IPv4 Multicast-related Concepts
Before configuring IPv4 multicast services, familiarize yourself with basic multicast concepts, multicast models, IPv4 multicast addresses, and multicast protocols.
Basic Concepts of Multicast
Multicast group: Each IP multicast address identifies a multicast group. Any host (or other receiving device) that joins a multicast group becomes a member of this group and can identify and receive the IP packets with the destination addresses being the IP multicast address of this group.
Multicast source: The source that takes a multicast group address as the destination address to forward IP packets is called a multicast source. A multicast source can simultaneously send data to multiple multicast groups. Multiple multicast sources can simultaneously send data to a multicast group.
Multicast group member: The members of a multicast group are dynamic. Hosts can randomly join and leave a multicast group on a network. Members may reside in any position of the network.
Multicast router: The router that supports the multicast function on a network is called a multicast router. A multicast router provides the following functions:
- Managing group members at the leaf segment network that connects to hosts
- Implementing multicast routing and guiding the forwarding of multicast packets
Multicast distribution tree (MDT): According to the distribution of multicast group members, the multicast routing protocol can set up a tree-type routing architecture to forward multicast packets.
- Rendezvous Point Tree (RPT): The MDT with a Rendezvous Point (RP) as the root and group members as leaves is called an RPT. RPT is only applicable to the Protocol Independent Multicast-Sparse Mode (PIM-SM).
- Shortest Path Tree (SPT): The MDT with the multicast source as the root and group members as leaves is called an SPT. SPT is applicable to PIM-SM and Protocol Independent Multicast-Source Specific Multicast (PIM-SSM).
Multicast Models
Any-Source Multicast (ASM)
The ASM model is the original model in which any sender can act as a multicast source and send data to a multicast group address. Receivers can receive the data to this multicast group by joining this group. Receivers do not know the location of the multicast source in advance but can join or leave the group at any time.
Source-Specific Multicast (SSM)
The SSM model is a more recent model in which an interested receiver of multicast data specifies both the group and the source (or sources) from which it would like to receive the data. In the SSM model, receivers know the location of the multicast source in advance and a multicast distribution tree (MDT) can be established directly between the receiver and the multicast source, dedicated for multicast data transmission.
The SSM and ASM models use different multicast group address ranges.
IPv4 Multicast Addresses
The IPv4 multicast addresses are Class D addresses, ranging from 224.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255. The multicast group address available for multicast services ranges from 224.0.2.0 to 239.255.255.255. Table 1 lists IPv4 multicast addresses and gives a brief introduction.
Class D Address Range |
Description |
|---|---|
224.0.0.0 to 224.0.0.255 |
The addresses in this range are group addresses reserved for local links. The Internet Assigned Number Authority (IANA) reserves the addresses in this range for routing protocols, and these addresses are called permanent multicast group addresses. The addresses are used to identify a group of specific network devices and these devices are not involved in multicast forwarding. |
224.0.1.0 to 231.255.255.255 233.0.0.0 to 238.255.255.255 |
The addresses in this range are Any-Source Multicast (ASM) addresses. The addresses in this range are valid on the entire network. |
232.0.0.0 to 232.255.255.255 |
The addresses in this range are Source-Specific Multicast (SSM) addresses. This is the default SSM group address range. The addresses in this range are valid on the entire network. |
239.0.0.0 to 239.255.255.255 |
The addresses in this range are administration multicast addresses. This is the default group address range of the Bootstrap Router (BSR) administrative domain. The addresses in this range are private addresses. Each address is valid only in the local BSR administrative domain. You can use the same address in different BSR administrative domains. |
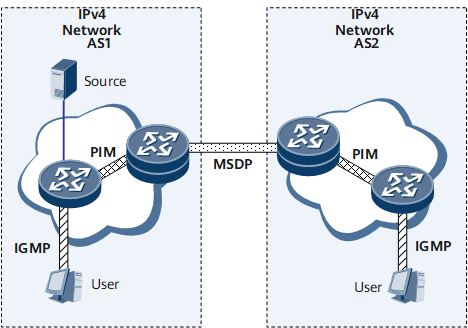
IPv4 Multicast Protocols
To implement a complete set of IPv4 multicast services, various multicast protocols need to be deployed on the network to cooperate with each other. Figure 1 shows various multicast protocols and application position of each multicast protocol.
Protocol |
Function |
Remarks |
|---|---|---|
Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) |
The Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) runs on between a Layer 3 multicast router and its attached user hosts to manage multicast group members on an IPv4 network. At the host side, IGMP enables the hosts to dynamically join or leave groups; at the network side, IGMP maintains and manages group memberships and completes interaction with the upper layer multicast routing protocol. |
At present, IGMP has three versions, IGMPv1, IGMPv2, and IGMPv3. All the three versions support the ASM model. IGMPv3 can be directly applied to the SSM model, whereas IGMPv1 and IGMPv2 require the support of SSM-mapping technology. |
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) |
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) is a multicast routing solution used to forward multicast data to the router that has attached multicast group members requesting the multicast data. |
In PIM-SM, ASM and SSM models are differentiated based on the multicast addresses in multicast data and protocol packets.
|
Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) |
The Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) is an inter-domain multicast solution developed for interconnection among multiple PIM-SM domains. It is used to discover information about multicast sources in other PIM-SM domains by sending Source-Active (SA) messages. |
MSDP is not required if PIM-SSM is used. |