Application Layer Association
Security Policy
The control plane is associated with the forwarding plane to control invalid packets, reduce attacks caused by device vulnerabilities, and ensure security on the control and forwarding planes. The control plane detects changes in protocols, centrally processes the characteristics of these changes, establishes a characteristics status table, and informs the forwarding plane of the changed status.
Protocol switch: Security policies can be configured on interfaces, boards, and an entire device. Packets for which the protocol switch is disabled are discarded or sent using very little bandwidth. This prevents exhaustion of CPU resources and ensures proper network operations.
Whitelist: A whitelist protects dynamic protocol sessions. Once a session is successfully established using TCP or UDP, the device dynamically sends a whitelist for this protocol and ensures that packets are sent reliably using sufficient bandwidth. The whitelist matching condition contains a quintuple, which includes the source IP address, destination IP address, source port ID, destination port ID, and protocol ID.
When processing protocol packets, an application layer association first matches them with the whitelist. The packets matching the whitelist are sent using sufficient bandwidth at a higher rate. Secondly, the application layer association matches protocol packets with an enabled protocol and then sends the packets matching the protocol at a specified rate. If the protocol has not been configured, the system assigns the default minimum bandwidth to packets of this protocol.
Finally, policies can be set for the packets that do not match any whitelist or protocol so that packets are either discarded or sent at a specified low rate.
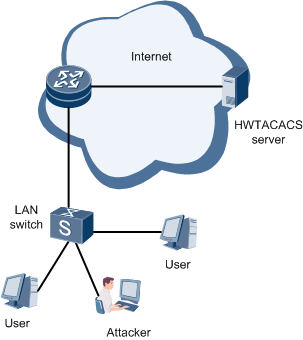
Attack Methods
In Figure 1, a device is connected to a large number of users. Additionally, several services (such as routing, HWTACACS, ICMP, IGMP, and MPLS) are enabled on the device, but these services do not need to be transmitted using Telnet. If an attacker sends an excessive number of Telnet requests, the device has to waste resources processing these requests. To prevent this risk, you can disable Telnet on the device. The device then assigns the default minimum bandwidth to Telnet packets, regardless of how many Telnet packets need to be processed. This implementation helps improve system security and prevent Telnet packets from consuming excessive resources.

You can also configure the system to discard Telnet packets, not to assign minimum bandwidth.
For enabled services or protocols, the device can send packets at the specified rate. This protects the CPU from attacks and ensures proper network operations.
Configuration and Maintenance Methods
Run the application-apperceive default-action { drop | min-to-cp } command to configure the default action for packets. The default action is taken when no matching application layer association policy is found.
Configuration and Maintenance Suggestions
Configuration and maintenance methods are irrelevant to configurations.