GTSM
Security Policy
The Generalized TTL Security Mechanism (GTSM) checks whether time to live (TTL) values are valid to protect TCP/IP-based control plane protocols from CPU-utilization (CPU overload) attacks.
Currently, BGP, BGP4+, OSPF, OSPFv3, RIP, and LDP support GTSM.
BGP/BGP4+ supports BGP-peer-specific GTSM policies. A GTSM policy can be configured for each BGP peer relationship.
OSPF/OSPFv3 supports protocol-specific GTSM policies. On a public network, only one type of GTSM policy can be deployed. On a private network, GTSM policies are deployed based on the VPN instances, and a GTSM policy can be configured for each OSPF/OSPFv3 VPN.
LDP supports LDP-peer-specific GTSM policies. A GTSM policy can be configured to each LDP peer.
- RIP supports protocol-specific GTSM policies. On a public network, only one type of GTSM policy can be deployed. On a private network, GTSM policies are deployed based on the VPN instances, and a GTSM policy can be configured for each RIP VPN.
A GTSM policy is generated after a GTSM command is executed on a service module. The policy matching conditions vary with protocols:
BGP/BGP4+: GTSM policy matching conditions include the source IP address, VRF index, source port ID, and destination port ID.
OSPF/OSPFv3: A GTSM policy matching condition includes the VRF index.
LDP: GTSM policy matching conditions include the source IP address, source port ID, and destination port ID.
- RIP: A GTSM policy matching condition includes the VRF index.
A GTSM policy is deployed as follows:
If GTSM for a specific protocol is disabled on a device, packets are sent to the control plane, without being verified.
If GTSM for a specific protocol is enabled on a device, the device performs GTSM policy matching. If a matching GTSM policy is found, the device checks whether the TTL in a packet is within the specified range. If the TTL is out of the specified range, the device determines that the packet is an attack packet and drops it.
Attack Modes
An attacker simulates a routing protocol and continuously sends packets to a device. The device becomes extremely busy processing these attack packets, leading to high CPU usage. To prevent CPU overload, GTSM can be deployed to protect IP-forwarded services by checking whether the TTL value in the IP header of an IP packet is within a pre-defined range.
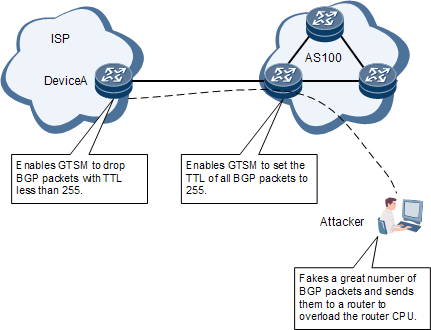
Configuration and Maintenance Methods
BGP is used as an example here. Set the valid TTL range for received packets to [255, 255].
[~DeviceA] bgp 10 [*DeviceA-bgp] peer 10.1.1.2 valid-ttl-hops 1 [*DeviceA-bgp] commit [~DeviceA-bgp] quit
Run the display gtsm statistics all command to view GTSM statistics, including the total number of packets, number of passed packets, and number of dropped packets. For example,
[DeviceA] display gtsm statistics all GTSM Statistics Table --------------------------------------------------------------- SlotId Protocol Total Counters Drop Counters Pass Counters --------------------------------------------------------------- 2 BGP 18 0 18 2 BGPv6 0 0 0 2 OSPF 0 0 0 2 LDP 0 0 0 2 OSPFv3 0 0 0 2 RIP 0 0 0 ---------------------------------------------------------------
Configuration and Maintenance Suggestions
GTSM is suitable for small networks. The anti-attack effect can be achieved only when the GTSM policy is deployed on the entire network.