NG MVPN Routing
- The multicast source can be registered by the directly connected multicast source DR to the RP, or receive the Join message sent by the receiver DR, to send multicast data to the receiver. For details about multicast source registration, see Understanding PIM.
- A multicast user joins a multicast group through IGMP/MLD, and then the multicast device to which the multicast group belongs sends a Join message to the multicast source through PIM. In this manner, the multicast user can receive multicast data. For details about how multicast users join multicast groups on VPNs, see Understanding IGMP and Understanding MLD.
On an NG MVPN, after a BGP peer relationship is established between PEs in the BGP MVPN address family, the BGP MVPN extended community attribute can be used to carry the VPN multicast route (C-multicast route) to transmit the join/leave information of multicast users.
MVPN Extended Community Attributes
Source AS Extended Community: carried in VPNv4 routes advertised by PEs. This attribute is an AS extended community attribute and is mainly used in inter-AS scenarios.
VRF Route Import Extended Community: carried in VPNv4 routes advertised by sender PEs to receiver PEs. When a receiver PE sends a BGP C-multicast route to a sender PE, the receiver PE attaches this attribute to the route. In a scenario in which many sender PEs exist, this attribute helps a sender PE that receives the BGP C-multicast route to determine whether to process the route and to which VPN instance routing table the BGP C-multicast route should be added.
The value of the VRF Route Import Extended Community is in the format of "Administrator field value:Local Administrator field value". The Administrator field is set to the local MVPN ID, whereas the Local Administrator field is set to the local VPN instance ID of the sender PE.
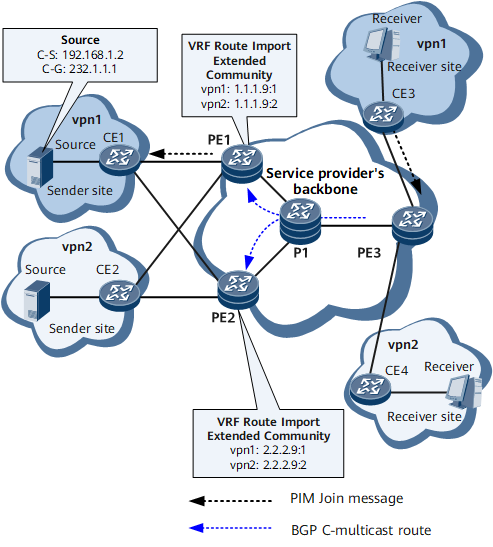
On the network shown in Figure 1, PE1 and PE2 are both sender PEs, and PE3 is a receiver PE. PE1 and PE2 connect to both vpn1 and vpn2. On PE1, the VRF Route Import Extended Community is 1.1.1.9:1 for vpn1 and 1.1.1.9:2 for vpn2; on PE2, the VRF Route Import Extended Community is 2.2.2.9:1 for vpn1 and 2.2.2.9:2 for vpn2.
After PE1 and PE2 both establish BGP MVPN peer relationships with PE3, PE1 and PE2 both send to PE3 a VPNv4 route destined for the multicast source 192.168.1.2. The VRF Route Import Extended Community carried in the VPNv4 route sent by PE1 is 1.1.1.9:1 and that carried in the VPNv4 route sent by PE2 is 2.2.2.9:1. After PE3 receives the two VPNv4 routes, PE3 adds the preferred route (VPNv4 route sent by PE1 in this example) to the vpn1 routing table and stores the VRF Route Import Extended Community value carried in the preferred route locally for later BGP C-multicast route generation.
Upon receipt of a PIM Join message from CE3, PE3 generates a BGP C-multicast route with the RT-import attribute and sends this route to PE1 and PE2. The RT-import attribute value of this route is the same as the locally stored VRF Route Import Extended Community value, 1.1.1.9:1.- Upon receipt of the BGP C-multicast route, PE1 checks the RT-import attribute of this route. After PE1 finds that the Administrator field value is 1.1.1.9, which is the same as its local MVPN ID, PE1 accepts this route and adds it to the vpn1 routing table based on the Local Administrator field value (1).
- Upon receipt of the BGP C-multicast route, PE2 also checks the RT-import attribute of this route. After PE2 finds that the Administrator field value is 1.1.1.9, which is different from its local MVPN ID 2.2.2.9, PE2 drops this route.
This section describes the process of transmitting VPN multicast routes through the (S, G) and (*, G) Join/Leave processes of multicast members.
- PIM (S, G) Join/Prune
- Multicast receiver joins/leaves a multicast group in PIM (S, G) modes.
- PIM (*, G) Join/Prune
- Multicast receivers join/leave a multicast group in PIM (*, G) mode.