Example for Configuring PIM-SM Intra-domain Multicast
This section provides an example for configuring basic PIM-SM functions for a PIM-SM domain.
Networking Requirements
On the ISP network shown in Figure 1, multicast services are deployed. The network is deployed with an IGP and is connected to the Internet. The unicast routing routes work normally. It is required that hosts receive VoD information in multicast mode.

Interfaces 1, 2, 3, and 4 in this example represent GE 0/1/0, GE 0/1/8, GE 0/1/16, and GE 0/1/1, respectively.
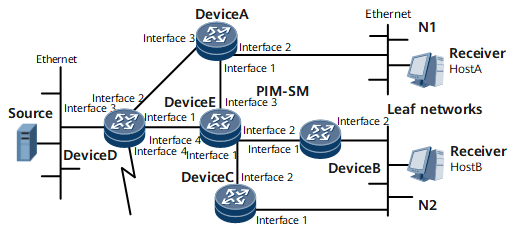
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
Device A |
GE 0/1/0 |
192.168.9.1/24 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/16 |
192.168.1.1/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
10.110.1.1/24 |
|
DeviceB |
GE 0/1/0 |
192.168.2.1/24 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
10.110.2.1/24 |
|
DeviceC |
GE 0/1/8 |
192.168.3.1/24 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/0 |
10.110.2.2/24 |
|
DeviceD |
GE 0/1/0 |
192.168.4.2/24 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
192.168.1.2/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/1 |
10.110.4.1/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/16 |
10.110.5.1/24 |
|
DeviceE |
GE 0/1/0 |
192.168.3.2/24 |
GigabitEthernet0/1/8 |
192.168.2.2/24 |
|
GigabitEthernet0/1/16 |
192.168.9.2/24 |
|
GE 0/1/1 |
192.168.4.1/24 |
Precautions
When configuring PIM-SM intra-domain multicast, note the following precautions:
PIM-SM must be enabled before IGMP is enabled.
To use a static Rendezvous Point (RP), configure the same RP address on all routers.
Use the Protocol Independent Multicast - Source-specific Multicast (PIM-SSM) service when the users need to receive data from a specified multicast source. Ensure that all routers share the same SSM group address range.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure an IP address for each router interface and configure a unicast routing protocol.
Enable multicast routing on all multicast routers.
Enable PIM-SM on all router interfaces.
Enable IGMP on router interfaces that directly connect to hosts.
Configure RPs. An RP is a rendezvous point tree (RPT)'s root node on a PIM-SM network. Configuring a router that has more multicast branches as an RP is recommended. For example, configure Device E as an RP on the network shown in Figure 1.
(Optional) Configure BootStrap router (BSR) boundaries on interfaces connected to the Internet. Bootstrap messages cannot pass through the BSR boundaries, and each BSR serves only the local PIM-SM domain.
(Optional) Set the same SSM group address range on all routers, so a multicast router provides services only for the multicast groups in the SSM group address range.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
Multicast group address
Multicast source address
SSM group address range
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each router interface and a unicast routing protocol. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Enable multicast routing on each router and PIM-SM on each router interface.
# Configure Device E. Repeat this step for Device A, Device B, Device C, and Device D. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceE] multicast routing-enable [*DeviceE] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/0 [*DeviceE-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] pim sm [*DeviceE-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*DeviceE] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceE-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] pim sm [*DeviceE-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit [*DeviceE] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/16 [*DeviceE-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] pim sm [*DeviceE-GigabitEthernet0/1/16] quit [*DeviceE] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [*DeviceE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim sm [*DeviceE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~DeviceE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
- Enable IGMP on interfaces that directly connect to hosts.
# Configure Device A. Repeat this step for Device B, Device C, Device D, and Device E. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/8 [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] igmp enable [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] igmp version 3 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/8] quit
- Configure RPs.

You can configure both a static RP and a BSR RP, or only one of them. When both a static RP and a BSR RP are configured, the BSR RP is used by default. To use the static RP, specify preferred in the static-rp rp-address command.
The following shows how to configure both a static RP and a BSR RP, with the BSR RP being preferred and the static RP being the backup.
# Configure a BSR RP. Perform the following configurations on one or several routers in the PIM-SM domain. For example, on Device E, set the range of groups severed by the RP and addresses of Candidate-BootStrap Routers (C-BSRs) and Candidate-Rendezvous Points (C-RPs).
[~DeviceE] acl number 2000 [*DeviceE-acl4-basic-2000] rule permit source 225.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceE-acl4-basic-2000] quit [*DeviceE] pim [*DeviceE-pim] c-bsr GigabitEthernet 0/1/8 [*DeviceE-pim] c-rp GigabitEthernet 0/1/8 group-policy 2000 priority 0 [*DeviceE-pim] commit [~DeviceE-pim] quit
# Configure a static RP on Device E. Repeat this step for Device A, Device B, Device C, and Device D. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceE] pim [*DeviceE-pim] static-rp 192.168.4.1 [*DeviceE-pim] commit [~DeviceE-pim] quit
- (Optional) Configure a BSR boundary on the interface that connects Device D to the Internet.
[~DeviceD] interface GigabitEthernet 0/1/1 [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] pim bsr-boundary [*DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~DeviceD-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
- (Optional) Set the SSM group address range to 232.1.1.0/24 on all routers.
# Configure Device E. Repeat this step for Device A, Device B, Device C, and Device D. For configuration details, see Configuration Files in this section.
[~DeviceE] acl number 2001 [*DeviceE-acl4-basic-2001] rule permit source 232.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 [*DeviceE-acl4-basic-2001] quit [*DeviceE] pim [*DeviceE-pim] ssm-policy 2001 [*DeviceE-pim] commit [~DeviceE-pim] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Run the display pim interface command to view information about PIM interfaces on each router. The following example uses the command output on Device E.
<DeviceE> display pim interface VPN-Instance: public net Interface State NbrCnt HelloInt DR-Pri DR-Address GigabitEthernet0/1/0 up 1 30 1 192.168.3.2(local) GigabitEthernet0/1/8 up 1 30 1 192.168.2.2(local) GigabitEthernet0/1/16 up 1 30 1 192.168.9.2(local) GigabitEthernet0/1/1 up 1 30 1 192.168.4.2
# Run the display pim bsr-info command to check information about the BSRs on each router. The following examples use the command outputs on Device D and Device E (C-BSR information is also displayed on Device E).
<DeviceD> display pim bsr-info VPN-Instance: public net Elected AdminScope BSR Count: 0 Elected BSR Address: 192.168.2.2 Priority: 0 Hash mask length: 30 State: Accept Preferred Scope: Not scoped Uptime: 02:08:57 Expires: 00:01:15 C-RP Count: 1 <DeviceE> display pim bsr-info VPN-Instance: public net Elected AdminScope BSR Count: 0 Elected BSR Address: 192.168.2.2 Priority: 0 Hash mask length: 30 State: Elected Scope: Not scoped Uptime: 02:25:03 Next BSR message scheduled at: 00:00:57 C-RP Count: 1 Candidate AdminScope BSR Count: 0 Candidate BSR Address: 192.168.2.2 Priority: 0 Hash mask length: 30 State: Elected Scope: Not scoped Wait to be BSR: 0
# Run the display pim rp-info command to view information about the RPs on the routers. The following examples use the command outputs on Device D and Device E.
<DeviceD> display pim rp-info VPN-Instance: public net PIM-SM BSR RP Number:1 Group/MaskLen: 225.1.1.0/24 RP: 192.168.2.2 Priority: 0 Uptime: 02:27:17 Expires: 00:02:15 PIM SM static RP Number:1 Static RP: 192.168.4.1 <DeviceE> display pim rp-info VPN-Instance: public net PIM-SM BSR RP Number:1 Group/MaskLen: 225.1.1.0/24 RP: 192.168.2.2 (local) Priority: 0 Uptime: 02:27:27 Expires: 00:02:03 PIM SM static RP Number:1 Static RP: 192.168.4.1 (local)
# Run the display pim routing-table command to view the PIM routing table on each router. Host A needs to receive traffic sent to multicast group 225.1.1.1/24, and Host B needs to receive traffic that multicast source 10.110.5.100/24 sends to multicast group 232.1.1.1/24. The following examples use the command outputs on Device D and Device E.
<DeviceD> display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 0 (*, G) entry; 2 (S, G) entries (10.110.5.100, 225.1.1.1) RP: 192.168.2.2 Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: SPT LOC ACT UpTime: 00:57:20 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/16, Refresh time: 00:57:20 Upstream neighbor: NULL RPF prime neighbor: 10.110.5.100 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/8 Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:57:20, Expires: 00:03:02 (10.110.5.100, 232.1.1.1) Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag: LOC UpTime: 00:31:21 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/16, Refresh time: 00:31:21 Upstream neighbor: NULL RPF prime neighbor: 10.110.5.100 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Protocol: pim-ssm, UpTime: 00:31:21, Expires: 00:03:09 <DeviceE> display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 (*, G) entry; 1 (S, G) entry (*, 225.1.1.1) RP: 192.168.2.2 (local) Protocol: pim-sm, Flag: WC UpTime: 00:21:40 Upstream interface: register, Refresh time: 00:21:40 Upstream neighbor: 192.168.4.2 RPF prime neighbor: 192.168.4.2 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/16 Protocol: pim-sm, UpTime: 00:21:40, Expires: 00:02:43 (10.110.5.100, 232.1.1.1) Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag: UpTime: 00:18:44 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/1, Refresh time: 00:18:44 Upstream neighbor: 192.168.4.2 RPF prime neighbor: 192.168.4.2 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/0 Protocol: pim-ssm, UpTime: 00:18:44, Expires: 00:02:43
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # multicast routing-enable # acl number 2001 rule 5 permit source 232.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0001.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.9.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.110.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable igmp version 3 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # pim ssm-policy 2001 static-rp 192.168.4.1 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # multicast routing-enable # acl number 2001 rule 5 permit source 232.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0002.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 10.110.2.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable igmp version 3 isis enable 1 # pim ssm-policy 2001 static-rp 192.168.4.1 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # multicast routing-enable # acl number 2001 rule 5 permit source 232.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0003.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 10.110.2.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable igmp version 3 isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.3.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # pim ssm-policy 2001 static-rp 192.168.4.1 # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # multicast routing-enable # acl number 2001 rule 5 permit source 232.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0004.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.4.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 10.110.5.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.110.4.1 255.255.255.0 pim bsr-boundary pim sm isis enable 1 # pim ssm-policy 2001 static-rp 192.168.4.1 # return
Device E configuration file
# sysname DeviceE # multicast routing-enable # acl number 2000 rule 5 permit source 225.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # acl number 2001 rule 5 permit source 232.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 # isis 1 network-entity 10.0000.0000.0005.00 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.3.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.9.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.4.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm isis enable 1 # pim ssm-policy 2001 static-rp 192.168.4.1 c-bsr GigabitEthernet0/1/8 c-rp GigabitEthernet0/1/8 group-policy 2000 # return