Basic Concepts
Basic Concepts
Ethernet devices can be configured as nodes with different roles on an RRPP ring. RRPP ring nodes exchange and process RRPP packets to detect the status of the ring network and communicate any topology changes throughout the network. The master node on the ring blocks or unblocks the secondary port depending on the status of the ring network. If a device or link on the ring network fails, the backup link immediately starts to eliminate loops.
RRPP ring
An RRPP ring consists of interconnected devices configured with the same control VLAN. An RRPP ring has a major ring and subring. Sub-ring protocol packets are transmitted through the major ring as data packets; major ring protocol packets are transmitted only within the major ring.
Control VLAN
The control VLAN is a concept relative to the data VLAN. In an RRPP ring, a control VLAN is used to transmit only RRPP packets, whereas a data VLAN is used to transmit data packets.
Node type
Master node: The master node determines how to handle topology changes. Each RRPP ring must have only one master node. Any device on the Ethernet ring can serve as the master node.
Transit node: On an RRPP ring, all nodes except the master node are transit nodes. Each transit node monitors the status of its directly connected RRPP link and notifies the master node of any changes in link status.
Edge node and assistant edge node: A device can serve as an edge node or assistant edge node on the sub-ring, and as a transit node on the major ring. On an RRPP sub-ring, either of the two nodes crossed with the major ring can be specified as an edge node, and if one of the two nodes crossed with the major ring is specified as an edge node, the other node is the assistant edge node. Each sub-ring must have only one edge node and one assistant edge node.
RRPP Packets
Table1 shows the RRPP protocol packet types.
Packet Type |
Description |
|---|---|
HEALTH(HELLO) |
A packet sent from the master node to detect whether a loop exists on a network. |
LINK-DOWN |
A packet sent from a transit, edge, or assistant edge node to notify the master node that a port has gone Down and the loop has disappeared. |
COMMON-FLUSH-FDB |
A packet sent from the master node to instruct the transit, edge, or assistant edge node to update its MAC address forwarding table, ARP entries, and ND entries. |
COMPLETE-FLUSH-FDB |
A packet sent from the master node to instruct the transit, edge, or assistant edge node to update its MAC address forwarding table, ARP entries, and ND entries. In addition, this packet instructs the transit node to unblock the temporarily blocked ports. |
EDGE-HELLO |
A packet sent from an edge port of a sub-ring and received by an assistant edge port on the same sub-ring. The packet is used to check the completeness of the major ring in the domain where the sub-ring is located. |
MAJOR-FAULT |
A packet sent from an assistant edge node to notify the edge node that the major ring in the domain fails if the assistant edge node does not receive the Edge-Hello packet from the edge port within a specified period. |
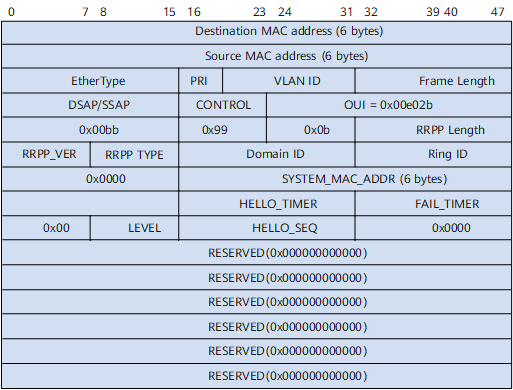
Figure1 shows the RRPP packet format.
- Destination MAC Address: indicates the destination MAC address of an RRPP packet.
- Source Mac Address: indicates the source MAC address for an RRPP packet, which is the bridge MAC address of the device.
- EtherType: indicates the encapsulation type. This field occupies 16 bits and has a fixed value of 0x8100 for tagged encapsulation.
- PRI: indicates the priority of Class of Service (COS). This field occupies 4 bits and has a fixed value of 0xe.
- VLAN ID: indicates the ID of a VLAN to which the packet belongs.
- Frame Length: indicates the ID of a VLAN to which the packet belongs.
- RRPP_LENGTH: indicates the length of an RRPP data unit. This field occupies 16 bits and has a fixed value of 0x0040.
- RRPP_VER: indicates the version of an RRPP packet. This field occupies 8 bits, and the current version is 0x01.
- RRPP TYPE: indicates the type of an RRPP packet.
- HEALTH = 0x05
- COMPLETE-FLUSH-FDB = 0x06
- COMMON-FLUSH-FDB = 0x07
- LINK-DOWN = 0x08
- EDGE-HELLO = 0x0a
- MAJOR-FAULT= 0x0b
- SYSTEM_MAC_ADDR: indicates the bridge MAC address from which the packet is sent. This field occupies 48 bits.