Multicast Source Cloning-based PIM FRR
Multicast source cloning-based PIM FRR protects multicast services against link and node failures by cloning multicast source Join messages, allowing you to manually specify reverse path forwarding (RPF) vector paths, cloning multicast traffic from sources, and transmitting cloned traffic along different RPF vector paths. This feature implements rapid traffic switchover if a link failure occurs, with the multicast traffic interruption being less than 50 ms, minimizing service loss.

Only NetEngine 8000 F1A supports multicast source cloning-based PIM FRR.
Background
PIM FRR replies on unicast route FRR or multicast static route FRR when establishing backup paths. Such implementation enables PIM FRR to improve link and node reliability, but cannot effectively provide an end-to-end node and link protection mechanism in complex networking scenarios.
Multicast source cloning-based PIM FRR can address this issue. This feature enables a device to send cloned multicast source Join messages to a multicast source and then sends cloned multicast traffic to multicast receivers along user-planned RPF vector paths. Normally, a multicast traffic receive device permits the traffic on the primary link and discards that on the backup link. However, the device starts to permit the traffic on the backup link immediately after detecting a primary link failure, minimizing service loss.

Multicast source cloning-based PIM FRR applies only to IPv4 PIM-SM, IPv4 PIM-SSM, and Rosen MVPN scenarios.
Implementation
Multicast source cloning-based PIM FRR implements dual feed and selective receiving of multicast traffic by cloning multicast source Join messages, allowing you to manually specify two paths to the same multicast source, cloning multicast traffic from the source, and transmitting cloned traffic along the user-planned paths.
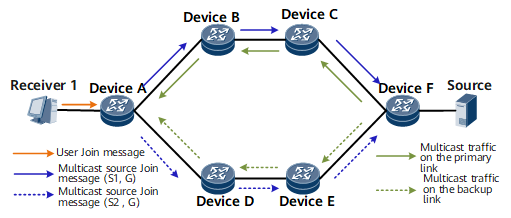
The implementation of multicast source cloning-based PIM FRR involves the following steps:
Cloning multicast source Join messages on the user-side device
The user-side device clones an (S, G) source Join message to (S1, G) and (S2, G) Join messages, and then sends the cloned messages to the multicast source.
Specifying RPF vector paths on the user-side device
After RPF vector paths to S1 and S2 are manually specified, the multicast source Join messages are forwarded along the specified paths. You can specify strict or loose explicit RPF vector paths. When specifying a strict explicit RPF vector path, you must use the IP address of the next hop (PIM neighbor) interface that is directly connected to the current node as the next hop address of the path. When specifying a loose explicit RPF vector path, you can use any interface IP address of the next hop as the next hop IP address of the path.
Cloning multicast traffic on the multicast source-side device
The multicast source-side device clones the traffic of the multicast group (S, G) to the traffic of the multicast groups (S1, G) and (S2, G) and sends the cloned traffic to the receiver along the specified RFP vector paths.
Usage Scenario
Multicast Source Cloning-based PIM FRR Through Strict Explicit Paths in PIM-SM/PIM-SSM Scenarios
On the network shown in the following figure, Device A is connected to a multicast user (Receiver 1). The user's terminal runs IGMPv3 for multicast services. The multicast source is connected to Device F.
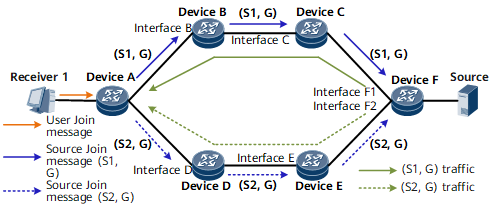
The implementation process is as follows:
- Enable Device A to clone (S, G) source Join messages to (S1, G) and (S2, G) source Join messages. Specify explicit paths to S1 and S2. Configure the path to S1 as the primary path and the path to S2 as the backup path. The path to S1 passes through Interface B, Interface C, and Interface F1. The path to S2 passes through Interface D, Interface E, and Interface F2. Both paths pass through Device F.
- Enable Device F to clone multicast traffic, so that Device F can replicate the traffic of the (S, G) group to the traffic of the (S1, G) and (S2, G) groups and forward the cloned traffic. In this manner, two copies of the same multicast traffic flow are forwarded along the primary and backup paths established for the multicast source Join messages.
- Device A permits the traffic on the primary path but discards that on the backup path. However, Device A starts to permit the traffic on the backup path immediately after detecting a primary path failure.
Multicast Source Cloning-based PIM FRR Through Loose Explicit Paths in PIM-SM/PIM-SSM Scenarios
On the network shown in the following figure, Device A is connected to a multicast user (Receiver 1). The user's terminal runs IGMPv3 for multicast services. The multicast source is connected to Device F.
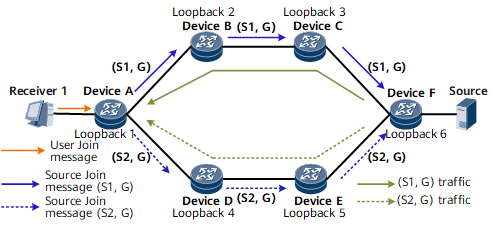
The implementation process is as follows:
- Enable Device A to clone (S, G) source Join messages to (S1, G) and (S2, G) source Join messages. Specify explicit paths to S1 and S2. Configure the path to S1 as the primary path and the path to S2 as the backup path. The path to S1 passes through Loopback 2, Loopback 3, and Loopback 6. The path to S2 passes through Loopback 4, Loopback 5, and Loopback 6. Both paths pass through Device F.
- Enable Device F to clone multicast traffic, so that Device F can replicate the traffic of the (S, G) group to the traffic of the (S1, G) and (S2, G) groups and forward the cloned traffic. In this manner, two copies of the same multicast traffic flow are forwarded along the primary and backup paths established for the multicast source Join messages.
- Device A permits the traffic on the primary path but discards that on the backup path. However, Device A starts to permit the traffic on the backup path immediately after detecting a primary path failure.
Multicast Source Cloning-based PIM FRR Through Strict Explicit Paths in Rosen MVPN Scenarios
On the network shown in the following figure, Device A is connected to a multicast user (Receiver 1). The user's terminal runs IGMPv3 for multicast services. The multicast source is connected to Device F. Device A, Device C, and Device E are PEs, and Device F is a CE. Both the user-side and multicast source-side networks are VPN networks.
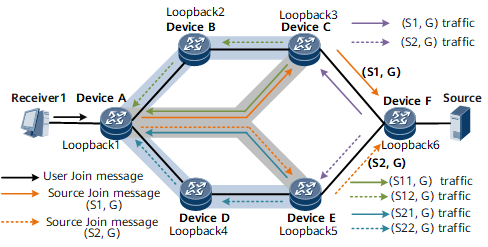
The implementation process is as follows:
- Enable Device A to clone (S, G) source Join messages to (S1, G) and (S2, G) source Join messages. Specify explicit paths to S1 and S2 on the VPN network. Configure the path to S1 as the primary path and the path to S2 as the backup path. The path to S1 passes through Loopback 3. The path to S2 passes through Loopback 5. After receiving an (S, G) source Join message, both Device C and Device D forward the message to Device F (multicast source-side device) on the VPN network.
- Device F forwards the multicast traffic to Device C and Device E. Configure Device C and Device E to clone multicast traffic. Device C clones the traffic of (S, G) to the traffic of (S11, G) and (S12, G) and forwards the cloned traffic. Device E clones the traffic of (S, G) to the traffic of (S21, G) and (S22, G) and forwards the cloned traffic. The traffic of (S11, G) and (S21, G) is sent to Device A along the public network strict explicit path specified on Device A. The traffic of (S12, G) and (S22, G) is sent to Device B and Device D and then forwarded to Device A along the public network strict explicit path specified on Device A. Four copies of the same multicast flow are sent to Device A
- Device A permits the traffic on the primary path but discards that on the backup path. However, Device A starts to permit the traffic on the backup path immediately after detecting a primary path failure.

Note the following when the feature is used in Rosen MVPN scenarios:
- If the multicast traffic on a VPN network is discontinuous and multicast source cloning-based PIM FRR is deployed on the public network, configure a policy on the root node to allow discontinuous traffic to be forwarded through the share-group on the public network.
- RPF vector paths can only be strict explicit paths.
- Multicast source cloning-based PIM FRR cannot protect the multicast traffic of share-groups.
- The IP address configured in the strict explicit path must be the IP address of the BGP peer.
Benefits
Multicast source cloning-based PIM FRR helps improve the reliability of multicast services and minimize service loss for users.