Configuring PBB-EVPN
This section describes how to configure provider backbone bridge Ethernet VPN (PBB-EVPN).
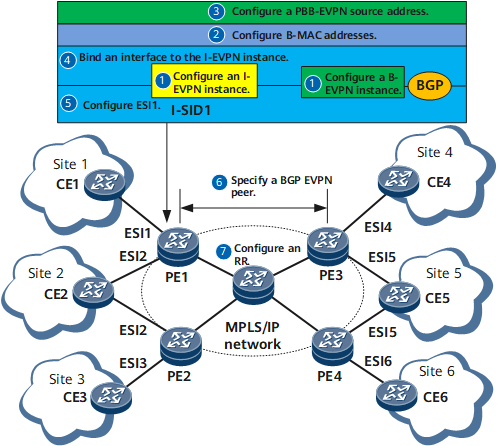
Usage Scenario
Configure EVPN instances on each PE.
Configure B-MAC addresses for EVPN instances.
Bind an AC interface to each I-EVPN instance.
Configure PBB-EVPN source addresses to identify PEs in EVPN networking.
Configure an Ethernet segment identifier (ESI) for each PE interface connecting to a CE. PE interfaces connecting to the same CE have the same ESI.
Configure EVPN Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) peer relationships between PEs on the backbone network to allow MAC addresses to be advertised over routes.
Configure a route reflector (RR) to decrease the number of BGP EVPN peer relationships required.
Configure LDP Auto FRR if LDP tunnels are used.
Configure MPLS TE FRR or MPLS TE Auto FRR if TE tunnels are used.
Pre-configuration Tasks
Before configuring PBB-EVPN, complete the following tasks:
Configure an IGP on the backbone network to ensure IP connectivity.
Configure MPLS LDP tunnels on the backbone network.
(Optional) Configure primary and backup MPLS TE tunnels and a tunnel policy for tunnel selection if you want to use MPLS TE tunnels.
Configure Layer 2 connections between CEs and PEs.
- Configuring a PBB-EVPN Instance
- Provider edges (PEs) use provider backbone bridge Ethernet VPN (PBB-EVPN) instances to interconnect private networks with the public network.
- Binding an Interface to an I-EVPN Instance
- After an interface is bound to an I-EVPN instance, the interface becomes a part of the provider backbone bridge (PBB-EVPN). Packets entering the interface will then be forwarded based on PBB-EVPN instance traffic forwarding entries.
- Configuring PBB-EVPN B-MAC Addresses
- Provider backbone bridge (PBB) precedes customer MAC (C-MAC) addresses with backbone MAC (B-MAC) addresses in packets to completely separate the user network from the carrier network.
- Configuring a PBB-EVPN Source Address
- A provider backbone bridge Ethernet VPN (PBB-EVPN) source address uniquely identifies a provider edge (PE) in PBB-EVPN networking.
- Configuring an ESI
- The same Ethernet segment identifier (ESI) must be configured for provider edge (PE) interfaces connecting to the same customer edge (CE).
- Configuring a BGP EVPN Peer Relationship
- After two provider edges (PEs) establish a Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) Ethernet VPN (EVPN) peer relationship, they can exchange EVPN routes.
- (Optional) Configuring a PBB-EVPN RR
- Configuring a provider backbone bridge Ethernet VPN (PBB-EVPN) route reflector (RR) helps reduce the number of required BGP EVPN peer relationships, and therefore conserves network resources.
- Verifying the PBB-EVPN Configuration
- After configuring provider backbone bridge Ethernet VPN (PBB-EVPN), check the operating status and information about PBB-EVPN functions.