Configuring Manually Triggered Dual-Device ND Hot Backup
This section describes how to enable dual-device ND hot backup to back up ND entries between devices. This allows fast service switching if a network node or link fails, enhancing service reliability.
Prerequisites
Before configuring manually triggered dual-device ND hot backup, ensure that the same ND configuration has been performed on the master and backup devices. Otherwise, downstream traffic may be interrupted after a master/backup switchover.
Context
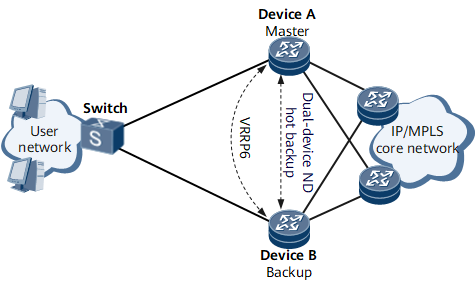
On the network shown in Figure 1, users access Device A and Device B over a switch. A Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol for IPv6 (VRRP6) group is configured on Device A and Device B, with Device A as the master device and Device B as the backup device.
In normal circumstances, Device A forwards both upstream and downstream traffic. If Device A or the link between Device A and the switch fails, a master/backup VRRP6 switchover is triggered and Device B becomes the master device. Then, Device B needs to advertise a network segment route to network-side devices so that downstream traffic is directed from the network side to Device B. However, if Device B has not learned ND entries from user-side devices, the downstream traffic is interrupted. Device B can properly forward downstream traffic only after it learns ND entries from user-side devices.
If ND entries are not synchronized from Device A to Device B and a master/backup switchover occurs, downstream traffic may be interrupted because Device B fails to learn ND entries from users-side devices in time. To resolve this problem, deploy dual-device ND hot backup on Device A and Device B.
Perform the following steps on the devices that back up ND entries from each other: