Multicast Traffic Transmission Using NG MVPN
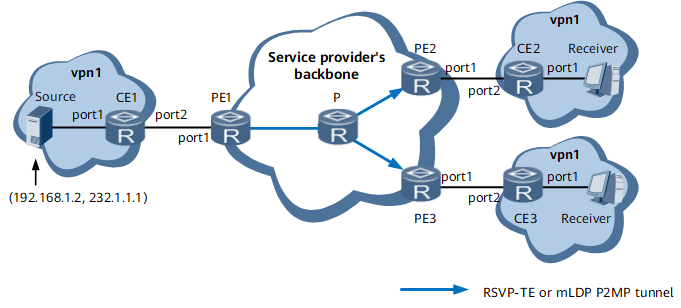
After a public-network PMSI tunnel is established and multicast users join a multicast group, carriers can provide MVPN services over BGP/MPLS IP VPN.

On a leaf PE, a P2MP tunnel can be mapped to only one VPN instance. Therefore, the import VPN target of each VPN instance must be unique on a leaf PE. If multiple VPN instances with the same import VPN target exist on a leaf PE, only the downstream node of one VPN instance can receive multicast traffic.
Table 1 describes how an IP multicast packet is transmitted using NG MVPN.
Step |
Device |
Action |
Multicast Forwarding Table |
|---|---|---|---|
1 |
CE1 |
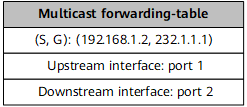
After receiving an IP multicast packet from the multicast source, CE1 searches its multicast forwarding table and forwards the packet to PE1. |
|
2 |
PE1 |
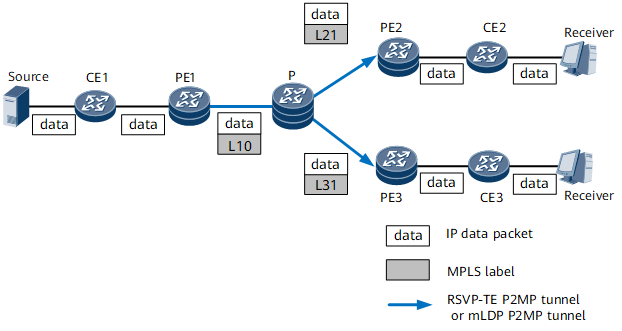
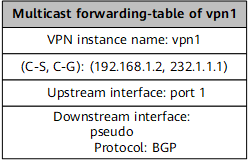
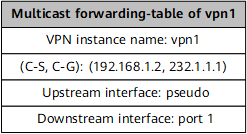
After receiving the IP multicast packet, PE1 searches its VPN instance multicast forwarding table for the corresponding (C-S, C-G) entry, adds an MPLS label to the packet, and sends the packet over a P2MP tunnel to the P. |
|
3 |
P |
After receiving the MPLS packet, the P removes the MPLS label from the packet and replicates the packet. Then, the P adds a new MPLS label to one copy and sends the copy to PE2, and adds another MPLS label to another copy and sends the copy to PE3. |
- |
4 |
PE2/PE3 |
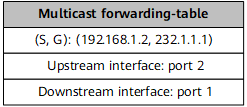
After receiving the MPLS packet, PE2/PE3 removes the MPLS label, searches its VPN instance multicast forwarding table for the corresponding (C-S, C-G) entry, and forwards the IP multicast packet to CE2/CE3. |
|
5 |
CE2/CE3 |
After receiving the packet, CE2/CE3 searches its multicast forwarding table and forwards the packet to all receivers in the multicast group. |
|