Example for Configuring PIM-SM Inter-domain Multicast
You can set up MSDP peer relationships between Rendezvous Points (RPs) in different PIM-SM domains in the same autonomous system (AS) or between the RPs in different ASs that have set up BGP peer relationships so that hosts can receive multicast data from the source in another PIM-SM domain in the AS or from the source in another AS.
Networking Requirements
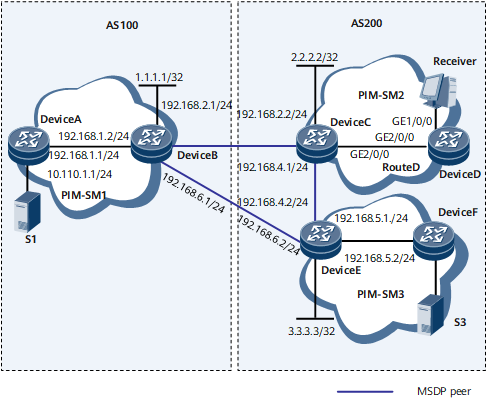
On the network shown in Figure 1, there are two ASs. Each AS contains at least one PIM-SM domain and each PIM-SM domain may contain no or one multicast source and receiver. To enable the receiver in PIM-SM2 domain to receive both multicast data sent by S3 in PIM-SM3 domain and multicast data sent by S1 in PIM-SM1 domain, configure PIM-SM inter-domain multicast.
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
DeviceA |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.110.1.1/24 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
192.168.1.1/24 |
|
DeviceB |
Loopback0 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
192.168.2.1/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
192.168.1.2/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/16 |
192.168.6.1/24 |
|
DeviceC |
Loopback0 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
192.168.2.2/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
192.168.3.1/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/16 |
192.168.4.1/24 |
|
DeviceD |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.110.2.1/24 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
192.168.3.2/24 |
|
DeviceE |
Loopback0 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
192.168.5.1/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/16 |
192.168.4.2/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/1 |
192.168.6.2/24 |
|
DeviceF |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.110.3.1/24 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
192.168.5.2/24 |
Precautions
Note the following precautions during configuration:
Establish an MSDP peer relationship between BGP peers only when the RP and the unicast autonomous system boundary router (ASBR) are configured on the same router.
The address of the interface on which the MSDP peer is configured must be the same as that of the interface on which the External Border Gateway Protocol (EBGP) peer is configured.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IP address for each router interface and configure OSPF in the ASs to ensure that unicast routes are reachable between the ASs.
Establish an EBGP peer relationship between ASs and configure BGP and OSPF to import routes from each other to ensure that unicast routes are reachable between the ASs.
Enable multicast routing, enable PIM-SM on each interface, configure BSR boundaries to divide PIM-SM domains, and enable IGMP on interfaces connected to hosts.
Configure the Candidate-BootStrap Router (C-BSR) and the Candidate-Rendezvous Point (C-RP). Configure the RPs of PIM-SM1 and PIM-SM2 on the ASBRs in the two domains.
Establish MSDP peer relationships between RPs of PIM-SM domains.
Add all MSDP peers in the same and different ASs to the same mesh group.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Multicast group address
AS number of DeviceA and DeviceB; router ID of DeviceB
AS number of DeviceC and DeviceD; router ID of DeviceC
AS number of DeviceE and DeviceF
Name of the mesh group that MSDP peers join
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each router interface and configure OSPF in the ASs. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Establish an EBGP peer relationship between ASs and configure BGP and OSPF to import routes from each other.
# Configure EBGP on DeviceB and import OSPF routes.
[~DeviceB] bgp 100 [*DeviceB-bgp] router-id 1.1.1.1 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 192.168.2.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 192.168.2.2 ebgp-max-hop 255 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 192.168.6.2 as-number 200 [*DeviceB-bgp] peer 192.168.6.2 ebgp-max-hop 255 [*DeviceB-bgp] import-route ospf 1 [*DeviceB-bgp] commit [~DeviceB-bgp] quit
# Configure EBGP on DeviceC and import OSPF routes.
[~DeviceC] bgp 200 [*DeviceC-bgp] router-id 2.2.2.2 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 192.168.2.1 as-number 100 [*DeviceC-bgp] peer 192.168.2.1 ebgp-max-hop 255 [*DeviceC-bgp] import-route ospf 1 [*DeviceC-bgp] commit [~DeviceC-bgp] quit
# Configure EBGP on DeviceE and import OSPF routes.
[~DeviceE] bgp 200 [*DeviceE-bgp] router-id 3.3.3.3 [*DeviceE-bgp] peer 192.168.6.1 as-number 100 [*DeviceE-bgp] peer 192.168.6.1 ebgp-max-hop 255 [*DeviceE-bgp] import-route ospf 1 [*DeviceE-bgp] commit [~DeviceE-bgp] quit
# Import BGP routes to OSPF on DeviceB. Repeat this step for DeviceC and DeviceE. The configurations of DeviceC and DeviceE are similar to that of DeviceB. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceB] ospf 1 [*DeviceB-ospf-1] import-route bgp [*DeviceB-ospf-1] commit [~DeviceB-ospf-1] quit
- Enable multicast routing, enable PIM-SM on interfaces, and configure BSR boundaries.
# Enable multicast routing on DeviceB and enable PIM-SM on each interface. Repeat this step for other routers. The configurations of other routers are similar to that of DeviceB. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceB] multicast routing-enable [*DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim sm [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim sm [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/16 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim sm [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit
# Configure a BSR boundary on GE 0/1/0 and GE 0/1/1 on DeviceB.
Repeat this step for GE 0/1/16 and GE 0/1/1 on DeviceE, as well as GE 0/1/0 and GE 0/1/16 on DeviceC. The configurations of DeviceE and DeviceC are similar to that of DeviceB. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[*DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim bsr-boundary [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [~DeviceB] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/16 [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim bsr-boundary [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
- Enable IGMP on interfaces connected to hosts.
# Enable IGMP on the interface connecting DeviceD to hosts.
[~DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] igmp enable [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Configure a C-BSR and a C-RP.
# Create Loopback 0 on DeviceB and configure Loopback 0 as both a C-BSR and a C-RP. The configurations of DeviceC and DeviceE are similar to the configuration of DeviceB. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceB] interface loopback 0 [*DeviceB-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 [*DeviceB-LoopBack0] pim sm [*DeviceB-LoopBack0] quit [*DeviceB] pim [*DeviceB-pim] c-bsr loopback 0 [*DeviceB-pim] c-rp loopback 0 [*DeviceB-pim] commit [~DeviceB-pim] quit
- Establish MSDP peer relationships.
# Configure an MSDP peer on DeviceB.
[~DeviceB] msdp [*DeviceB-msdp] peer 192.168.2.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*DeviceB-msdp] peer 192.168.6.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 [*DeviceB-msdp] commit [~DeviceB-msdp] quit
# Configure an MSDP peer on DeviceC.
[~DeviceC] msdp [*DeviceC-msdp] peer 192.168.2.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 [*DeviceC-msdp] peer 192.168.4.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 [*DeviceC-msdp] commit [~DeviceC-msdp] quit
# Configure an MSDP peer on DeviceE.
[~DeviceE] msdp [*DeviceE-msdp] peer 192.168.4.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 [*DeviceE-msdp] peer 192.168.6.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 [*DeviceE-msdp] commit [~DeviceE-msdp] quit
- Add all MSDP peers in the same and different ASs to the same mesh group.
# Add DeviceB to the mesh group group1.
[~DeviceB] msdp [*DeviceB-msdp] peer 192.168.2.2 mesh-group group1 [*DeviceB-msdp] peer 192.168.6.2 mesh-group group1 [*DeviceB-msdp] commit [~DeviceB-msdp] quit
# Add DeviceC to the mesh group group1.
[~DeviceC] msdp [*DeviceC-msdp] peer 192.168.2.1 mesh-group group1 [*DeviceC-msdp] peer 192.168.4.2 mesh-group group1 [*DeviceC-msdp] commit [~DeviceC-msdp] quit
# Add DeviceE to the mesh group group1.
[~DeviceE] msdp [*DeviceE-msdp] peer 192.168.4.1 mesh-group group1 [*DeviceE-msdp] peer 192.168.6.1 mesh-group group1 [*DeviceE-msdp] commit [~DeviceE-msdp] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display bgp peer command. The command output shows BGP peer relationships established between routers. For example, the BGP peer relationship between DeviceB and DeviceC is displayed as follows:
<DeviceB> display bgp peer BGP local router ID : 1.1.1.1 Local AS number : 100 Total number of peers : 1 Peers in established state : 1 Peer V AS MsgRcvd MsgSent OutQ Up/Down State PrefRcv 192.168.2.2 4 200 52 49 0 00:42:37 Established 7# Run the display bgp routing-table command. The command output shows BGP routing tables on routers. For example, the BGP routing table on DeviceC is displayed as follows:
<DeviceC> display bgp routing-table BGP Local router ID is 2.2.2.2 Status codes: * - valid, > - best, d - damped, x - best external, a - add path, h - history, i - internal, s - suppressed, S - Stale Origin : i - IGP, e - EGP, ? - incomplete Total Number of Routes: 10 Network NextHop MED LocPrf PrefVal Path/Ogn *> 1.1.1.1/32 192.168.2.1 0 0 100? *> 2.2.2.2/32 0.0.0.0 0 0 ? *> 3.3.3.3/32 0.0.0.0 1 0 ? *> 10.110.1.0/24 192.168.2.1 2 0 100? *> 10.110.2.0/24 0.0.0.0 2 0 ? *> 10.110.3.0/24 0.0.0.0 3 0 ? *> 192.168.1.0 192.168.2.1 1 0 100? *> 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.0 1 0 ? *> 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.0 1 0 ? *> 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.0 2 0 ?
# Run the display msdp brief command. The command output shows MSDP peer relationships established between routers. The brief information about MSDP peer relationships established between DeviceB and DeviceC and DeviceE is displayed as follows:
<DeviceB> display msdp brief MSDP Peer Brief Information of VPN-Instance: public net Configured Up Listen Connect Shutdown Down 2 2 0 0 0 0 Peer's Address State Up/Down time AS SA Count Reset Count 192.168.2.2 Up 00:12:27 200 13 0 192.168.6.2 Up 01:13:08 200 13 0 <DeviceC> display msdp brief MSDP Peer Brief Information of VPN-Instance: public net Configured Up Listen Connect Shutdown Down 2 2 0 0 0 0 Peer's Address State Up/Down time AS SA Count Reset Count 192.168.2.1 Up 01:07:08 100 8 0 192.168.4.2 Up 00:06:39 200 13 0 <DeviceE> display msdp brief MSDP Peer Brief Information of VPN-Instance: public net Configured Up Listen Connect Shutdown Down 2 2 0 0 0 0 Peer's Address State Up/Down time AS SA Count Reset Count 192.168.4.1 Up 00:15:32 200 8 0 192.168.6.1 Up 01:18:40 100 8 0
# Run the display msdp peer-status command. The command output shows detailed information about MSDP peer relationships established between routers. The detailed information about MSDP peer relationships on DeviceB is displayed as follows:
<DeviceB> display msdp peer-status MSDP Peer Information of VPN-Instance: public net MSDP Peer 192.168.2.2, AS 200 Description: Information about connection status: State: Up Up/down time: 00:15:47 Resets: 0 Connection interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 (192.168.2.1) Number of sent/received messages: 16/16 Number of discarded output messages: 0 Elapsed time since last connection or counters clear: 00:17:51 Mesh group peer joined: group1 Information about (Source, Group)-based SA filtering policy: Import policy: none Export policy: none Information about SA-Requests: Policy to accept SA-Request messages: none Sending SA-Requests status: disable Minimum TTL to forward SA with encapsulated data: 0 SAs learned from this peer: 0, SA-cache maximum for the peer: none Input queue size: 0, Output queue size: 0 Counters for MSDP message: Count of RPF check failure: 0 Incoming/outgoing SA messages: 0/0 Incoming/outgoing SA requests: 0/0 Incoming/outgoing SA responses: 0/0 Incoming/outgoing data packets: 0/0 Peer authentication: unconfigured Peer authentication: none MSDP Peer 192.168.6.2, AS 200 Description: Information about connection status: State: Up Up/down time: 01:10:49 Resets: 0 Connection interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/16 (192.168.6.1) Number of sent/received messages: 71/71 Number of discarded output messages: 0 Elapsed time since last connection or counters clear: 01:11:50 Mesh group peer joined: group1 Information about (Source, Group)-based SA filtering policy: Import policy: none Export policy: none Information about SA-Requests: Policy to accept SA-Request messages: none Sending SA-Requests status: disable Minimum TTL to forward SA with encapsulated data: 0 SAs learned from this peer: 0, SA-cache maximum for the peer: none Input queue size: 0, Output queue size: 0 Counters for MSDP message: Count of RPF check failure: 0 Incoming/outgoing SA messages: 0/0 Incoming/outgoing SA requests: 0/0 Incoming/outgoing SA responses: 0/0 Incoming/outgoing data packets: 0/0 Peer authentication: unconfigured Peer authentication type: none
# Run the display pim routing-table command. The command output shows PIM routing tables on routers. When S1 (10.110.1.2/24) in PIM-SM1 domain and S3 (10.110.3.2/24) in PIM-SM3 domain send multicast data to G (225.1.1.1/24), Receiver (10.110.2.2/24) in PIM-SM2 domain can receive the multicast data. Information about the PIM routing tables on DeviceB and DeviceC is as follows:
<DeviceB> display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (10.110.1.2, 225.1.1.1) RP: 1.1.1.1(local) Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT 2MSDP ACT UpTime: 00:00:42 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/8, Refresh time: 00:00:42 Upstream neighbor: 192.168.1.1 RPF neighbor: 192.168.1.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:00:42, Expires:- <DeviceC> display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 (*, G) entry; 2 (S, G) entries (*, 225.1.1.1) RP: 2.2.2.2(local) Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: WC UpTime: 00:13:46 Upstream interface: NULL, Refresh time: 00:13:46 Upstream neighbor: NULL RPF prime neighbor: NULL Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/8, Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:13:46, Expires:- (10.110.1.2, 225.1.1.1) RP: 2.2.2.2 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT MSDP ACT UpTime: 00:00:42 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0, Refresh time: 00:00:42 Upstream neighbor: 192.168.2.1 RPF neighbor: 192.168.2.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:00:42, Expires:- (10.110.3.2, 225.1.1.1) RP: 2.2.2.2 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT MSDP ACT UpTime: 00:00:42 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/16, Refresh time: 00:00:42 Upstream neighbor: 192.168.4.2 RPF neighbor: 192.168.4.2 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:00:42, Expires:-
Configuration Files
DeviceB configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 pim bsr-boundary pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.6.1 255.255.255.0 pim bsr-boundary pim sm # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 pim sm # pim c-bsr LoopBack0 c-rp LoopBack0 # ospf 1 import-route BGP area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 # bgp 100 router-id 1.1.1.1 peer 192.168.2.2 as-number 200 peer 192.168.6.2 as-number 200 peer 192.168.2.2 ebgp-max-hop 255 peer 192.168.6.2 ebgp-max-hop 255 # ipv4-family unicast import-route ospf 1 peer 192.168.2.2 enable peer 192.168.6.2 enable peer 192.168.2.2 route-update-interval 0 # msdp peer 192.168.2.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 peer 192.168.2.2 mesh-group group1 peer 192.168.6.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 peer 192.168.6.2 mesh-group group1 # return
DeviceC configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 pim bsr-boundary pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.4.1 255.255.255.0 pim bsr-boundary pim sm # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 pim sm # pim c-bsr LoopBack0 c-rp LoopBack0 # ospf 1 import-route BGP area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 # bgp 200 router-id 2.2.2.2 peer 192.168.2.1 as-number 100 peer 192.168.2.1 ebgp-max-hop 255 # ipv4-family unicast import-route ospf 1 peer 192.168.2.1 enable peer 192.168.2.1 route-update-interval 0 # msdp peer 192.168.2.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 peer 192.168.2.1 mesh-group group1 peer 192.168.4.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 peer 192.168.4.2 mesh-group group1 # return
DeviceE configuration file
# sysname DeviceE # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.4.2 255.255.255.0 pim bsr-boundary pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.6.2 255.255.255.0 pim bsr-boundary pim sm # interface LoopBack0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 pim sm # pim c-bsr LoopBack0 c-rp LoopBack0 # ospf 1 import-route BGP area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 # bgp 200 router-id 3.3.3.3 peer 192.168.6.1 as-number 100 peer 192.168.6.1 ebgp-max-hop 255 # ipv4-family unicast import-route ospf 1 peer 192.168.6.1 enable # msdp peer 192.168.4.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 peer 192.168.4.1 mesh-group group1 peer 192.168.6.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 peer 192.168.6.1 mesh-group group1 # return