NG MVPN Control Messages
The key mechanisms of NG MVPN are VPN multicast route transmission and public network tunnel establishment. The two mechanisms are implemented by transmitting BGP messages on the public network. These messages are NG MVPN control messages.
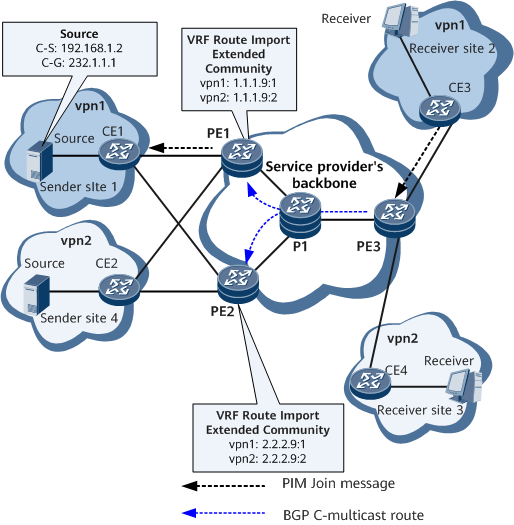
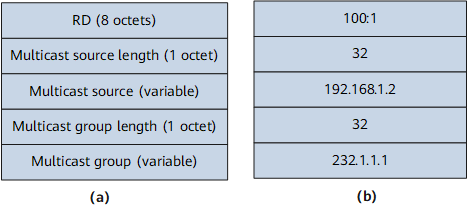
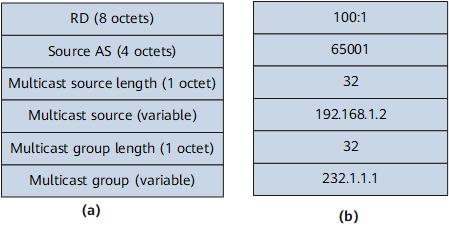
- The service provider's backbone network provides both unicast and multicast VPN services for vpn1. The AS number of the backbone network is 65001.
- The multicast source resides at Site1, accesses PE1 through CE1, and sends multicast traffic to multicast group 232.1.1.1.
- Multicast receivers reside at Site2 and Site3.
- The backbone network provides MVPN services for vpn1 over RSVP-TE or mLDP P2MP tunnels.
MVPN NLRI
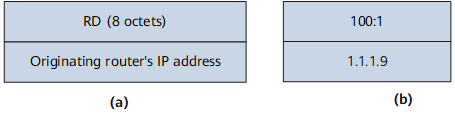
In NG MVPN, MVPN routing information is carried in the network layer reachability information (NLRI) field of BGP Update messages. The NLRI containing MVPN routing information is called MVPN NLRI. The SAFI of the MVPN NLRI is 5. Figure 2 shows the MVPN NLRI format.
Field |
Description |
|---|---|
Route type |
Type of an MVPN route. Seven types of MVPN routes are available. For more information, see Table 2. |
Length |
Length of the Route type specific field in the MVPN NLRI. |
Route type specific |
MVPN routing information. The value of this field depends on the Route type field. For details, see Table 2. |
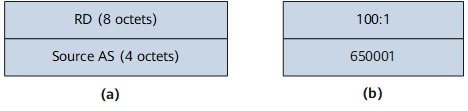
Table 2 describes the types and functions of MVPN routes. Type 1-5 routes are called MVPN A-D routes. These routes are used for MVPN membership autodiscovery and P2MP tunnel establishment. Type 6 and Type 7 routes are called C-multicast routes (C is short for Customer. C-multicast routes refer to multicast routes from the private network). These routes are used for VPN multicast group joining and VPN multicast traffic forwarding.
Type |
Function |
Route Type Specific Field Format |
Parameter Description |
|---|---|---|---|
1: Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route |
Used for MVPN membership autodiscovery in intra-AS scenarios. MVPN-capable PEs use Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D routes to advertise and learn intra-AS MVPN membership information. |
|
|
2: Inter-AS I-PMSI A-D route |
Used for MVPN membership autodiscovery in inter-AS scenarios. MVPN-capable ASBRs use Inter-AS I-PMSI A-D routes to advertise and learn inter-AS MVPN membership information. |
|
|
3: S-PMSI A-D route |
Used by a sender PE to initiate a selective P-tunnel for a particular (C-S, C-G). |
|
|
4: Leaf A-D route |
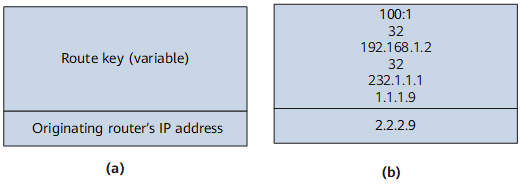
Used to respond to a Type 1 Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route with the flags field in the PMSI attribute being 1 or a Type 3 S-PMSI A-D route. If a receiver PE has a request for establishing an S-PMSI tunnel, it sends a Leaf A-D route to help the sender PE collect tunnel information. |
NOTE:
The Route key is set to the MVPN NLRI of the S-PMSI A-D route received. |
|
5: Source Active A-D route |
Used by PEs to learn the identity of active VPN multicast sources. |
|
|
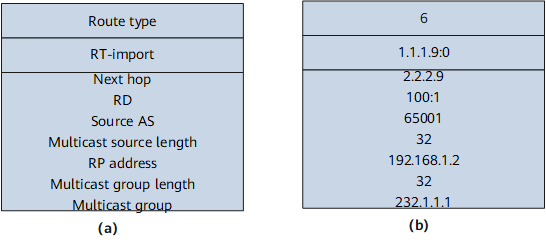
6: Shared Tree Join route |
Used in (*, G) scenarios. A Shared Tree Join route is originated when a receiver PE receives a (C-*, C-G) PIM Join message. A receiver PE sends the Shared Tree Join route to sender PEs with which it has established BGP peer relationships.
NOTE:
The (*, G) PIM-SM join initiated by a VPN is called a (C-*, C-G) PIM join. |
NOTE:
Shared Tree Join routes and Source Tree Join routes have the same NLRI format. The multicast source address is the RP address for (C-*, C-G) joins. |
|
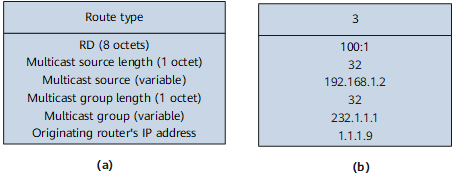
7: Source Tree Join route |
Used in (S, G) scenarios. A Source Tree Join route is originated when a receiver PE receives a (C-S, C-G) PIM Join message. A receiver PE sends the Source Tree Join route to sender PEs with which it has established BGP peer relationships.
NOTE:
The (S, G) PIM-SSM join initiated by a VPN is called a (C-S, C-G) PIM join. |
|
Route Type Specific field format
PMSI Tunnel attribute
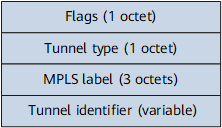
The PMSI Tunnel attribute carries P-tunnel information used for P-tunnel establishment. The following figure shows the PMSI Tunnel attribute format.
Format |
Field |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Flags |
Flags bits. Currently, only one flag indicating whether leaf information is required is specified:
|
Tunnel type |
Tunnel type, which can be:
|
|
MPLS label |
MPLS labels are used for VPN tunnel multiplexing. Currently, tunnel multiplexing is not supported. |
|
Tunnel identifier |
Tunnel identifier. Its value depends on the value set in the Tunnel type field:
|
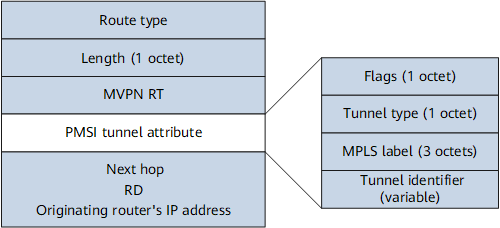
On an NG MVPN, the sender PE sets up the P-tunnel, and therefore is responsible for originating the PMSI Tunnel attribute. The PMSI Tunnel attribute can be attached to intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route, inter-AS I-PMSI A-D routes, or S-PMSI A-D routes and sent to receiver PEs. Figure 10 is an example that shows the format of an Intra-AS I-PMSI A-D route carrying the PMSI Tunnel attribute.