Example for Configuring PIM over GRE
This section provides an example for configuring PIM over GRE.
Networking Requirements
On the multicast network shown in Figure 1, a GRE tunnel is established between Device A and Device B to carry multicast traffic.
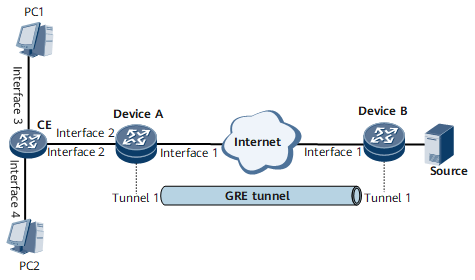
Interfaces 1, 2, 3, and 4 in this example represent GE 0/1/1, GE 0/1/2, GE 0/1/3, and GE 0/1/4, respectively.
Device Name |
Interface |
IP Address |
|---|---|---|
Device A |
GE 0/1/1 |
10.1.1.1/24 |
GE 0/1/2 |
10.1.6.1/24 |
|
Loopback 1 |
192.168.1.1/32 |
|
Tunnel 1 |
10.0.1.1/32 |
|
Device B |
GE 0/1/1 |
10.1.1.19/24 |
GE 0/1/2 |
10.1.5.1/24 |
|
Loopback 1 |
192.168.1.2/32 |
|
Tunnel 1 |
10.0.1.2/32 |
|
CE |
GE 0/1/2 |
10.1.6.2/24 |
GE 0/1/3 |
10.1.7.1/24 |
|
GE 0/1/4 |
10.1.8.1/24 |
Configuration Roadmap
Assign IP addresses to router interfaces and configure a unicast routing protocol. Run OSPF on the network between Device A and Device B, and set an OSPF process ID and area ID to 1 and 0.0.0.0, respectively. Run OSPF on the network where multicast users are connected to Device A. Set an OSPF process ID and area ID to 1 and 0.0.0.1, respectively.
Create a GRE tunnel between Device A and Device B so that data is transmitted between them through the GRE tunnel.
Enable the multicast function on all routers providing multicast services.
Enable PIM-SM on the interface connecting Device A to the user network, the interface connecting Device B to the multicast source, and all GRE tunnel interfaces. Enable PIM-SM on the interface connecting the CE to Device A, and enable PIM-SM and IGMP on the interfaces connecting the CE to multicast users.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
GRE tunnel's source and destination addresses on each end
Tunnel interfaces' IP addresses on each end
IP addresses of router interfaces
Procedure
- Assign IP addresses to router interfaces and configure a unicast routing protocol. For configuration details, see Configuration Files.
- Configure tunnel interfaces.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] interface loopback1 [*DeviceA-LoopBack1] binding tunnel gre [*DeviceA-LoopBack1] commit [~DeviceA-LoopBack1] quit [~DeviceA] interface tunnel 1 [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] tunnel-protocol gre [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] source 192.168.1.1 [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] destination 192.168.1.2 [*DeviceA-Tunnel1] quit [*DeviceA] commit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] interface loopback1 [*DeviceB-LoopBack1] binding tunnel gre [*DeviceB-LoopBack1] commit [~DeviceB-LoopBack1] quit [~DeviceB] interface tunnel 1 [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] tunnel-protocol gre [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] ip address 10.0.1.2 255.255.255.0 [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] source 192.168.1.2 [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] destination 192.168.1.1 [*DeviceB-Tunnel1] quit [*DeviceB] commit
After the configuration is complete, the tunnel interfaces go Up and can ping each other.
# The following example uses the command output on Device A.
[~DeviceA] ping -a 10.0.1.1 10.0.1.2 PING 10.0.1.2: 56 data bytes, press CTRL_C to break Reply from 10.0.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=1 ttl=255 time=24 ms Reply from 10.0.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=2 ttl=255 time=33 ms Reply from 10.0.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=3 ttl=255 time=48 ms Reply from 10.0.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=4 ttl=255 time=33 ms Reply from 10.0.1.2: bytes=56 Sequence=5 ttl=255 time=36 ms --- 10.0.1.2 ping statistics --- 5 packet(s) transmitted 5 packet(s) received 0.00% packet loss round-trip min/avg/max = 24/34/48 ms
- Configure static routes for the tunnel interfaces.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] ip route-static 10.1.5.0 255.255.255.0 Tunnel1 10.0.1.2 [*DeviceA] commit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] ip route-static 10.1.6.0 255.255.255.0 Tunnel1 10.0.1.1 [*DeviceB] ip route-static 10.1.7.0 255.255.255.0 Tunnel1 10.0.1.1 [*DeviceB] ip route-static 10.1.8.0 255.255.255.0 Tunnel1 10.0.1.1 [*DeviceB] commit
- Enable the multicast function on each router, and enable PIM-SM on router interfaces.
# Configure the CE. The configurations on Device A and Device B are similar to the configuration on the CE. For configuration details, see Configuration Files.
[~CE] multicast routing-enable [*CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] pim sm [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] pim sm [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit [*CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/4 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/4] pim sm [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/4] commit [~CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/4] quit
- # Enable IGMP on the interfaces connecting the CE to the PCs.
[~CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [~CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] igmp enable [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] igmp version 3 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] commit [~CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit [*CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/4 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/4] igmp enable [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/4] igmp version 3 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/4] commit [~CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/4] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# On the CE's GE 0/1/3, configure IGMP users to statically join the multicast group 232.1.1.1, with the multicast source set to 10.1.5.10.
[~CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/3 [~CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] igmp static-group 232.1.1.1 source 10.1.5.10 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] commit [~CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/3] quit
# View PIM routing information on Device A and Device B.
<DeviceA> display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 (S, G) entry (10.1.5.10, 232.1.1.1) Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag: UpTime: 00:01:14 Upstream interface: Tunnel1, Refresh time: 00:01:14 Upstream neighbor: 10.0.1.2 RPF prime neighbor: 10.0.1.2 Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: GigabitEthernet0/1/2 Protocol: pim-ssm, UpTime: 00:01:14, Expires: 00:03:16 <DeviceB> display pim routing-table VPN-Instance: public net Total 1 (S, G) entry (10.1.5.10, 232.1.1.1) Protocol: pim-ssm, Flag: LOC UpTime: 00:00:41 Upstream interface: GigabitEthernet0/1/2, Refresh time: 00:00:41 Upstream neighbor: NULL RPF prime neighbor: NULL Downstream interface(s) information: Total number of downstreams: 1 1: Tunnel1 Protocol: pim-ssm, UpTime: 00:00:41, Expires: 00:02:49
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.1 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.6.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface LoopBack1 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.255 binding tunnel gre # interface Tunnel1 ip address 10.0.1.1 255.255.255.0 tunnel-protocol gre source 192.168.1.1 destination 192.168.1.2 pim sm # interface NULL0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.1.1 0.0.0.0 area 0.0.0.1 network 10.1.6.0 0.0.0.255 # pim static-rp 10.0.1.1 # ip route-static 10.1.5.0 255.255.255.0 Tunnel1 10.0.1.2 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.1.19 255.255.255.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.5.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface LoopBack1 ip address 192.168.1.2 255.255.255.255 binding tunnel gre # interface Tunnel1 ip address 10.0.1.2 255.255.255.0 tunnel-protocol gre source 192.168.1.2 destination 192.168.1.1 pim sm # interface NULL0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 10.1.1.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.1.2 0.0.0.0 # pim static-rp 10.0.1.1 # ip route-static 10.1.6.0 255.255.255.0 Tunnel1 10.0.1.1 ip route-static 10.1.7.0 255.255.255.0 Tunnel1 10.0.1.1 ip route-static 10.1.8.0 255.255.255.0 Tunnel1 10.0.1.1 # return
CE configuration file
# sysname CE # multicast routing-enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.6.2 255.255.255.0 pim sm # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/3 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.7.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable igmp version 3 igmp static-group 232.1.1.1 source 10.1.5.10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/4 undo shutdown ip address 10.1.8.1 255.255.255.0 pim sm igmp enable igmp version 3 # interface NULL0 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.1 network 10.1.6.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.7.0 0.0.0.255 network 10.1.8.0 0.0.0.255 # pim static-rp 10.0.1.1 # ip route-static 0.0.0.0 0.0.0.0 10.1.6.1 # return