Example for Configuring Basic PIM-DM Functions
This section provides an example for configuring basic PIM-DM functions, so that a user can receive data from any multicast source in a normal unicast routing AS.
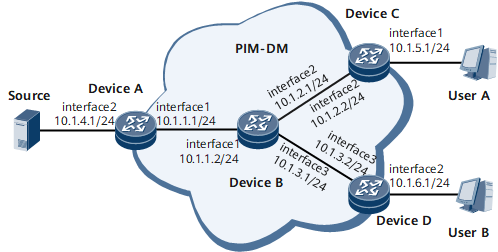
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, multicast is required on the router, so that client hosts on the network can receive VoD traffic in multicast mode. PIM-DM applies to small-scale networks with densely distributed multicast group members.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Enable multicast on all routers.
Enable PIM-DM on all router interfaces.
Configure IGMP on all router interfaces connected to hosts.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Multicast group (G) address: 225.1.1.1/24
Multicast source (S) address: 10.1.4.100/24
Version number of IGMP running between the router and client hosts: 2
Procedure
- Assign an IP address to each router interface and configure a unicast routing protocol. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable multicast and PIM-DM on all interfaces.
# Configure Device A.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceA [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceA] multicast routing-enable [*DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim dm [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim dm [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*DeviceA] commit
The configurations of Device B, Device C, and Device D are similar to the configuration of Device A. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure IGMP on all router interfaces connected to hosts.
# Configure Device C.
[~DeviceC] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [~DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] igmp enable [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] igmp static-group 225.1.1.1 [*DeviceC-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceC] commit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] igmp enable [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] igmp static-group 225.1.1.1 [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*DeviceD] commit
- Verify the configuration.
# After completing the configurations, run the display pim interface command. The command output shows the PIM-DM configurations and operating status on interfaces of the router. The following example uses the command output about PIM-DM configurations on Device B.
<DeviceB> display pim interface VPN-Instance: public net Interface State NbrCnt HelloInt DR-Pri DR-Address GE0/1/0 up 1 30 1 10.1.1.2 (local) GE0/1/1 up 1 30 1 10.1.2.2 GE0/1/2 up 1 30 1 10.1.3.2
# Run the display pim neighbor command. The command output shows the PIM-DM neighbor relationship between routers. The following example uses the command output about PIM-DM neighbor relationships on Device B.
<DeviceB> display pim neighbor VPN-Instance: public net Total Number of Neighbors = 3 Neighbor Interface Uptime Expires Dr-Priority BFD-Session 10.1.1.1 GE0/1/0 04:34:59 00:01:18 1 N 10.1.2.2 GE0/1/1 04:29:56 00:01:23 1 N 10.1.3.2 GE0/1/2 04:24:22 00:01:28 1 N
# Run the display pim routing-table command. The command output shows the router PIM routing table. In a scenario where both User A and User B need to receive messages from multicast group G (225.1.1.1/24), when the multicast source S (10.1.4.100/24) sends data to G, a multicast forwarding tree is formed through flooding. (S, G) entries are created on each router along the path. When User A and User B join G, an (*, G) entry is created on Device C and Device D. The following example uses the command output on these devices.
<DeviceA> display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (10.1.4.100, 225.1.1.1) Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: LOC ACT UpTime: 00:08:18 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/1, Refresh time: 00:08:18 Upstream neighbor: NULL RPF prime neighbor: NULL Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:08:18, Expires: never <DeviceB> display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 0 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (10.1.4.100, 225.1.1.1) Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: ACT UpTime: 00:10:25 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/0, Refresh time: 00:10:25 Upstream neighbor: 10.1.1.1 RPF prime neighbor: 10.1.1.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 2 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:06:48, Expires: never 2: GigabitEthernet0/1/2 Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:05:53, Expires: never <DeviceC> display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (*, 225.1.1.1) Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: WC UpTime: 00:11:47 Upstream interface: NULL, Refresh time: 00:11:47 Upstream neighbor: NULL RPF prime neighbor: NULL Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Protocol: static, UpTime: 00:11:47, Expires: never (10.1.4.100, 225.1.1.1) Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: ACT UpTime: 00:17:13 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/1, Refresh time: 00:17:13 Upstream neighbor: 10.1.2.1 RPF prime neighbor: 10.1.2.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:11:47, Expires: - <DeviceD> display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (*, 225.1.1.1) Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: WC UpTime: 00:05:26 Upstream interface: NULL, Refresh time: 00:05:26 Upstream neighbor: NULL RPF prime neighbor: NULL Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Protocol: static, UpTime: 00:05:26, Expires: never (10.1.4.100, 225.1.1.1) Protocol: pim-dm, Flag: ACT UpTime: 00:09:58 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/2, Refresh time: 00:09:58 Upstream neighbor: 10.1.3.1 RPF prime neighbor: 10.1.3.1 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/1 Protocol: pim-dm, UpTime: 00:05:26, Expires: -
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim dm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.4.1 255.255.255.0 pim dm # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.4.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim dm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.1 255.255.255.0 pim dm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.1 255.255.255.0 pim dm # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.5.1 255.255.255.0 pim dm igmp enable igmp static-group 225.1.1.1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.2.2 255.255.255.0 pim dm # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.2.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.5.0 0.0.0.255 # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.6.1 255.255.255.0 pim dm igmp enable igmp static-group 225.1.1.1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.3.2 255.255.255.0 pim dm # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.3.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.6.0 0.0.0.255 # return