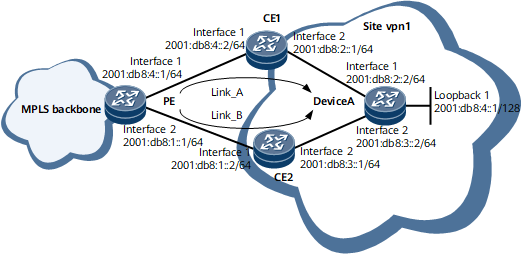
Example for Configuring Private Network IPv6 FRR
Private network IPv6 FRR can be deployed if multiple CEs at an IPv6 VPN site access the same PE. If a route from the PE to a CE is unreachable, this feature quickly switches traffic to a link from the PE to another CE.
Networking Requirements
At a VPN site, different CEs use BGP to access the same PE. The PE learns multiple IPv6 VPN routes with the same VPN prefix from the CEs. To enable the system to select a primary route and a backup route, you can deploy FRR for IPv6 routes on the private network. After this feature is configured, the PE generates a primary route and a backup route to the same destination on the private network. After that, IPv6 traffic can be quickly switched to the link where the backup route resides in case the link where the primary route resides is faulty.
On the network shown in Figure 1, an EBGP peer relationship is set up between the PE and each CE. There are two BGP routes from the PE to the Loopback1 interface on Device A. The optimal route resides on Link_A; the sub-optimal route resides on Link_B. It is required that IPv6 Auto FRR be deployed on the PE so that if Link_A fails, IPv6 traffic can be quickly switched to Link_B.
Configuration Notes
In a VPN FRR scenario, after the primary path recovers, traffic switches back to this path. Because the order in which nodes undergo IGP convergence differs, packet loss may occur during the switchback. To resolve this problem, run the route-select delay delay-value command to configure a route selection delay so that traffic is switched back only after forwarding entries on the devices along the primary path are updated. The delay specified using delay-value depends on various factors, such as the number of routes on the devices. Set a proper delay as needed.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IGP at the VPN site to advertise the route to the Loopback1 interface on Device A to CE1 and CE2.
Configure an IPv6-address-family-supporting VPN instance named vpna on the PE, and bind GE 0/1/0 and GE 0/1/8 to vpna.
Establish an EBGP peer relationship between the PE and CE1, and between the PE and CE2. On CE1 and CE2, configure the IGP and BGP to import routes from each other.
Enable private network IPv6 auto FRR on the PE.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
VPN instance name (vpna) and attributes of the VPN instance IPv6 address family, for example, the RD (100:1) and VPN targets (100:100), on the PE
MEDs configured for the IGP routes imported into BGP on CE1 and CE2
Procedure
- Configure IPv6 addresses for the interfaces on the routers at the VPN site.
For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure an IGP at the VPN site to advertise the route to the Loopback1 interface on Device A to CE1 and CE2. This example uses OSPFv3 as the IGP.
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] ospfv3 1 [*CE1-ospfv3-1] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*CE1-ospfv3-1] quit [*CE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*CE1] commit
The configurations of CE2 and Device A are similar to the configuration of CE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
After completing the configurations, run the display ipv6 routing-table command on the CEs. The command output shows that CE1 and CE2 have learned the route to the Loopback1 interface on Device A. The following example uses the command output on CE1.
[~CE1] display ipv6 routing-table Routing Table : _public_ Destinations : 10 Routes : 10 Destination : ::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : InLoopBack0 Flags : D Destination : ::FFFF:127.0.0.0 PrefixLength : 104 NextHop : ::FFFF:127.0.0.1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : InLoopBack0 Flags : D Destination : ::FFFF:127.0.0.1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : InLoopBack0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:0:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:DB8:4::2 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:4::2 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:2:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:DB8:2::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:2::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:3:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : FE80::5451:0:FAC1:1 Preference : 10 Cost : 3124 Protocol : OSPFv3 RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:4::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : FE80::5451:0:FAC1:1 Preference : 10 Cost : 1562 Protocol : OSPFv3 RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Flags : D Destination : FE80:: PrefixLength : 10 NextHop : :: Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : NULL0 Flags : D
- Configure an IPv6-address-family-supporting VPN instance on each PE and bind the interface that connects a PE to a CE to the VPN instance on that PE.
# Configure a VPN instance named vpna on the PE, and bind GE 0/1/0 and GE 0/1/8 to the instance.
<PE> system-view [~PE] ip vpn-instance vpna [*PE-vpn-instance-vpna] ipv6-family [*PE-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] route-distinguisher 100:1 [*PE-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] vpn-target 100:100 [*PE-vpn-instance-vpna-af-ipv6] quit [*PE-vpn-instance-vpna] quit [*PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 enable [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ipv6 address 2001:DB8:4::1 64 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*PE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ip binding vpn-instance vpna [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ipv6 enable [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1::1 64 [*PE-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*PE] commit
- Establish EBGP peer relationships between the PE and CEs.
# Configure the PE.
[~PE] bgp 100 [*PE-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE-bgp6-vpna] peer 2001:DB8:4::2 as-number 65410 [*PE-bgp6-vpna] peer 2001:DB8:1::2 as-number 65410 [*PE-bgp6-vpna] quit [*PE-bgp] quit [*PE] commit
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] bgp 65410 [*CE1-bgp] peer 2001:DB8:4::1 as-number 100 [*CE1-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [*CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] peer 2001:DB8:4::1 enable [*CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] quit [*CE1-bgp] quit [*CE1] commit
The configuration of CE2 is similar to the configuration of CE1. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
After completing the configurations, run the display bgp vpnv6 vpn-instance vpna peer command on the PE. The command output shows that the status of the EBGP peer relationships between the PE and CEs is Established.
<PE> display bgp vpnv6 vpn-instance vpna peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 2 Peers in established state : 2 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 2001:DB8:4::2 4 65410 35 37 0 00:24:31 Established 3 2001:DB8:1::2 4 65410 41 43 0 00:24:03 Established 3
- Configure route exchange between OSPFv3 and BGP on the CEs.
Configure OSPFv3 routes on the CEs and import them into BGP. To make the PE select the route along Link_A as the optimal route, ensure that the MED configured for the OSPFv3 routes imported into BGP on CE1 is smaller than that configured on CE2.
# Configure CE1.
[~CE1] bgp 65410 [*CE1-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [*CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] import-route ospfv3 1 med 100 [*CE1-bgp-af-ipv6] quit [*CE1-bgp] quit [*CE1] commit
# Configure CE2.
[~CE2] bgp 65410 [*CE2-bgp] ipv6-family unicast [*CE2-bgp-af-ipv6] import-route ospfv3 1 med 500 [*CE2-bgp-af-ipv6] quit [*CE2-bgp] quit [*CE2] commit
# Import BGP routes into OSPFv3 on CE1.
[~CE1] ospfv3 1 [*CE1-ospfv3-1] import-route bgp [*CE1-ospfv3-1] quit [*CE1] commit
# Import BGP routes into OSPFv3 on CE2.
[~CE2] ospfv3 1 [*CE2-ospfv3-1] import-route bgp [*CE2-ospfv3-1] quit [*CE2] commit
After completing the configurations, run the display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance command on the PE. The command output shows the route to the Loopback1 interface on Device A.
<PE> display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpna Routing Table : vpna Destinations : 8 Routes : 8 Destination : 2001:DB8:0:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:DB8:4::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:4::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:1:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:DB8:1::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:1::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : ::1 Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:2:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:DB8:4::2 Preference : 255 Cost : 100 Protocol : BGP RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:3:: PrefixLength : 64 NextHop : 2001:DB8:1::2 Preference : 255 Cost : 0 Protocol : BGP RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Flags : D Destination : 2001:DB8:4::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : 2001:DB8:4::2 Preference : 255 Cost : 100 Protocol : BGP RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : D Destination : FE80:: PrefixLength : 10 NextHop : :: Preference : 0 Cost : 0 Protocol : Direct RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : NULL0 Flags : D - Enable private network IPv6 auto FRR on the PE.
# Configure the PE.
[~PE] bgp 100 [~PE-bgp] ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna [*PE-bgp6-vpna] auto-frr [*PE-bgp6-vpna] route-select delay 300 [*PE-bgp6-vpna] quit [*PE-bgp] quit [*PE] commit

The auto-frr command run in the BGP-VPN instance IPv6 address family view is valid only for BGP routes.
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance command on the PE. The command output shows that the next hop of the route to 2001:DB8:4::1/128 is 2001:DB8:4::2, and the route has a backup next hop and a backup outbound interface.
[~PE] display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpna 2001:DB8:4::1 verbose Routing Table : vpna Summary Count : 1 Destination : 2001:DB8:4::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : 2001:DB8:4::2 Preference : 255 Neighbour : 2001:DB8:4::2 ProcessID : 0 Label : NULL Protocol : BGP State : Active Adv Cost : 100 Entry ID : 27 EntryFlags : 0x80004100 Reference Cnt: 2 Tag : 0 IndirectID : 0x6 Age : 3sec RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Flags : D BkNextHop : 2001:DB8:1::2 BkInterface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8 BkLabel : NULL BkTunnelID : 0x0 BkPETunnelID : 0x0 BkIndirectID : 0x5
Disable IPv6 on GE 0/1/8 on CE1 so that IPv6 routes cannot be transmitted over Link_A.
[~CE1] interface Gigabitethernet0/1/8 [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] undo ipv6 enable [*CE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*CE1] commit
Run the display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance command again on the PE. The command output shows that the next hop to 2001:db8:4::1/128 is 2001:db8:1::2, and the PE does not have a backup next hop or a backup outbound interface.
[~PE] display ipv6 routing-table vpn-instance vpna 2001:DB8:4::1 verbose Routing Table : vpna Summary Count : 1 Destination : 2001:DB8:4::1 PrefixLength : 128 NextHop : 2001:DB8:1::2 Preference : 255 Neighbour : 2001:DB8:1::2 ProcessID : 0 Label : NULL Protocol : BGP State : Active Adv Cost : 500 Entry ID : 27 EntryFlags : 0x80004100 Reference Cnt: 2 Tag : 0 IndirectID : 0x6 Age : 3sec RelayNextHop : :: TunnelID : 0x0 Interface : GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Flags : D
Private network IPv6 auto FRR has taken effect.
Configuration Files
- PE configuration file
# sysname PE # ip vpn-instance vpna ipv6-family route-distinguisher 100:1 apply-label per-instance vpn-target 100:100 export-extcommunity vpn-target 100:100 import-extcommunity # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:4::1/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip binding vpn-instance vpna ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1::1/64 # bgp 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family vpnv6 policy vpn-target # ipv6-family vpn-instance vpna auto-frr route-select delay 300 peer 2001:DB8:4::2 as-number 65410 peer 2001:DB8:1::2 as-number 65410 # return
- CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # ospfv3 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 import-route bgp # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:4::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::1/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65410 peer 2001:DB8:4::1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization import-route ospfv3 1 med 100 peer 2001:DB8:4::1 enable # return
- CE2 configuration file
# sysname CE2 # ospfv3 1 router-id 3.3.3.3 import-route bgp area 0.0.0.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1::2/64 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:3::1/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface LoopBack1 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # bgp 65410 peer 2001:DB8:1::1 as-number 100 # ipv4-family unicast undo synchronization # ipv6-family unicast undo synchronization import-route ospfv3 1 med 500 peer 2001:DB8:1::1 enable # return
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # ospfv3 1 router-id 4.4.4.4 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:3::2/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface LoopBack1 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:4::1/128 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 # return