Example for Configuring a Dot1q VLAN Tag Termination Sub-Interface in a VSI to Support IGMP Snooping
You can configure a dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface to support Internet Group Management Protocol (IGMP) on only the router's Layer 3 interfaces rather than Layer 2 interfaces.
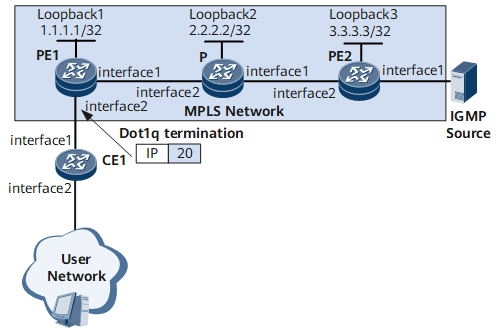
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, CE1 labels each multicast protocol packet received from hosts with one tag, and then sends the packets to PE1. After the dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface is configured on PE1, PE1 accesses the virtual private LAN service (VPLS) network. After terminating the pseudo wire (PW), PE2 joins the related multicast VLAN and accesses the multicast source.
PE2 functions as a Superstratum PE (SPE) device, and PE1 functions an Underlayer PE (UPE) device. When the hierarchical virtual private LAN service (HVPLS) is deployed, multicast packets are broadcast in a virtual switching instance (VSI) if PE1 and PE2 do not support IGMP snooping. This wastes network resources.
After IGMP snooping is configured, multicast packets are sent to only access devices of multicast receivers.
In a stable network, the PW on PE1 is configured as a static router port in the VSI. In this manner, receivers can steadily receive the multicast data.
To reduce the number of IGMP Query packets from the upstream router, you are advised to configure PE2 as a querier. This saves bandwidths.

Interfaces 1 and 2 in this example represent GE 0/1/1 and GE 0/1/2, respectively.
Device |
Interface |
IP Address |
PE1 |
GE0/1/2 |
- |
PE1 |
GE0/1/1 |
192.168.12.1/24 |
PE1 |
Loopback1 |
1.1.1.1/32 |
P |
GE0/1/0 |
192.168.12.2/24 |
P |
GE0/1/1 |
192.168.23.1/24 |
P |
Loopback2 |
2.2.2.2/32 |
PE2 |
GE0/1/2 |
192.168.23.2/24 |
PE2 |
GE0/1/1 |
- |
PE2 |
Loopback3 |
3.3.3.3/32 |
Configuration Roadmap
The configuration roadmap is as follows:
Configure the termination mode on PE1 to be the user termination mode.
Configure basic VPLS functions.
Enable global IGMP snooping and IGMP snooping for a VSI.
Bind a VSI to an AC interface on PE1 and PE2 respectively.
Configure a PW on PE1, P, and PE2, and PE1, P, and PE2 accesses the VPLS network in asymmetrical mode.
Configure static router ports and configure PE2 as a querier.
Data Preparation
To complete the configuration, you need the following data:
PE1's multicast VLAN ID: 20; PE2's multicast VLAN ID: 10
CE1's VLAN ID: 20
VSI name: v123; VSI ID: 123
PE1's Multiprotocol Label Switching (MPLS) LSR ID: 1.1.1.1; P's MPLS LSR ID: 2.2.2.2; PE2's MPLS LSR ID: 1.1.1.1
Procedure
- Configure dot1q termination on PE1.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE1 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2.1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] control-vid 1 dot1q-termination [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] dot1q termination vid 20 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] commit [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] quit
- Configure an IGP on the MPLS backbone network. In this example, OSPF is adopted to advertise routes. When configuring OSPF, advertise the 32-bit loopback interface addresses of PE1, P, and PE2.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] interface loopback 1 [*PE1-LoopBack1] ip address 1.1.1.1 32 [*PE1-LoopBack1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 192.168.12.1 24 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*PE1] ospf [*PE1-ospf-1] area 0 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE1-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*PE1-ospf-1] commit [~PE1-ospf-1] quit
# Configure P.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname P [*HUAWEI] commit [~P] interface loopback 2 [*P-LoopBack2] ip address 2.2.2.2 32 [*P-LoopBack2] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] ip address 192.168.12.2 24 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] undo shutdown [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] ip address 192.168.23.1 24 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*P] ospf [*P-ospf-1] area 0 [*P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 [*P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 [*P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 [*P-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*P-ospf-1] commit [~P-ospf-1] quit
# Configure PE2.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname PE2 [*HUAWEI] commit [~PE2] interface loopback 3 [*PE2-LoopBack3] ip address 3.3.3.3 32 [*PE2-LoopBack3] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] ip address 192.168.23.2 24 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] undo shutdown [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] quit [*PE2] ospf [*PE2-ospf-1] area 0 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 [*PE2-ospf-1-area-0.0.0.0] quit [*PE2-ospf-1] commit [~PE2-ospf-1] quit
- Configure basic MPLS functions and LDP.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 [*PE1] mpls [*PE1-mpls] quit [*PE1] mpls ldp [*PE1-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1]commit [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1]quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 [*PE2] mpls [*PE2-mpls] quit [*PE2] mpls ldp [*PE2-mpls-ldp] quit [*PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2] mpls ldp [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2]commit [~PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/2]quit
# Configure P.
[~P] mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 [*P] mpls [*P-mpls] quit [*P] mpls ldp [*P-mpls-ldp] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/0 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] mpls ldp [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/0] quit [*P] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] mpls ldp [*P-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] commit [~P-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit
- Enable MPLS L2VPN and configure a VSI.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls l2vpn [*PE1-l2vpn] quit [*PE1] vsi v123 static [*PE1-vsi-v123] pwsignal ldp [*PE1-vsi-v123-ldp] vsi-id 123 [*PE1-vsi-v123-ldp] peer 3.3.3.3 [*PE1-vsi-v123-ldp] quit [*PE1-vsi-v123] commit [~PE1-vsi-v123] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls l2vpn [*PE2-l2vpn] quit [*PE2] vsi v123 static [*PE2-vsi-v123] pwsignal ldp [*PE2-vsi-v123-ldp] vsi-id 123 [*PE2-vsi-v123-ldp] peer 1.1.1.1 upe [*PE2-vsi-v123-ldp] quit [*PE2-vsi-v123] commit [~PE2-vsi-v123] quit
- Configure remote MPLS LDP sessions for PE1 and PE2.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] mpls ldp remote-peer PE2 [*PE1-mpls-ldp-remote-PE2] remote-ip 3.3.3.3 [*PE1-mpls-ldp-remote-PE2] commit [~PE1-mpls-ldp-remote-PE2] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] mpls ldp remote-peer PE1 [*PE2-mpls-ldp-remote-PE1] remote-ip 1.1.1.1 [*PE2-mpls-ldp-remote-PE1] commit [~PE2-mpls-ldp-remote-PE1] quit
- Bind the interface on a PE.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] vlan 1 [*PE1-vlan1] quit [*PE1] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2.1 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] l2 binding vsi v123 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] commit [~PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/2.1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1.1 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] vlan-type dot1q 20 [*PE1-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] l2 binding vsi v123 [*PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] commit [~PE2-GigabitEthernet0/1/1.1] quit
- Enable IGMP snooping on PE1 and PE2 in the VSI.
# Configure PE1. The configurations of PE2 are similar to the configuration of PE1 and are not mentioned here.
[~PE1] igmp-snooping enable [*PE1] vsi v123 [*PE1-vsi-v123] igmp-snooping enable [*PE1-vsi-v123] igmp-snooping version 3 [*PE1-vsi-v123] commit [~PE1-vsi-v123] quit
- Configure the PW on PE1 as a static router port, and configure the querier on PE2. The default values are used for the querier.
# Configure PE1.
[~PE1] vsi v123 [*PE1-vsi-v123] igmp-snooping static-router-port remote-peer 3.3.3.3 [*PE1-vsi-v123] commit [~PE1-vsi-v123] quit [*PE1] quit
# Configure PE2.
[~PE2] igmp-snooping send-query enable [*PE2] vsi v123 [*PE2-vsi-v123] igmp-snooping querier enable [*PE2-vsi-v123] commit [~PE2-vsi-v123] quit [*PE2] quit
- Verify the configuration.
Run the display dot1q information termination interface command on PE1, and you can view information about the configured dot1q VLAN tag termination sub-interface.
The following example uses the command output on PE1.
[~PE1] display dot1q information termination interface gigabitethernet 0/1/2.1 GigabitEthernet 0/1/2.1 Total QinQ Num: 1 dot1q termination vid 20 Total vlan-group Num: 0 encapsulation dot1q-termination
Run the display mpls ldp session command, and you view that MPLS LDP sessions on PE1, P, and PE2 are in the Operational state.
Take the display of PE1 as an example.
[~PE1] display mpls ldp session LDP Session(s) in Public Network Codes: LAM(Label Advertisement Mode), SsnAge Unit(DDDD:HH:MM) An asterisk (*) before a session means the session is being deleted. -------------------------------------------------------------------------- PeerID Status LAM SsnRole SsnAge KASent/Rcv -------------------------------------------------------------------------- 2.2.2.2:0 Operational DU Passive 0000:00:04 19/19 3.3.3.3:0 Operational DU Passive 0000:00:03 17/16 -------------------------------------------------------------------------- TOTAL: 2 Session(s) Found.
Run the display igmp-snooping querier vsi command on PE2, and you can check whether the configuration of the querier succeeds. If the Enable state is displayed in the following output, it indicates that the querier is enabled for VSI v123.
[~PE2] display igmp-snooping querier vsi v123 VSI Querier-state Querier --------------------------------------------------------------- v123 Enable 192.168.0.1Run the display igmp-snooping router-port vsi command on PE1, and you can check whether the configuration of the static router port succeeds. If STATIC is displayed as shown in the following output, it indicates that PW (1.1.1.1/123) is configured as a static router port.
[~PE1] display igmp-snooping router-port vsi v123 Port Name UpTime Expires Flags -------------------------------------------------------------------------- VSI v123, 1 router-port(s) PW(3.3.3.3/123) 00:09:16 -- STATICRun the display igmp-snooping port-info command on PE1, and you can view information about multicast VLAN tags and multicast groups on a specified dot1q interface.
[~PE1] display igmp-snooping port-info ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- Flag: S:Static D:Dynamic M:Ssm-mapping A:Active P:Protocol F:Fast-channel (Source, Group) Port Flag ------------------------------------------------------------------------------- VSI v123, 1 Entry(s) (1.1.1.1, 234.1.1.1) P-- GE0/1/2.1(PE:20) S-- 1 port(s) include -------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Configuration Files
PE1 configuration file
# sysname PE1 # vlan batch 20 # igmp-snooping enable igmp-snooping send-query enable # mpls lsr-id 1.1.1.1 # mpls # mpls l2vpn # vsi v123 static pwsignal ldp vsi-id 123 peer 3.3.3.3 igmp-snooping enable igmp-snooping version 3 igmp-snooping static-router-port remote-peer 3.3.3.3 # mpls ldp # mpls ldp remote-peer pe2 remote-ip 3.3.3.3 # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/2 undo shutdown # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/2.1 encapsulation dot1q-termination dot1q termination vid 20 l2 binding vsi v123 # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.12.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack1 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 1.1.1.1 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 # return
P configuration file
# sysname P # mpls lsr-id 2.2.2.2 # mpls # mpls ldp # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/0 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.12.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/1 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.23.1 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface LoopBack2 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 2.2.2.2 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.12.0 0.0.0.255 network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 # return
PE2 configuration file
# sysname PE2 # vlan batch 10 # igmp-snooping enable igmp-snooping send-query enable # mpls lsr-id 3.3.3.3 # mpls # mpls l2vpn # vsi 123 # vsi v123 static pwsignal ldp vsi-id 123 peer 1.1.1.1 igmp-snooping enable igmp-snooping version 3 igmp-snooping querier enable # mpls ldp # mpls ldp remote-peer pe1 remote-ip 1.1.1.1 # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/2 undo shutdown ip address 192.168.23.2 255.255.255.0 mpls mpls ldp # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/1 undo shutdown # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/1.1 vlan-type dot1q 20 l2 binding vsi v123 igmp-snooping static-router-port vsi v123 # interface LoopBack3 ip address 3.3.3.3 255.255.255.255 # ospf 1 area 0.0.0.0 network 3.3.3.3 0.0.0.0 network 192.168.23.0 0.0.0.255 # return
CE1 configuration file
# sysname CE1 # vlan batch 20 # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/2 portswitch port default vlan 20 # interface Gigabitethernet0/1/1 portswitch port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # return