Example for Configuring a Dot1q VLAN Tag Termination Sub-Interface to Support DHCP Relay
This example shows how to configure the dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface to support Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP) relay so that the DHCP relay agent transmits DHCP request packets from DHCP clients to a DHCP server. This configuration enables the clients to dynamically obtain IP addresses from the DHCP server.
Networking Requirements
If the DHCP client and DHCP server belong to different sub-nets, you need to deploy a DHCP relay agent to forward DHCP request packets from the client to the server so that the client can dynamically obtain IP addresses from the DHCP server.
If a DHCP client connects to a DHCP relay agent through a VLAN tag termination sub-interface, you need to configure the sub-interface to support DHCP relay on the DHCP relay agent. Without the configuration, the DHCP relay agent considers the received user packets with VLAN tags to be invalid. As a result, the DHCP client cannot dynamically obtain IP addresses from a DHCP server.
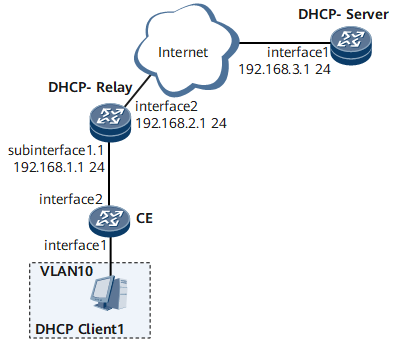
On the network shown in Figure 1, a DHCP client and a DHCP server belong to different network segments. The DHCP client is connected to a DHCP relay agent through a CE and then connected to the DHCP server through the DHCP relay agent. The packets sent from the CE to the DHCP relay agent carry one VLAN tag. On the DHCP relay agent, the dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface needs to be configured to support DHCP relay, ensuring that the DHCP client can dynamically obtain an IP address from the DHCP server.
Precautions
If the DHCP client sends broadcast packets, the interface that has DHCP relay enabled must support broadcast.
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Create a VLAN and configure the Layer 2 forwarding function on the CE so that the packets sent from the CE to the DHCP relay agent carry one VLAN tag.
Configure DHCP relay on the DHCP relay agent and configure the dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface to support DHCP relay so that the DHCP client and server can communicate using DHCP packets.
Enable basic DHCP functions and configure an address pool on the DHCP server so that the DHCP server can assign IP addresses correctly.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
- User VLAN ID
- Names of the interfaces that connect the CE and the DHCP client
- Names and IP addresses of the interfaces that connect the DHCP relay agent and the CE
- Names and IP addresses of the interfaces that connect the DHCP relay agent and the DHCP server
- IP address pool range of the DHCP server
Procedure
- Create a VLAN and configure the Layer 2 forwarding function on the CE.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname CE [*HUAWEI] commit [~CE] vlan 10 [*CE-vlan10] quit [*CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port link-type access [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port default vlan 10 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*CE] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] portswitch [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port link-type trunk [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 [*CE-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*CE] commit
- Configure DHCP relay on the DHCP relay agent, and configure the dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface to support DHCP relay.
# Enable DHCP.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DHCP-Relay [*HUAWEI] commit [~DHCP-Relay] dhcp enable [*DHCP-Relay] commit
# Assign an IP address to the network-side GE 0/1/2 on the DHCP relay agent.
[~DHCP-Relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ip address 192.168.2.1 24 [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*DHCP-Relay] commit
# Assign an IP address to the user-side GE 0/1/1.1 on the DHCP relay agent. This IP address must be on the same network segment as the IP address of the DHCP client.
[~DHCP-Relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*DHCP-Relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] ip address 192.168.1.1 24 [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] ip relay address 192.168.3.1 [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] dhcp select relay [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] commit
# Configure the dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface to support DHCP relay.
[*DHCP-Relay] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] control-vid 1 dot1q-termination [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] dot1q termination vid 10 [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] arp broadcast enable [*DHCP-Relay-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] quit [*DHCP-Relay] commit

If Option82 is not configured on the dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface on the DHCP relay agent, the sub-interface encapsulates only the smallest VLAN ID configured on it in DHCP packets and forwards the packets to DHCP clients.
In this example, if dot1q termination vid 10 and dot1q termination vid 20 are configured on the dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface, the sub-interface encapsulates VLAN 10 in the DHCP packets and forwards the packets to the DHCP client. In this case, DHCP clients in VLAN 20 cannot obtain IP addresses.
If Option82 is configured on the dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface on the DHCP relay agent, the sub-interface encapsulates the corresponding VLAN IDs in the DHCP packets and forwards the packets to DHCP clients.
- Configure a DHCP server.
The configuration details are not provided here.
- When configuring the DHCP server, ensure that an IP address pool is configured on the DHCP server so that the DHCP server can assign IP addresses to DHCP clients.
- It is recommended that the address pool lease be configured to improve IP address utilization.
- Verify the configuration.
After the configurations are complete, run the display dhcp relay address command on the DHCP relay agent to view the DHCP configuration on the interface that has DHCP relay enabled.
[~DHCP-Relay] display dhcp relay address all ** GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 DHCP Relay Address ** Dhcp Option Relay Agent IP Server IP * - 192.168.3.1
The DHCP client can obtain an IP address from the DHCP server through the DHCP relay agent.
Configuration Files
Configuration file of the DHCP relay agent
# sysname DHCP-Relay # dhcp enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1 encapsulation dot1q-termination dot1q termination vid 10 ip address 192.168.1.1 255.255.255.0 ip relay address 192.168.3.1 dhcp select relay arp broadcast enable # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.2.1 255.255.255.0 # return
Configuration file of the CE
# sysname CE # vlan batch 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/2 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type trunk port trunk allow-pass vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 portswitch undo shutdown port link-type access port default vlan 10 # return