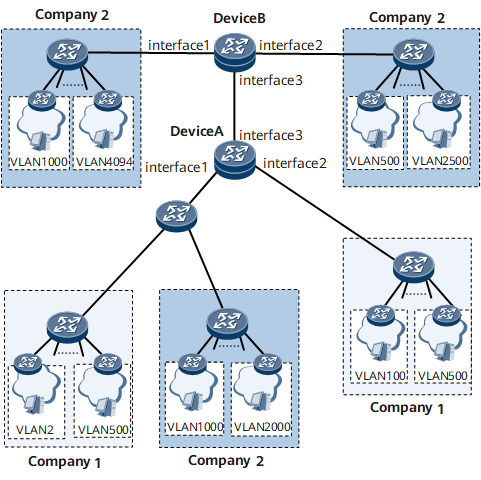
Example for Configuring Selective QinQ
This section provides an example for configuring selective QinQ. Selective QinQ is an extension to QinQ tunneling and is more flexible. When receiving packets, a selective QinQ-enabled interface adds different outer tags depending on the inner tags of the packets.
Networking Requirements
On the network shown in Figure 1, company 1 and company 2 each have multiple offices.
Selective QinQ is required on GE 0/1/1 of Device A on the carrier network so that the office networks of each company can communicate with each other, but the office networks of different companies cannot.
Procedure
- Create default outer VLAN IDs on Layer 2 interfaces.
# Configure Device A.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceA [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceA] vlan batch 10 20 [*DeviceA] commit
# Configure Device B.
<HUAWEI> system-view [~HUAWEI] sysname DeviceB [*HUAWEI] commit [~DeviceB] vlan batch 20 [*DeviceB] commit
- Configure selective QinQ on Layer 2 interfaces.
# Configure Device A.
[*DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port vlan-stacking vlan 2 to 500 stack-vlan 10 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port vlan-stacking vlan 1000 to 2000 stack-vlan 20 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/9 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] portswitch [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] port vlan-stacking vlan 100 to 500 stack-vlan 10 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] undo shutdown [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] quit
# Configure Device B.
[~DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/1 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] portswitch [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] port vlan-stacking vlan 1000 to 4094 stack-vlan 20 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] undo shutdown [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/1] quit [*DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/9 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] portswitch [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] port vlan-stacking vlan 501 to 2500 stack-vlan 20 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] undo shutdown [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] commit [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/9] quit
- Configure other interfaces.
# Configure GE 0/1/17 on Device A to forward packets carrying outer VLAN ID 20.
[*DeviceA] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/17 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/17] portswitch [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/17] port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/17] undo shutdown [*DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/17] commit [~DeviceA-GigabitEthernet0/1/17] quit
# Configure GE 0/1/17 on Device B to forward packets carrying outer VLAN ID 20.
[*DeviceB] interface gigabitethernet 0/1/17 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/17] portswitch [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/17] port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/17] undo shutdown [*DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/17] commit [~DeviceB-GigabitEthernet0/1/17] quit
- Verify the configuration.
Hosts in different offices but the same VLAN can ping each other in company 1.
Hosts in different offices but the same VLAN can ping each other in company 2.
Hosts in company 1 and hosts in company 2 cannot ping each other.
Configuration Files
-
# sysname DeviceA # vlan batch 10 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown portswitch port vlan-stacking vlan 2 to 500 stack-vlan 10 port vlan-stacking vlan 1000 to 2000 stack-vlan 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/9 undo shutdown portswitch port vlan-stacking vlan 100 to 500 stack-vlan 10 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/17 undo shutdown portswitch port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # return
-
# sysname DeviceB # vlan batch 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/1 undo shutdown portswitch port vlan-stacking vlan 1000 to 4094 stack-vlan 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/9 undo shutdown portswitch port vlan-stacking vlan 500 to 2500 stack-vlan 20 # interface GigabitEthernet0/1/17 undo shutdown portswitch port trunk allow-pass vlan 20 # return