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 4.4.4.9 enable [*PE1-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [*PE1-bgp] commit [~PE1-bgp] quit

The configuration of PE2 is similar to that of PE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
After PE1 and PE2 are configured, run the display mpls ldp session command on either of them. The command output shows that the LDP session has been set up successfully. Run the display bgp peer command on either of them. The command output shows that the BGP peer relationship has been established. Run the display isis peer command on either of them. The command output shows that the IS-IS neighbor relationship is Up.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display mpls ldp session LDP Session(s) in Public Network Codes: LAM(Label Advertisement Mode), SsnAge Unit(DDDD:HH:MM) A '*' before a session means the session is being deleted. ---------------------------------------------------------------- PeerID Status LAM SsnRole SsnAge KASent/Rcv ---------------------------------------------------------------- 4.4.4.9:0 Operational DU Active 0000:00:01 8/8 ---------------------------------------------------------------- TOTAL: 1 session(s) Found. [~PE1] display bgp peer BGP local router ID : 3.3.3.9 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 4.4.4.9 4 100 7 8 0 00:02:47 Established 0 [~PE1] display isis peer Peer information for ISIS(1) System Id Interface Circuit Id State HoldTime Type PRI ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- 0000.0000.0005 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 0000.0000.0005.01 Up 7s L1(L1L2) 64 0000.0000.0005 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 0000.0000.0005.01 Up 7s L2(L1L2) 64 Total Peer(s): 2
- Configure the Level 2 carriers' networks.
Configure OSPF as an IGP, and enable LDP between PE3 and CE1 and between PE4 and CE2.
# Configure PE3.
<~HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE3 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE3] interface loopback 1 [*PE3-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.9 32 [*PE3-LoopBack1] quit [*PE3] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 [*PE3] mpls [*PE3-mpls] quit [*PE3] mpls ldp [*PE3-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 40.1.1.1 24 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls ldp [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [~PE3] ospf 1 [*PE3-ospf-1] area 0 [*PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 [*PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~PE3-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~PE3-ospf-1] quit
# Configure CE1.
<~HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE1] interface loopback 1 [*CE1-LoopBack1] ip address 2.2.2.9 32 [*CE1-LoopBack1] quit [*CE1] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 [*CE1] mpls [*CE1-mpls] quit [*CE1] mpls ldp [*CE1-mpls-ldp] quit [*CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*CE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] ip address 40.1.1.2 24 [*CE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] mpls [*CE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*CE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] commit [~CE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] quit [~CE1] ospf 1 [*CE1-ospf-1] area 0 [*CE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*CE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 [*CE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~CE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~CE1-ospf-1] quit
After the configuration is complete, PE3 and CE1 can establish an LDP peer relationship and an OSPF neighbor relationship.

The configuration of the connection between PE4 and CE2 is similar to that of the connection between PE3 and CE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure Level 1 carrier CEs to access Level 1 carrier PEs.
# Configure PE1.

To ensure normal forwarding, configure only the per-route per-label mode in a VPN instance.
[~PE1] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 200:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] apply-label per-route [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] vpn-target 1:1 both [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE1] bgp 100 [*PE1-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] import-route ospf 1 [*PE1-bgp-vpn1] quit [*PE1-bgp] quit [*PE1] mpls ldp vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-mpls-ldp-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE1] ospf 1 vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-ospf-1] import-route bgp [*PE1-ospf-1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] ip address 11.1.1.2 24 [*PE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] mpls [*PE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*PE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] mpls ldp transport-address interface [*PE1-Gigabitethernet0/1/0] commit [~PE1] ospf 1 [*PE1-ospf-1] area 0 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [~PE1-ospf-1] quit
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip address 11.1.1.1 24 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls ldp [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] mpls ldp transport-address interface [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [~CE1] ospf 1 [*CE1-ospf-1] area 0 [*CE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*CE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] commit [~CE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit
After the configuration is complete, PE1 and CE1 can establish an LDP peer relationship and an OSPF neighbor relationship.

The configuration of the connection between PE2 and CE2 is similar to that of the connection between PE1 and CE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure the Level 2 carrier's customers to access the Level 2 carrier PE.
# Configure CE3.
<~HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE3 [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 172.16.1.1 24 [*CE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*CE3] bgp 65410 [*CE3-bgp] peer 172.16.1.2 as-number 100 [*CE3-bgp] import-route direct [*CE3-bgp] commit [~CE3-bgp] quit
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] ip vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1] ipv4-family [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE1-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] apply-label per-route [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] vpn-target 1:1 both [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1-af-ipv4] quit [*PE3-vpn-instance-vpn1] quit [*PE3] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 172.16.1.2 24 [*PE3-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE3] bgp 100 [*PE3-bgp] ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 [*PE3-bgp-vpn1] peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 65410 [*PE3-bgp-vpn1] import-route direct [*PE3-bgp-vpn1] commit [~PE3-bgp-vpn1] quit [~PE3-bgp] quit
After the configuration is complete, the BGP peer relationship has been set up successfully between CE3 and PE3, and the peer status is Established.

The configuration of the connection between PE4 and CE4 is similar to that of the connection between PE3 and CE3. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Establish an MP-IBGP peer relationship between Level 2 carrier PEs to exchange VPN routes of Level 2 carrier CEs.
# Configure PE3.
[~PE3] bgp 100 [*PE3-bgp] peer 6.6.6.9 as-number 100 [*PE3-bgp] peer 6.6.6.9 connect-interface loopback 1 [*PE3-bgp] ipv4-family vpnv4 [*PE3-bgp-af-vpnv4] peer 6.6.6.9 enable [*PE3-bgp-af-vpnv4] commit [~PE3-bgp-af-vpnv4] quit [~PE3-bgp] quit

The configuration of PE4 is similar to that of PE3. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Verify the configuration.
After completing the configuration, run the display ip routing-table command on PE1 and PE2. The command output shows that only routes from the Level 1 carrier's network exist in the public routing tables on PE1 and PE2. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: Public Destinations : 7 Routes : 7 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 3.3.3.9/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 4.4.4.9/32 ISIS 15 10 D 30.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 30.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 30.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 30.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 30.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 30.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Run the display ip routing-table vpn-instance command on PE1 and PE2. The command output shows that the Level 2 carriers' internal routes instead of the Level 2 carriers' external routes exist in the VPN instances of PE1 and PE2. The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: vpn1 Destinations : 10 Routes : 10 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.9/32 OSPF 10 2 D 11.1.1.1 Gigabitethernet0/1/0 2.2.2.9/32 OSPF 10 1 D 11.1.1.1 Gigabitethernet0/1/0 5.5.5.9/32 IBGP 255 0 RD 4.4.4.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 6.6.6.9/32 IBGP 255 0 RD 4.4.4.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 40.1.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 11.1.1.1 Gigabitethernet0/1/0 11.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 11.1.1.1 Gigabitethernet0/1/0 11.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 11.1.1.2 Gigabitethernet0/1/0 11.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Gigabitethernet0/1/0 20.1.1.0/24 IBGP 255 0 RD 4.4.4.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 21.1.1.0/24 IBGP 255 0 RD 4.4.4.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8
Run the display ip routing-table command on CE1 and CE2. The command output shows that the Level 2 carriers' internal routes instead of the Level 2 carriers' external routes exist in the public routing tables of CE1 and CE2. The following example uses the command output on CE1.
[~CE1] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: Public Destinations : 14 Routes : 14 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.9/32 OSPF 10 1 D 40.1.1.2 Gigabitethernet0/1/0 2.2.2.9/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 5.5.5.9/32 OSPF 10 3 D 11.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 6.6.6.9/32 OSPF 10 4 D 11.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 40.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 40.1.1.2 Gigabitethernet0/1/0 40.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 40.1.1.1 Gigabitethernet0/1/0 40.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 11.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 11.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 11.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 11.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 11.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 Gigabitethernet0/1/8 20.1.1.0/24 OSPF 10 4 D 11.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 21.1.1.0/24 OSPF 10 3 D 11.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Run the display ip routing-table command on PE3 and PE4. The command output shows that the Level 2 carriers' internal routes exist in the public routing tables of PE3 and PE4. The following example uses the command output on PE3.
[~PE3] display ip routing-table Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: Public Destinations : 13 Routes : 13 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 1.1.1.9/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 2.2.2.9/32 OSPF 10 1 D 40.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 5.5.5.9/32 OSPF 10 4 D 40.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 6.6.6.9/32 OSPF 10 5 D 40.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 40.1.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 40.1.1.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 40.1.1.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 40.1.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 40.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 11.1.1.0/24 OSPF 10 2 D 40.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 20.1.1.0/24 OSPF 10 5 D 40.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 20.1.1.1/32 EBGP 255 0 RD 6.6.6.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 21.1.1.0/24 OSPF 10 4 D 40.1.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/8 127.0.0.0/8 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0 127.0.0.1/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 InLoopBack0
Run the display ip routing-table vpn-instance command on PE3 and PE4. The command output shows that the Level 2 carriers' external routes exist in the VPN instances of PE3 and PE4. The following example uses the command output on PE3.
[~PE3] display ip routing-table vpn-instance vpn1 Route Flags: R - relay, D - download to fib, T - to vpn-instance, B - black hole route ------------------------------------------------------------------------------ Routing Table: vpn1 Destinations : 3 Routes : 3 Destination/Mask Proto Pre Cost Flags NextHop Interface 172.16.1.0/24 Direct 0 0 D 172.16.1.2 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 172.16.1.2/32 Direct 0 0 D 127.0.0.1 GigabitEthernet0/1/0 172.16.2.0/24 EBGP 255 0 RD 6.6.6.9 GigabitEthernet0/1/8
PE3 and PE4 can ping each other.
[~PE3] ping 20.1.1.2 PING 20.1.1.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 20.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=252 time=127 ms Reply from 20.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=252 time=97 ms Reply from 20.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=252 time=83 ms Reply from 20.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=252 time=70 ms Reply from 20.1.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=252 time=60 ms --- 20.1.1.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 60/87/127 msCE3 and CE4 can ping each other.
[~CE3] ping 172.16.2.1 PING 172.16.2.1: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 172.16.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=252 time=102 ms Reply from 172.16.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=252 time=69 ms Reply from 172.16.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=252 time=105 ms Reply from 172.16.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=252 time=88 ms Reply from 172.16.2.1: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=252 time=87 ms --- 172.16.2.1 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 69/90/105 ms
Configuration Files
CE3 configuration file
# sysname CE3 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.1.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65410 peer 172.16.1.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 172.16.1.2 enable # returnPE3 configuration file
# sysname PE3 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-route vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 172.16.1.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 40.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 6.6.6.9 as-number 100 peer 6.6.6.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 6.6.6.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 6.6.6.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 peer 172.16.1.1 as-number 65410 import-route direct # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.9 0.0.0.0 network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 40.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 11.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp mpls ldp transport-address interface # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.9 0.0.0.0 network 40.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:1 apply-label per-route vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.9 mpls # mpls ldp # mpls ldp vpn-instance vpn1 # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 11.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 30.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 4.4.4.9 as-number 100 peer 4.4.4.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 4.4.4.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 4.4.4.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route ospf 1 # ospf 1 vpn-instance vpn1 import-route bgp area 0.0.0.0 network 11.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 200:2 apply-label per-route vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 4.4.4.9 mpls # mpls ldp # mpls ldp vpn-instance vpn1 # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00 # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 30.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 isis enable 1 mpls mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 21.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 4.4.4.9 255.255.255.255 isis enable 1 # bgp 100 peer 3.3.3.9 as-number 100 peer 3.3.3.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 3.3.3.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 import-route ospf 1 # ospf 1 vpn-instance vpn1 import-route bgp area 0.0.0.0 network 21.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
CE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # mpls lsr-id 5.5.5.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 21.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp mpls ldp transport-address interface # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 20.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 5.5.5.9 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 5.5.5.9 0.0.0.0 network 21.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE4 configuration file
# sysname PE4 # ip vpn-instance vpn1 ipv4-family route-distinguisher 100:2 apply-label per-route vpn-target 1:1 export-extcommunity vpn-target 1:1 import-extcommunity # mpls lsr-id 6.6.6.9 mpls # mpls ldp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpn1 ip address 172.16.2.2 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 20.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 6.6.6.9 255.255.255.255 # bgp 100 peer 1.1.1.9 as-number 100 peer 1.1.1.9 connect-interface LoopBack1 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 1.1.1.9 enable # ipv4-family vpnv4 policy vpn-target peer 1.1.1.9 enable # ipv4-family vpn-instance vpn1 peer 172.16.2.1 as-number 65420 import-route direct # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 6.6.6.9 0.0.0.0 network 20.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # return
CE4 configuration file
# sysname CE4 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 172.16.2.1 255.255.255.0 # bgp 65420 peer 172.16.2.2 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization import-route direct peer 172.16.2.2 enable # return