Rate Limiting on ND Miss Messages
Background
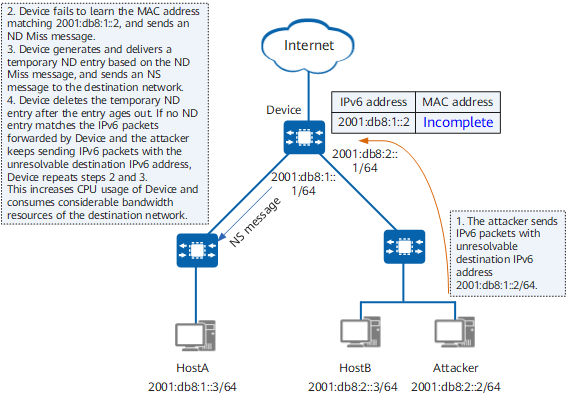
If a device is flooded with IPv6 packets that contain unresolvable destination IPv6 addresses, the device generates a large number of ND Miss messages. This is because the device has no ND entry that matches the next hop of the route. IPv6 packets, which trigger ND Miss messages, are sent to the CPU for processing. As a result, the device generates and delivers many temporary ND entries based on ND Miss messages, and sends a large number of NS messages to the destination network. This increases CPU usage of the device and consumes considerable bandwidth resources of the destination network. As shown in Figure 1, the attacker sends IPv6 packets with the unresolvable destination IPv6 address 2001:db8:1::2 /64 to the gateway (Device).
Related Concepts
- Limiting the rate of ND Miss messages globally: If a device is flooded with IPv6 packets that contain unresolvable destination IPv6 addresses, the number of ND Miss messages to be processed on the device is limited.
- Specified source IPv6 address-based rate limiting on ND Miss messages: limits the rate of ND Miss messages with a specified source IPv6 address.
- Any source IPv6 address-based rate limiting on ND Miss messages: limits the rate of ND Miss messages with any source IPv6 address.
- Limiting the rate of ND Miss messages on an interface: If an interface is flooded with IPv6 packets that contain unresolvable destination IPv6 addresses, the number of ND Miss messages to be processed on the interface is limited. The configuration on an interface does not affect IPv6 packet forwarding on other interfaces.
- Specified source IPv6 address-based rate limiting on ND Miss messages: limits the rate of ND Miss messages with a specified source IPv6 address on an interface.
Benefits
Rate limiting on ND Miss messages helps reduce CPU resource consumption by ND Miss messages, protecting other services.