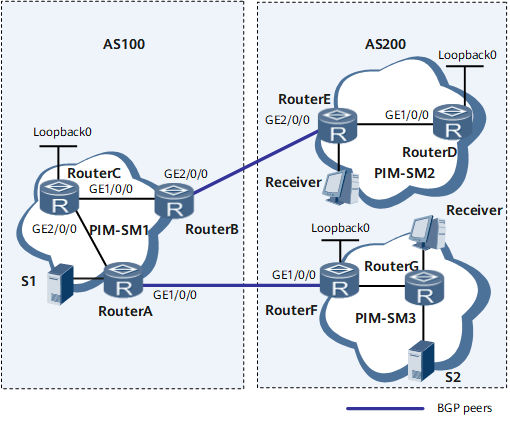
Example for Configuring Inter-AS Multicast by Using Static RPF Peers
You can set up MSDP peer relationships between Rendezvous Points (RPs) in different PIM-SM domains in the same autonomous system (AS) or static Reverse Path Forwarding (RPF) relationships between the RPs in different ASs so that hosts can receive multicast data from the source in another PIM-SM domain in the AS or from the source in another AS.
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, there are two ASs. Each AS contains at least one PIM-SM domain and each PIM-SM domain may contain no or one multicast source and receiver. To enable the receiver in PIM-SM2 domain to receive both multicast data sent by S2 in PIM-SM3 domain and multicast data sent by S1 in PIM-SM1 domain, configure inter-AS multicast, without changing the unicast topology.
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
Device A |
GE 0/1/0 |
192.168.5.2/24 |
DeviceB |
GE 0/1/8 |
192.168.2.2/24 |
DeviceC |
GE 0/1/0 |
192.168.1.1/24 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
192.168.4.1/24 |
|
Loopback0 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
|
DeviceD |
GE 0/1/0 |
192.168.3.2/24 |
Loopback0 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
|
DeviceE |
GE 0/1/8 |
192.168.2.1/24 |
DeviceF |
GE 0/1/0 |
192.168.5.1/24 |
Loopback0 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
Precautions
If static RPF peers are incorrectly configured, source active (SA) message loops may occur. Therefore, exercise caution when configuring them.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IP address for each router interface; configure OSPF in each AS and configure External Border Gateway Protocol (EBGP) between ASs; configure BGP and OSPF to import routes from each other.
Enable multicast routing and PIM-SM on each interface. Configure loopback0 and specify it as a C-BSR and C-RP on DeviceC, DeviceD, and DeviceF in their PIM-SM domains.
Establish an MSDP peer relationship between RPs in different domains. Specifically, establish an MSDP peer relationship between DeviceC and DeviceD, and between DeviceC and DeviceF.
Specify static RPF peers for MSDP peers. Specifically, specify DeviceD and DeviceF as static RPF peers of DeviceC, and specify DeviceC as the static RPF peer of DeviceD and DeviceF.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
AS numbers and router IDs of DeviceA, DeviceB, and DeviceC
AS numbers and router IDs of DeviceD and DeviceE
AS numbers of DeviceF and DeviceG and router ID of DeviceF
Policy used by Device C to filter the SA messages received from Device D and Device F
Policy used by Device D and Device F to filter the SA messages received from Device C
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each router interface and configure OSPF in the ASs. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable multicast routing on each device and PIM-SM on each interface.
# Enable the multicast function on all routers and enable PIM-SM on involved interfaces. The configurations on other routers are similar to that on DeviceC. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceC] multicast routing-enable [*DeviceC] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim sm [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceC] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim sm [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
# Configure a BSR boundary on GE 0/1/0 on Device A and Device F, and GE 0/1/8 on Device B and Device E. The configurations of Device B, Device E, and Device F are similar to the configuration of Device A. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceA] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim bsr-boundary [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit
- Enable IGMP on interfaces connected to hosts. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure Loopback 0 as both a C-BSR and a C-RP.
# Create Loopback 0 and configure Loopback 0 as both a C-BSR and a C-RP on DeviceC, DeviceD, and DeviceF. The configurations of Device D and Device F are similar to the configuration of Device C. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceC] interface loopback 0 [*DeviceC-LoopBack0] ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 [*DeviceC-LoopBack0] pim sm [*DeviceC-LoopBack0] quit [*DeviceC] pim [*DeviceC-pim] c-bsr loopback 0 [*DeviceC-pim] c-rp loopback 0 [*DeviceC-pim] commit [~DeviceC-pim] quit
- Configure static RPF peers.
# Configure Device D and Device F as static RPF peers of Device C.
[~DeviceC] ip ip-prefix list-df permit 192.168.0.0 16 greater-equal 16 less-equal 32 [*DeviceC] msdp [*DeviceC-msdp] peer 192.168.3.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceC-msdp] peer 192.168.5.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceC-msdp] static-rpf-peer 192.168.3.2 rp-policy list-df [*DeviceC-msdp] static-rpf-peer 192.168.5.1 rp-policy list-df [*DeviceC-msdp] commit [~DeviceC-msdp] quit
# Configure Device C as static RPF peers of Device D and Device F. The configuration of Device F is similar to the configuration of Device D. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceD] ip ip-prefix list-c permit 192.168.0.0 16 greater-equal 16 less-equal 32 [*DeviceD] msdp [*DeviceD-msdp] peer 192.168.1.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceD-msdp] static-rpf-peer 192.168.1.1 rp-policy list-c [*DeviceD-msdp] commit [~DeviceD-msdp] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display bgp peer command. The command output shows BGP peer relationships established between routers. Device C has no output, which indicates that the BGP peer relationships are not set up between Device C and Device D, or between Device C and Device F.
# Run the display msdp brief command. The command output shows MSDP peer relationships established between routers. When S1 in PIM-SM1 domain sends multicast data, the receivers in PIM-SM2 and PIM-SM3 domains can receive the data. For example, the command output of MSDP peers on Device C, Device D, and Device F is as follows:
<DeviceC> display msdp brief MSDP Peer Brief Information of VPN-Instance: public net Configured Up Listen Connect Shutdown Down 2 2 0 0 0 0 Peer's Address State Up/Down time AS SA Count Reset Count 192.168.3.2 Up 01:07:08 ? 8 0 192.168.5.1 Up 00:16:39 ? 13 0 <DeviceD> display msdp brief MSDP Peer Brief Information of VPN-Instance: public net Configured Up Listen Connect Shutdown Down 1 1 0 0 0 0 Peer's Address State Up/Down time AS SA Count Reset Count 192.168.1.1 Up 01:07:09 ? 8 0 <DeviceF> display msdp brief MSDP Peer Brief Information of VPN-Instance: public net Configured Up Listen Connect Shutdown Down 1 1 0 0 0 0 Peer's Address State Up/Down time AS SA Count Reset Count 192.168.4.1 Up 00:16:40 ? 13 0
Configuration Files
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # multicast routing-enable ip ip-prefix list-df index 10 permit 192.168.0.0 16 greater-equal 16 less-equal 32 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.4.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface LoopBack0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 pim sm # pim c-bsr LoopBack0 c-rp LoopBack0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.4.0 0.0.0.255 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 # msdp peer 192.168.3.2 connect-interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 peer 192.168.5.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/8 static-rpf-peer 192.168.3.2 rp-policy list-df static-rpf-peer 192.168.5.1 rp-policy list-df # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # multicast routing-enable ip ip-prefix list-c index 10 permit 192.168.0.0 16 greater-equal 16 less-equal 32 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface LoopBack0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 pim sm # pim c-bsr LoopBack0 c-rp LoopBack0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.3.0 0.0.0.255 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 # msdp peer 192.168.1.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 static-rpf-peer 192.168.1.1 rp-policy list-c # return
Device F configuration file
# sysname DeviceF # multicast routing-enable ip ip-prefix list-c index 10 permit 192.168.0.0 16 greater-equal 16 less-equal 32 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.5.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface LoopBack0 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 pim sm # pim c-bsr LoopBack0 c-rp LoopBack0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.5.0 0.0.0.255 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 # msdp peer 192.168.4.1 connect-interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 static-rpf-peer 192.168.4.1 rp-policy list-c # return