NG MVPN Typical Deployment Scenarios on the Public Network
An NG MVPN uses a PMSI tunnel established on the public network BGP/MPLS VPN network to transmit multicast traffic. The NG MVPN deployment mode varies according to the public network architecture. According to whether the public network crosses ASs and whether the tunnel is segmented, there are the following scenarios:
- Intra-AS non-segmented NG MVPN: The public network contains only one AS, and only one MPLS protocol is deployed.
- Inter-AS non-segmented NG MVPN: The public network contains multiple ASs, and only one MPLS protocol is deployed in the ASs.
- Intra-AS segmented NG MVPN: The public network contains only one AS but multiple areas, and different MPLS protocols are deployed in adjacent areas.
Intra-AS Non-segmented NG MVPN
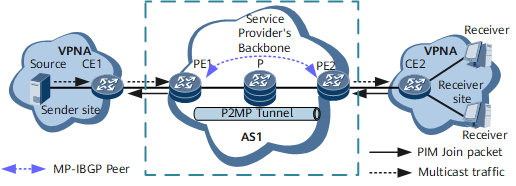
The public network that the multicast service traverses contains only one AS, and only one MPLS protocol is used between PE1 on the multicast source side and PE2 on the multicast user side, as shown in Figure 1.
The NG MVPN is established as follows:
- Establish an I-BGP peer relationship between PEs.
- Deploy MVPN on the PEs, so that the PEs in the same MVPN can automatically discover each other and use BGP to transmit BGP C-multicast routes.
- Configure a P2MP tunnel and use BGP to transmit BGP A-D routes to each other, so that PE1 and PE2 can establish a PMSI tunnel based on the P2MP tunnel to transmit multicast traffic.
Inter-AS Non-segmented NG MVPN
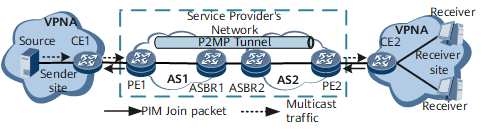
The public network that the multicast service traverses contains multiple ASs, and only one MPLS protocol is used between PE1 on the multicast source side and PE2 on the multicast user side, as shown in Figure 2.
This scenario supports three VPN modes: Option A, Option B, and Option C. In Option A mode, ASBRs use each other as CEs. The establishment process is similar to that in the intra-AS non-segment scenario.
In Option B mode, the NG MVPN is established as follows:
- Establish an IBGP peer relationship between a PE and an ASBR in the same AS. Establish an EBGP peer relationship between ASBRs in different ASs.
- Deploy MVPN on the PEs, so that the PEs in the same MVPN can automatically discover each other and use BGP to transmit BGP C-multicast routes through ASBRs.
- Configure a P2MP tunnel and use BGP to transmit BGP A-D routes to each other through ASBRs, so that PE1 and PE2 can establish a PMSI tunnel based on the P2MP tunnel to transmit multicast traffic.
In Option C mode, the NG MVPN is established as follows:
- Establish an IBGP peer relationship between a PE and an ASBR in the same AS. Establish an EBGP peer relationship between ASBRs in different ASs. Establish an MP-EBGP peer relationship between PE1 and PE2.
- Deploy MVPN on the PEs, so that the PEs in the same MVPN can automatically discover each other and use BGP to directly transmit BGP C-multicast routes over ASBRs.
- Configure a P2MP tunnel and use BGP to directly transmit BGP A-D routes to each other over ASBRs, so that PE1 and PE2 can establish a PMSI tunnel based on the P2MP tunnel to transmit multicast traffic.
Intra-AS Segmented NG MVPN
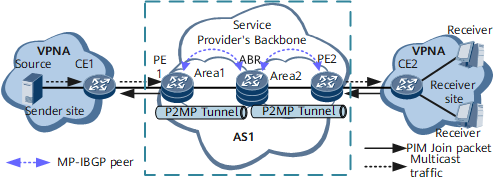
The public network that the multicast service traverses contains only one AS, and MPLS areas of different types are used between PE1 on the multicast source side and PE2 on the multicast user side, as shown in Figure 3.
The NG MVPN is established as follows:
- Establish an I-BGP peer relationship between the PE and ABR.
- Deploy MVPN on the PEs, so that the PEs in the same MVPN can automatically discover each other and use BGP to transmit BGP C-multicast routes.
- Configure a P2MP tunnel and use BGP to transmit BGP A-D routes to each other so that PE1 and the ABR can establish a PMSI tunnel based on the P2MP tunnel. The ABR and PE2 establish a PMSI tunnel based on the P2MP tunnel. The two tunnels are stitched on the ABR to carry the multicast traffic transmitted from PE1 to PE2.