Multicast Service Deployment on an IPv4 Network
This section describes several typical multicast usage scenarios on an IPv4 network and usage of multicast routing protocols and features in these scenarios, which helps you with multicast service configuration.

In a live network, you can customize a configuration scheme based on the network situation and service requirements. This section describes the deployment of only basic multicast services.

Prior to deploying IPv4 multicast services, ensure that IPv4 unicast routes are available on the network.
Typical multicast service scenarios include multicast services in a PIM domain, multicast services between PIM-SM domains, multicast services between autonomous systems (ASs), and multicast services in a VPN.
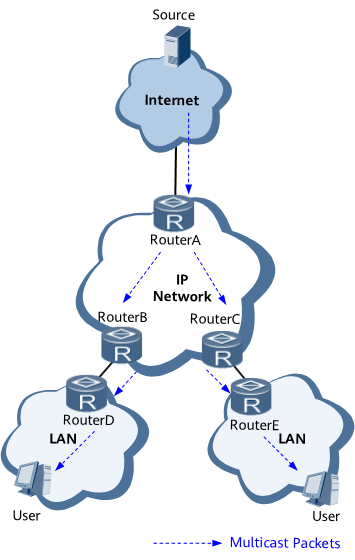
On a small-scale LAN, all the devices and hosts are in the same PIM-SM domain. Figure 1 and Table 1 show the multicast service deployment in such a scenario.
Table 1 Multicast protocols to be deployed Multicast Protocol
Location
Purpose
PIM-SM
(Mandatory)
All interfaces of routers in a PIM domain, including:All interfaces of Device A
All interfaces of Device B
All interfaces of Device C
For detailed configurations, see PIM Configuration.
PIM is used to send multicast data received from a multicast source server to Device B and Device C. These devices have attached users that require the multicast data.
IGMP
(Mandatory)
User-side interfaces of multicast routers
User-side interfaces of Device B
User-side interfaces of Device C
For detailed configurations, see IGMP Configuration.
IGMP enables user hosts to join or leave multicast groups by sending IGMP messages and enables Device B and Device C to manage multicast group members.
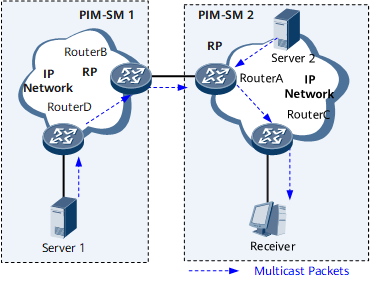
To simplify the management of multicast resources (multicast groups, multicast sources, and multicast members), network operators divide a network into different PIM-SM domains and isolate multicast resources in each PIM-SM domain. To implement multicast data exchanging between PIM-SM domains, Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) is required. Figure 2 and Table 2 show multicast service deployment in such a scenario.

MSDP is not required if Protocol Independent Multicast-Source-Specific Multicast (PIM-SSM) is used.
Table 2 Multicast protocols to be deployed Multicast Protocol
Location
Purpose
PIM-SM
(Mandatory)
All interfaces of routers in each PIM-SM domain, including:All interfaces of Device A
All interfaces of Device B
All interfaces of Device C
All interfaces of Device D
For detailed configurations, see PIM Configuration.
PIM-SM is used to send multicast data received from multicast source servers Server 1 and Server 2 to Device C that has attached users that require the multicast data. In PIM-SM, receiver hosts join multicast groups and multicast data is sent to the receiver hosts by a Rendezvous Point (RP).
IGMP
(Mandatory)
User-side interfaces of multicast routers in each PIM-SM domain
User-side interfaces of Device C
For detailed configurations, see IGMP Configuration.
IGMP enables user hosts to join or leave multicast groups by sending IGMP messages and enables Device C to manage multicast group members.
MSDP
(Mandatory)
RPs in PIM-SM domains that need to exchange multicast data, including:
Device A
Device B
For detailed configurations, see MSDP Configuration.
MSDP implements the exchange of multicast source information between PIM-SM1 and PIM-SM2.
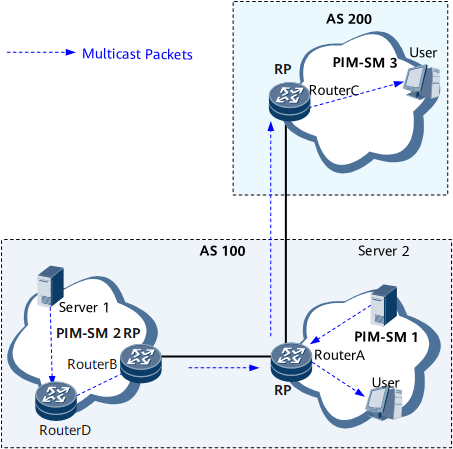
- PIM depends on a unicast routing table and therefore the multicast forwarding path is the same as the unicast forwarding path. Network operators may expect multicast traffic to flow between different ASs along a dedicated multicast forwarding path independent of the unicast forwarding path. Multicast Border Gateway Protocol (MBGP) is required in this situation. It generates a multicast routing table independent of the unicast routing table and forwards multicast data based on the multicast routing table. Figure 3 and Table 3 show multicast service deployment in such a scenario.

Prior to deploying MBGP to implement multicast data transmission between ASs, enable inter-AS BGP.
Table 3 Multicast protocols to be deployed Multicast Protocol
Location
Purpose
PIM-SM
(Mandatory)
All interfaces of routers in each PIM-SM domain, including:All interfaces of Device A
All interfaces of Device B
All interfaces of Device C
All interfaces of Device D
For detailed configurations, see PIM Configuration.
PIM-SM is used to send multicast data received from multicast source servers Server 1 and Server 2 to Device A and Device C that have attached users requiring the multicast data. In PIM-SM, receiver hosts join multicast groups and multicast data is sent to the receiver hosts by a Rendezvous Point (RP).
IGMP
(Mandatory)
User-side interfaces of multicast routers in each PIM-SM domain
User-side interfaces of Device A
User-side interfaces of Device C
For detailed configurations, see IGMP Configuration.
IGMP enables user hosts to join or leave multicast groups by sending IGMP messages and enables Device A and Device C to manage multicast group members.
MBGP
(Mandatory)
Edge multicast routers in ASs that need to exchange multicast data, including:
Device A
Device C
For detailed configurations, see MBGP Configuration.
MBGP is used when multicast source servers Server 1 and Server 2 are in a different AS from receiver hosts. In this situation, multicast data is transmitted based on a dedicated multicast routing table independent of the unicast routing table.
MSDP
(Mandatory)
RPs in PIM-SM domains that need to exchange multicast data, including:
Device A
Device B
Device C
For detailed configurations, see MSDP Configuration.
MSDP implements the exchange of multicast source information between PIM-SM1 and PIM-SM2, PIM-SM1 and PIM-SM3.
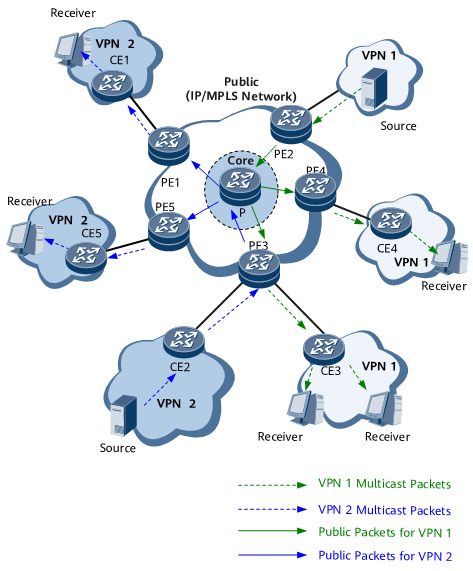
If network operators expect to provide multicast services on an MPLS BGP/VPN architecture, the multicast service deployment should be extensible and the backbone network should support the multicast capability. Figure 4 and Table 4 show multicast service deployment in such a scenario.
Table 4 Multicast protocols to be deployed Multicast Protocol
Location
Purpose
PIM-SM
(Mandatory)
All interfaces on multicast routers
For detailed configurations, see PIM Configuration.
PIM is used to send multicast data received from a multicast source to CEs that have attached users requiring the multicast data.
IPv4 multicast VPN
(Mandatory)
Edge multicast routers on an IP/MPLS network:
PE1
PE2
PE3
PE4
PE5
For detailed configurations, see Rosen MVPN Configuration.
IPv4 multicast VPN implements multicast data transmission from local sites in VPN1 and VPN2 to remote sites in VPN1 and VPN2 over the public IP/MPLS network. It isolates multicast data in VPN1 and VPN2.
IGMP
(Mandatory)
User-side interfaces of multicast routers
User-side interfaces of CE1
User-side interfaces of CE3
User-side interfaces of CE4
User-side interfaces of CE5
For detailed configurations, see IGMP Configuration.
IGMP enables user hosts to join or leave multicast groups by sending IGMP messages and enables CE1, CE3, CE4, and CE5 to manage multicast group members.