Example for Configuring an OSPFv3 NSSA
This section provides an example for configuring an OSPFv3 not-so-stubby area (NSSA).
Networking Requirements
An excessive number of entries in a routing table waste network resources and cause high CPU usage. To address the problem, configure a non-backbone area on the border of an AS as an NSSA. NSSAs can import AS external routes and advertise them within the entire AS, without learning external routes from other areas in the AS, which reduces bandwidth and storage resource consumption on the router.
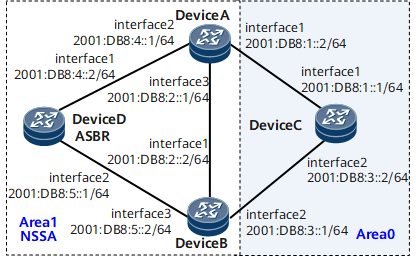
In Figure 1, OSPFv3 runs on all routers, and the entire AS is partitioned into two areas. router A and router B function as ABRs to forward inter-area routes; router D functions as an ASBR and imports the external static route 2001:DB8:6::1/128. To import AS external routes but reduce the number of LSAs to be advertised to area 1 without compromising route reachability, configure area 1 as an NSSA.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
- Configure basic OSPFv3 functions on all routers to ensure that they can communicate with each other using OSPFv3.
- Configure area 1 as an NSSA.
- Configure Device C to import the static route 2001:DB8:7::1/128.
- Configure Device D to import the static route 2001:DB8:6::1/128.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
- Router ID 1.1.1.1 of Device A, OSPFv3 process ID 1, network segment 2001:DB8:1::0/64 of area 0, and network segments 2001:DB8:2::0/64 and 2001:DB8:4::0/64 of area 1
- Router ID 2.2.2.2 of Device B, OSPFv3 process ID 1, network segment 2001:DB8:3::0/64 of area 0, and network segments 2001:DB8:2::0/64 and 2001:DB8:5::0/64 of area 1
- Router ID 3.3.3.3 of Device C, OSPFv3 process ID 1, and network segments 2001:DB8:1::0/64 and 2001:DB8:3::0/64 of area 0
- Router ID 4.4.4.4 of Device D, OSPFv3 process ID 1, and network segments 2001:DB8:4::0/64 and 2001:DB8:5::0/64 of area 1
Procedure
- Configure an IP address for each interface.
Configure an IP address to each interface according to Figure 1. For details about the configuration, see Configuration Files in this section.
- Configure basic OSPFv3 functions.
For detailed operations, see Example for Configuring Basic OSPFv3 Functions.
- Configure area 1 as an NSSA.
# Configure Device A.
[~DeviceA] ospfv3 [*DeviceA-ospfv3-1] area 1 [*DeviceA-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.1] nssa [*DeviceA-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.1] commit [~DeviceA-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit [~DeviceA-ospfv3-1] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] ospfv3 [*DeviceB-ospfv3-1] area 1 [*DeviceB-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.1] nssa [*DeviceB-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.1] commit [~DeviceB-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit [~DeviceB-ospfv3-1] quit
# Configure Device D.
[~DeviceD] ospfv3 [*DeviceD-ospfv3-1] area 1 [*DeviceD-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.1] nssa [*DeviceD-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.1] commit [~DeviceD-ospfv3-1-area-0.0.0.1] quit [~DeviceD-ospfv3-1] quit
- Configure Device C to import the static route 2001:DB8:7::1/128.
[~DeviceC] ipv6 route-static 2001:DB8:7::1 128 NULL0 [*DeviceC] ospfv3 [*DeviceC-ospfv3-1] import-route static [*DeviceC-ospfv3-1] commit [~DeviceC-ospfv3-1] quit
- Configure Device D to import the static route 2001:DB8:6::1/128.
[~DeviceD] ipv6 route-static 2001:DB8:6::1 128 NULL0 [*DeviceD] ospfv3 [*DeviceD-ospfv3-1] import-route static [*DeviceD-ospfv3-1] commit [~DeviceD-ospfv3-1] quit
- Verify the configuration.
# Display the OSPFv3 routing tables on Device C and Device D.
[~DeviceC] display ospfv3 routing Codes : E2 - Type 2 External, E1 - Type 1 External, IA - Inter-Area, N - NSSA Flags : A - Added to URT6 OSPFv3 Process (1) Destination Metric Next-hop 2001:DB8:1::/64 1 directly connected, Vlanif18, Flags : A IA 2001:DB8:2::/64 2 via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE21:1200, Vlanif18, Flags : A IA 2001:DB8:2::/64 2 via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE41:1200, Vlanif14, Flags : A 2001:DB8:3::/64 1 directly connected, Vlanif14, Flags : A IA 2001:DB8:4::/64 2 via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE21:1200, Vlanif18, Flags : A IA 2001:DB8:5::/64 2 via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE41:1200, Vlanif14, Flags : A E2 2001:DB8:6::1/128 1 via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE41:1200, Vlanif14, Flags : A [~DeviceD] display ospfv3 routing Codes : E2 - Type 2 External, E1 - Type 1 External, IA - Inter-Area, N - NSSA Flags : A - Added to URT6 OSPFv3 Process (1) Destination Metric Next-hop E2 ::/0 1 N via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE21:1200, Vlanif13, Flags : A E2 ::/0 1 N via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE41:1200, Vlanif11, Flags : A IA 2001:DB8:1::/64 2 via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE21:1200, Vlanif13, Flags : A 2001:DB8:2::/64 2 via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE21:1200, Vlanif13, Flags : A 2001:DB8:2::/64 2 via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE41:1200, Vlanif11, Flags : A IA 2001:DB8:3::/64 2 via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE41:1200, Vlanif11, Flags : A 2001:DB8:4::/64 1 directly connected, Vlanif13, Flags : A 2001:DB8:5::/64 1 directly connected, Vlanif11, Flags : A
The command output shows that Device C has imported an AS external route (2001:DB8:6::1/128) and that the router that advertises this route is DeviceB. In addition, the NSSA does not learn the 2001:DB8:7::1/128 route from area 0.
# Display routing information of the NSSA on routers. In the following example, the command output on Device A is used.
[~DeviceA] display ospfv3 routing nssa-routes Codes : E2 - Type 2 External, E1 - Type 1 External, IA - Inter-Area, N - NSSA Flags : A - Added to URT6 OSPFv3 Process (1) Destination Metric Next-hop E2 2001:DB8:6::1/128 1 N via FE80::3A6D:7CFF:FE11:1200, Vlanif13, Flags : A
# Display NSSA LSA information on routers. In the following example, the command output on Device A is used.
[~DeviceA] display ospfv3 lsdb nssa OSPFv3 Router with ID (1.1.1.1) (Process 1) NSSA-external-LSA (Area 0.0.0.1) LS Age: 391 LS Type: NSSA-external-LSA Link State ID: 0.0.0.0 Originating Router: 1.1.1.1 LS Seq Number: 0x80000001 Retransmit Count: 0 Checksum: 0x6ebe Length: 32 Flags: (E|-|T) Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path) Metric: 1 Prefix: ::/0 Prefix Options: 0 (-|-|-|-|-) Tag: 0 LS Age: 378 LS Type: NSSA-external-LSA Link State ID: 0.0.0.0 Originating Router: 2.2.2.2 LS Seq Number: 0x80000001 Retransmit Count: 0 Checksum: 0x50d8 Length: 32 Flags: (E|-|T) Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path) Metric: 1 Prefix: ::/0 Prefix Options: 0 (-|-|-|-|-) Tag: 0 LS Age: 429 LS Type: NSSA-external-LSA Link State ID: 0.0.0.1 Originating Router: 4.4.4.4 LS Seq Number: 0x80000001 Retransmit Count: 0 Checksum: 0xb7e0 Length: 48 Flags: (E|-|T) Metric Type: 2 (Larger than any link state path) Metric: 1 Prefix: 2001:DB8:6::1/128 Prefix Options: 8 (-|P|-|-|-)
Configuration Files
Device A configuration file
# sysname DeviceA # vlan batch 13 16 18 # ospfv3 1 router-id 1.1.1.1 area 0.0.0.0 area 0.0.0.1 nssa # interface Vlanif13 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:4::1/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.1 # interface Vlanif16 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::1/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.1 # interface Vlanif18 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1::2/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown port default vlan 18 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown port default vlan 13 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown port default vlan 16 # return
Device B configuration file
# sysname DeviceB # vlan batch 11 14 16 # ospfv3 1 router-id 2.2.2.2 area 0.0.0.0 area 0.0.0.1 nssa # interface Vlanif11 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:5::2/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.1 # interface Vlanif14 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:3::1/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface Vlanif16 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:2::2/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown port default vlan 16 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown port default vlan 14 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/16 undo shutdown port default vlan 11 # return
Device C configuration file
# sysname DeviceC # vlan batch 14 18 # ospfv3 1 router-id 3.3.3.3 import-route static area 0.0.0.0 # interface Vlanif14 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:3::2/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface Vlanif18 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:1::1/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.0 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown port default vlan 18 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown port default vlan 14 # ipv6 route-static 2001:DB8:7::1 128 NULL0 # return
Device D configuration file
# sysname DeviceD # vlan batch 11 13 # ospfv3 1 router-id 4.4.4.4 import-route static area 0.0.0.1 nssa # interface Vlanif11 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:5::1/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.1 # interface Vlanif13 ipv6 enable ipv6 address 2001:DB8:4::2/64 ospfv3 1 area 0.0.0.1 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/0 undo shutdown port default vlan 13 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/8 undo shutdown port default vlan 11 # ipv6 route-static 2001:DB8:6::1 128 NULL0 # return